Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Clin Cases. Sep 16, 2015; 3(9): 853-860
Published online Sep 16, 2015. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v3.i9.853
Published online Sep 16, 2015. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v3.i9.853
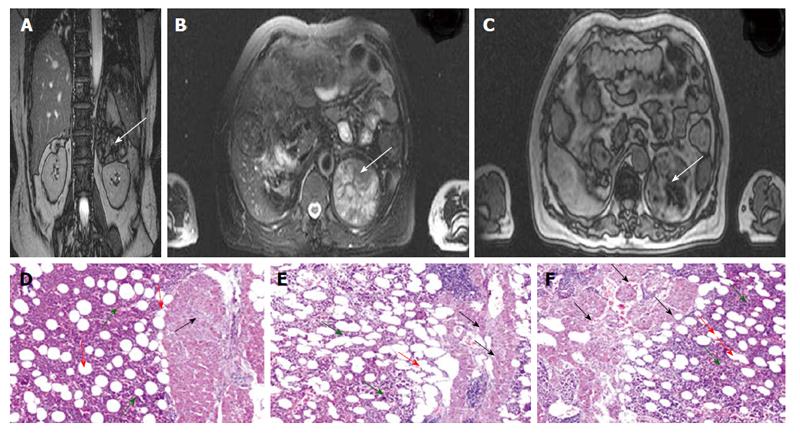
Figure 2 Diagnostic imaging and pathohistological examination results of patients B.
A-C: Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) results of adrenal myelolipomas (MRI scans were performed during the period between the first and the second surgical procedures). A 66 mm diameter circular mass (white arrow) with clear boundary shows mixed signals on T1 and T2 weighted MRI scans (short T1 mixed with slightly longer T2) in the left adrenal gland. The lesion is characterized by decreased T1WI signal intensity in the antiphase (out-of-phase); D: The histopathological features of the right adrenal myelolipoma that was excised in the first surgical procedure (stained with H and E); E and F: The histopathological features of the left adrenal myelolipoma that was removed in the second surgical procedure (stained with H and E). Tumor-like masses of extramedullary hematopoietic tissue is composed of adipose cells (red arrow) and hematopoietic cells (green arrow). Normal adrenal gland tissue (black arrow) is found to be surrounded by adrenal myelolipoma.
- Citation: Yang Y, Ye LY, Yu B, Guo JX, Liu Q, Chen Y. Two case reports of bilateral adrenal myelolipomas. World J Clin Cases 2015; 3(9): 853-860
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v3/i9/853.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v3.i9.853