Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Clin Cases. Jun 6, 2025; 13(16): 103373
Published online Jun 6, 2025. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v13.i16.103373
Published online Jun 6, 2025. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v13.i16.103373
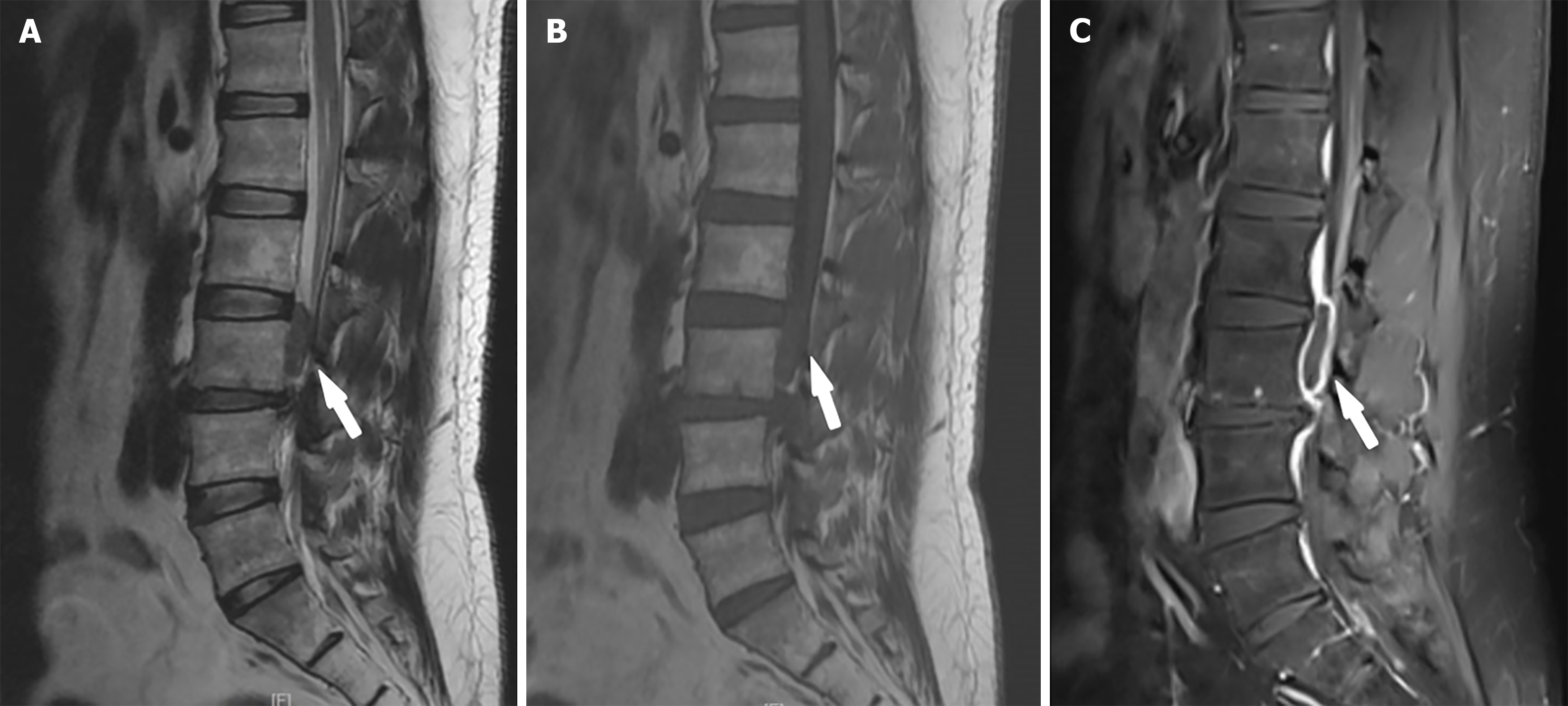
Figure 2 Lumbar spine sagittal weighted magnetic resonance imaging.
A: Sagittal T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the lumbar spine. The sagittal T2-weighted MRI scan revealed a significant reduction in the height of the L3-L4 intervertebral disc. A short T2 signal lesion is located posterior to the third lumbar vertebral body, as indicated by the arrow; B: Sagittal T1-weighted MRI of the lumbar spine. A long T1 signal lesion is located posterior to the third lumbar vertebral body, as indicated by the arrow; C: Sagittal T1-weighted enhanced MRI of the lumbar spine. In the sagittal MRI enhancement sequence, notable abnormalities were detected in the epidural elliptical signal located at the level of the third lumbar vertebra, as indicated by the arrow. These abnormalities were characterized by a prominent pattern of peripheral linear enhancement along the signal's edge, whereas the central region remained devoid of such enhancement.
- Citation: Zhou JG. Diagnosis and surgical challenges of extremely severe head and lumbar disc herniation in young patients: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2025; 13(16): 103373
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v13/i16/103373.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v13.i16.103373