Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Clin Cases. Feb 16, 2024; 12(5): 891-902
Published online Feb 16, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i5.891
Published online Feb 16, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i5.891
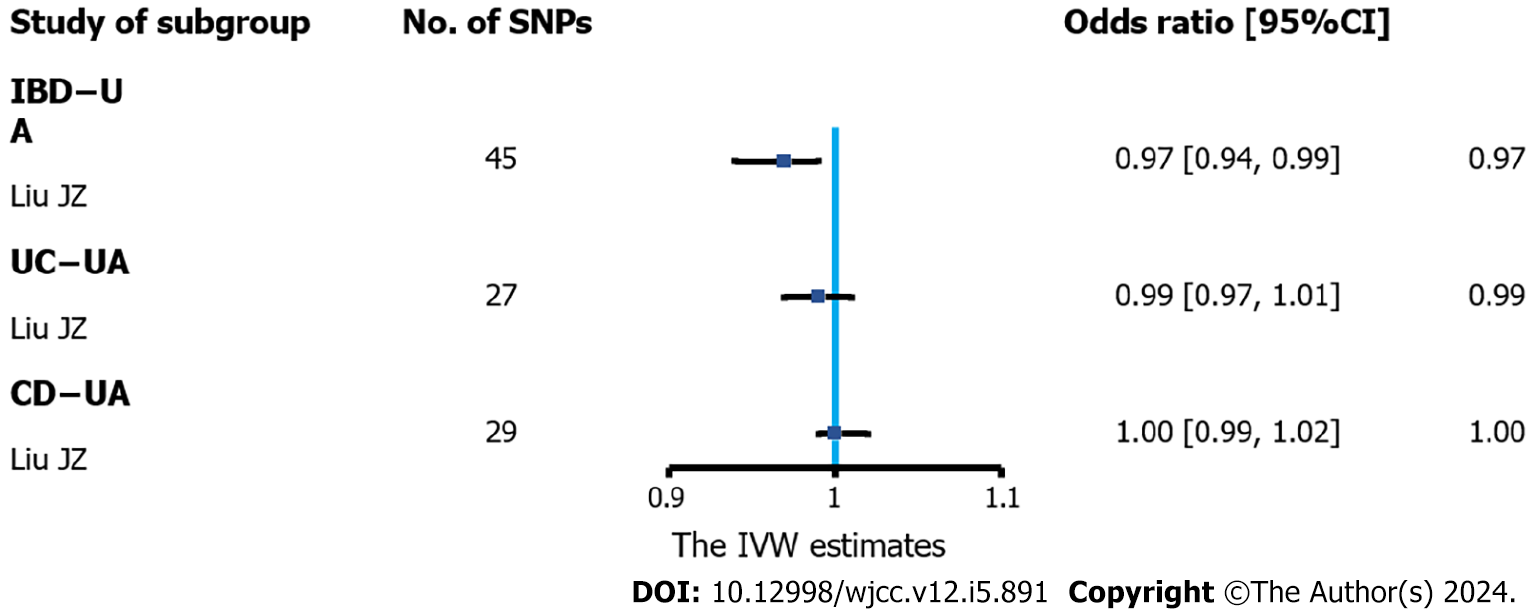
Figure 4 Association of inflammatory bowel disease and urate levels in Mendelian randomization analyses (inverse-variance weighted estimate).
Estimated odds ratio (OR) represent the effect of per log-OR increase in inflammatory bowel disease on urate levels, using inverse-variance weighted analysis with a fixed-effects model. IBD: Inflammatory bowel disease; UC: Ulcerative colitis; CD: Crohn’s disease; CI: Confidence interval; SNP: Single-nucleotide polymorphisms; UA: Ursolic acid; IVW: Inverse-variance weighted.
- Citation: Zhang S, Fang X, Kang L, Sui XY, Liu M, Luo YJ, Fu S, Li ZS, Zhao SB, Bai Y. Serum urate is associated with an increased risk of inflammatory bowel disease: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization study. World J Clin Cases 2024; 12(5): 891-902
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v12/i5/891.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v12.i5.891