Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Clin Cases. Feb 26, 2024; 12(6): 1050-1062
Published online Feb 26, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i6.1050
Published online Feb 26, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i6.1050
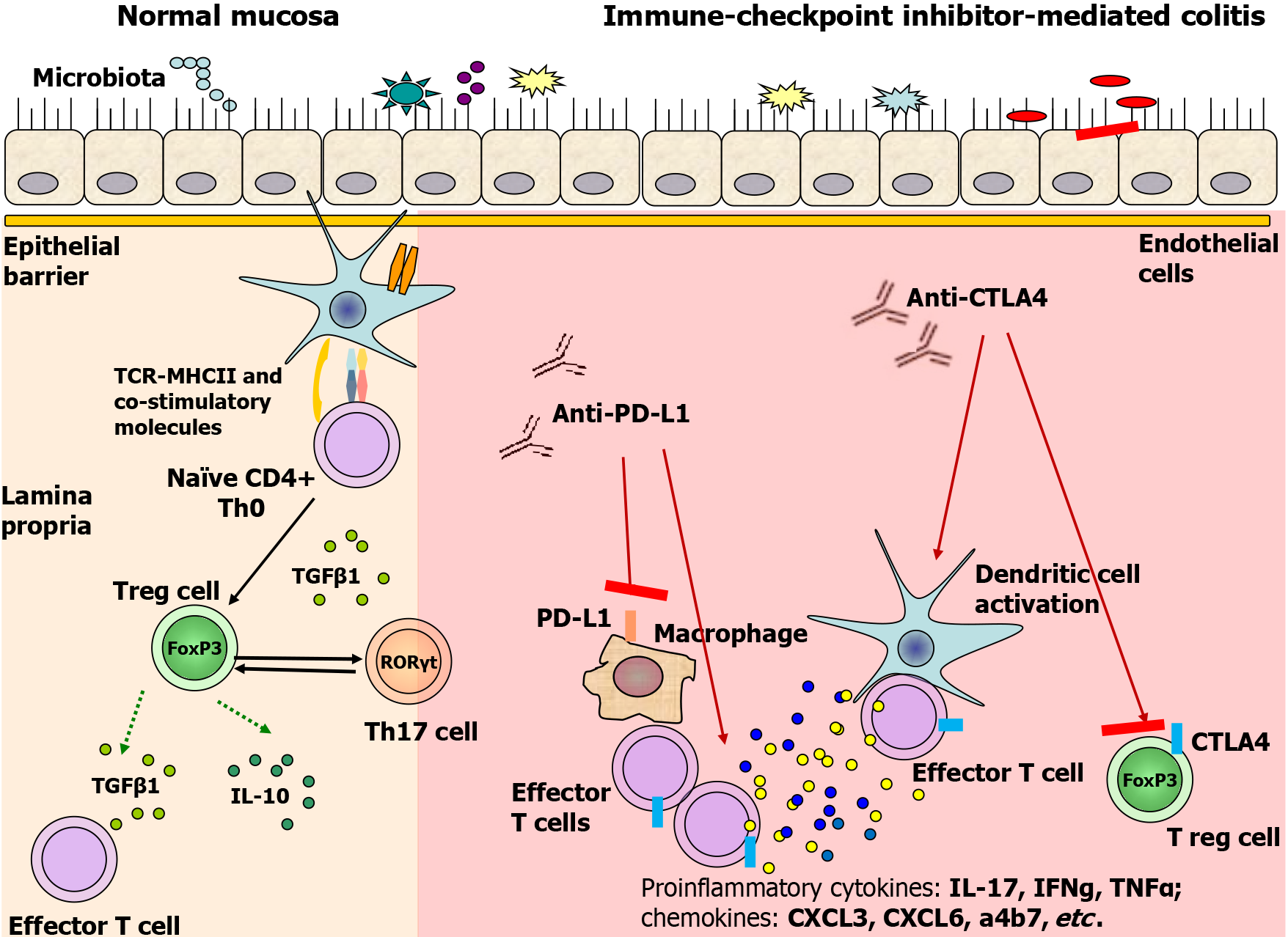
Figure 1 Proposed immune-mediated pathways of immune checkpoint inhibitor-mediated colitis.
In normal mucosa, T regulatory cells are fully capable of inducing tolerance while balancing pro-inflammatory cells and molecules (i.e. Th17 cells) and anti-inflammatory molecules (i.e. IL-10, TGFb, etc). By blocking cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen-4 (CTLA-4) or programmed cell death ligand-1, immune checkpoint inhibitors promote pro-inflammatory cytokines, chemokine production, Treg differentiation inhibition, and suppression of IL-10 and TGFb secretion. Parts of the figure were drawn by using pictures from Servier Medical Art. Servier Medical Art by Servier (https://smart.servier.com/) is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 Unported License (Supplementary material). CTLA-4: Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen-4; PD-L1: Programmed cell death ligand-1.
- Citation: Velikova T, Krastev B, Gulinac M, Zashev M, Graklanov V, Peruhova M. New strategies in the diagnosis and treatment of immune-checkpoint inhibitor-mediated colitis. World J Clin Cases 2024; 12(6): 1050-1062
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v12/i6/1050.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v12.i6.1050