Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Clin Cases. Feb 16, 2024; 12(5): 891-902
Published online Feb 16, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i5.891
Published online Feb 16, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i5.891
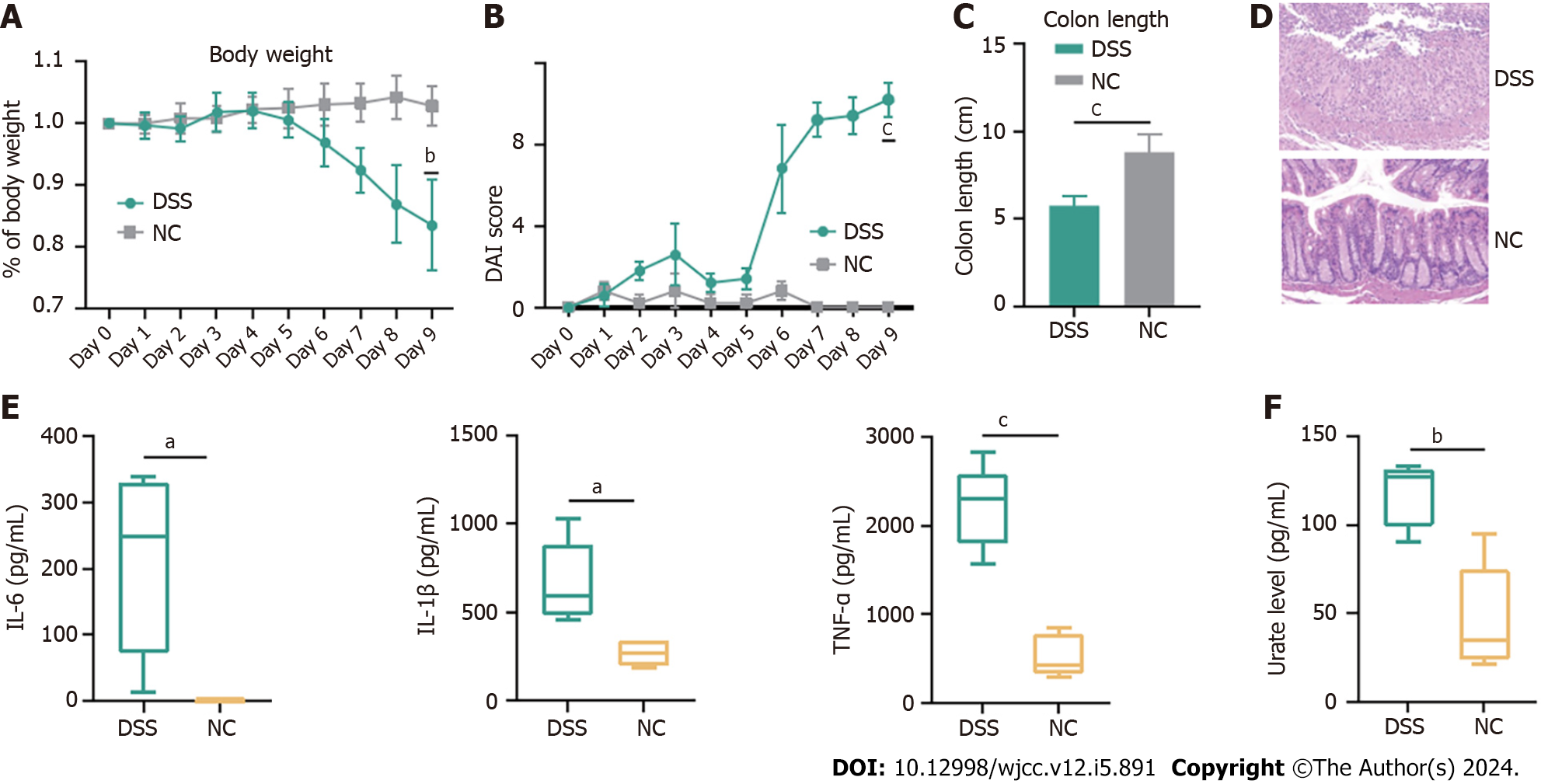
Figure 6 Dextran sulfate sodium contributed to increase of inflammation in inflammatory bowel disease mice.
C57BL/6 mice were administered dextran sulfate sodium (DSS) (2%) for 7 d (and a control group was provided with water only for comparison) and 2 d for water. A-E: DSS group (n = 5) exhibited a significant aggravation of inflammatory bowel disease-associated changes in of body weight (A), disease activity index (B), colon length (C), inflammatory infiltration (D) and increased levels of interleukin (IL)-6, IL-1β and tumor necrosis factor-α (E); F: Compared with control group (n = 5), DSS group demonstrated increased levels of urate levels. DSS: Dextran sulfate sodium; NC: Control group; IL: Interleukin; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; DAI: Disease activity index. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01; cP < 0.001.
- Citation: Zhang S, Fang X, Kang L, Sui XY, Liu M, Luo YJ, Fu S, Li ZS, Zhao SB, Bai Y. Serum urate is associated with an increased risk of inflammatory bowel disease: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization study. World J Clin Cases 2024; 12(5): 891-902
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v12/i5/891.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v12.i5.891