Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Clin Cases. Feb 16, 2024; 12(5): 903-912
Published online Feb 16, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i5.903
Published online Feb 16, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i5.903
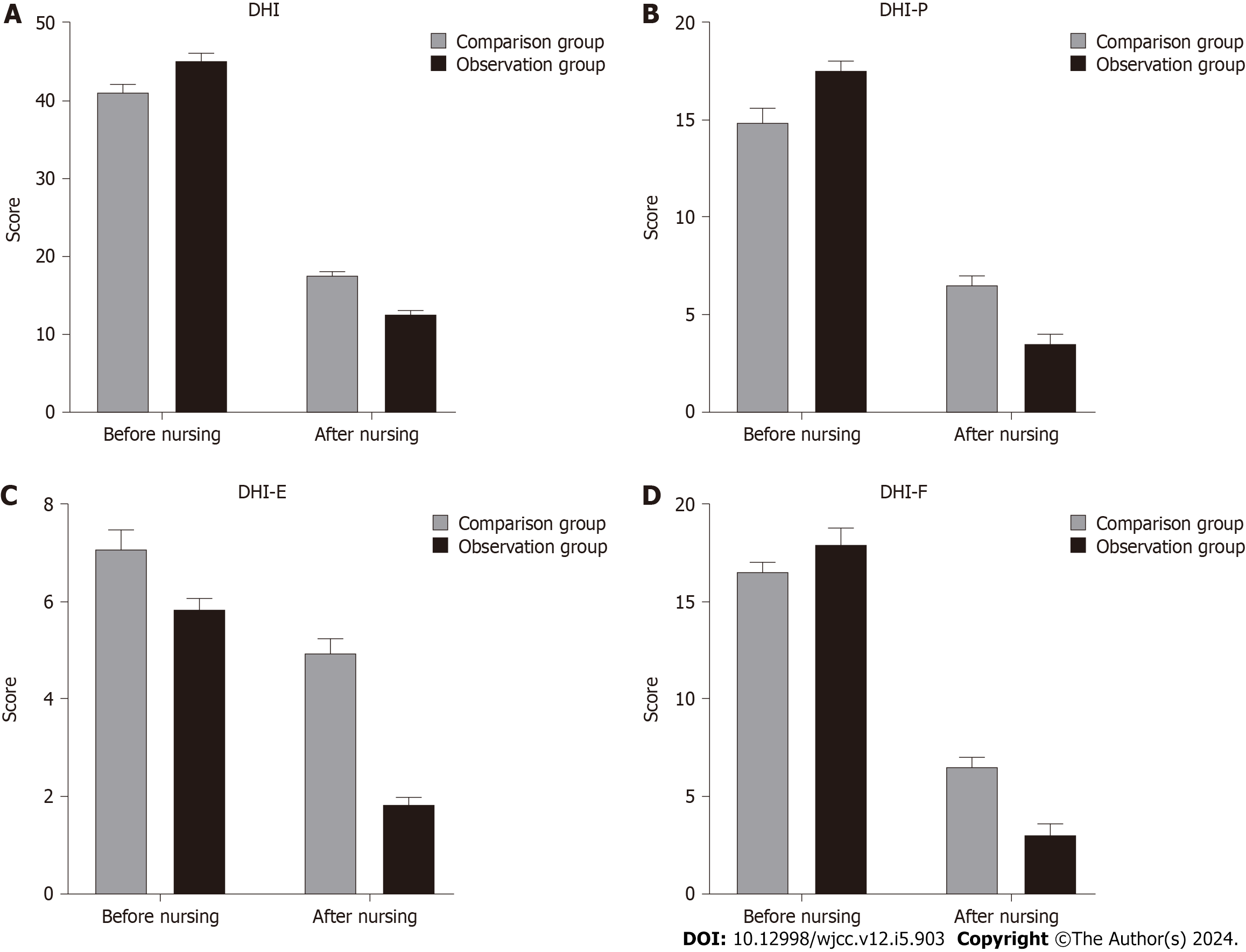
Figure 3 Quality of life comparison.
A: Dizziness Handicap Inventory (DHI) scores in the comparison group and observation group; B: DHI-P scores in the comparison group and observation group; C: DHI-E scores in the comparison group and observation group; D: DHI-F scores in the comparison group and observation group. All quality of life data in our study were checked by Excel double entry, SPSS23.0 was used for statistical analysis, and the mean ± SD was used for description. Using t test, it was found that the total score of DHI scale, DHI-P, DHI-E of the two groups of patients before nursing Compared with DHI-F dimension score, the difference was not statistically significant (P > 0.05). After nursing, the DHI scale and DHI-P, DHI-E and DHI-F scores in the two groups were decreased, and the scores in the nursing group were lower than those in the control group, and the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05).
- Citation: Shi Q, Wu RJ, Liu J. Effect of health education based on information-motivation-behavioral skills model on patients with unilateral vestibular dysfunction. World J Clin Cases 2024; 12(5): 903-912
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v12/i5/903.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v12.i5.903