Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Clin Cases. Mar 26, 2024; 12(9): 1585-1596
Published online Mar 26, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i9.1585
Published online Mar 26, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i9.1585
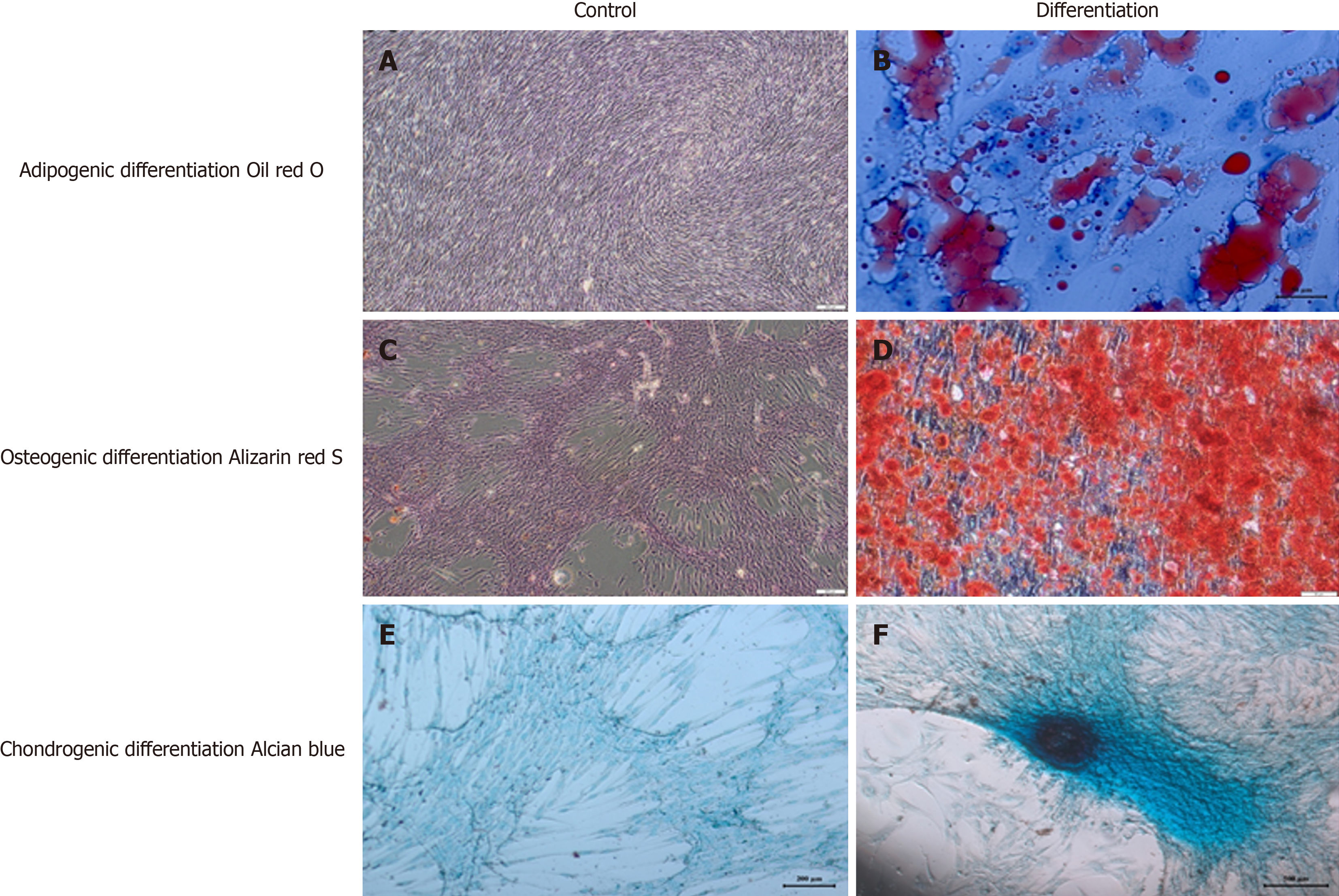
Figure 2 Detection of the differentiation potential of Wharton’s Jelly–derived-mesenchymal stem cells.
A and B: Wharton's Jelly Derived-mesenchymal stem cells (WJ-MSCs) were cultured without adipogenic induction and cultured for 3 wk in adipogenic differentiation medium. Adipogenic differentiation was evidenced by the formation of lipid vacuoles with oil red O staining; C and D: WJ-MSCs were cultured without osteogenic induction and cultured for 3 wk in osteogenic differentiation medium. Osteogenic differentiation was evidenced by the detection of calcium deposits with Alizarin red staining; E and F: WJ-MSCs were cultured without chondrogenic induction and cultured for 3 wk in chondrogenic differentiation medium. Chondrogenic differentiation was evidenced with Alcian blue staining.
- Citation: Boyalı O, Kabatas S, Civelek E, Ozdemir O, Bahar-Ozdemir Y, Kaplan N, Savrunlu EC, Karaöz E. Allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells may be a viable treatment modality in cerebral palsy. World J Clin Cases 2024; 12(9): 1585-1596
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v12/i9/1585.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v12.i9.1585