Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Clin Cases. Jan 26, 2024; 12(3): 525-537
Published online Jan 26, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i3.525
Published online Jan 26, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i3.525
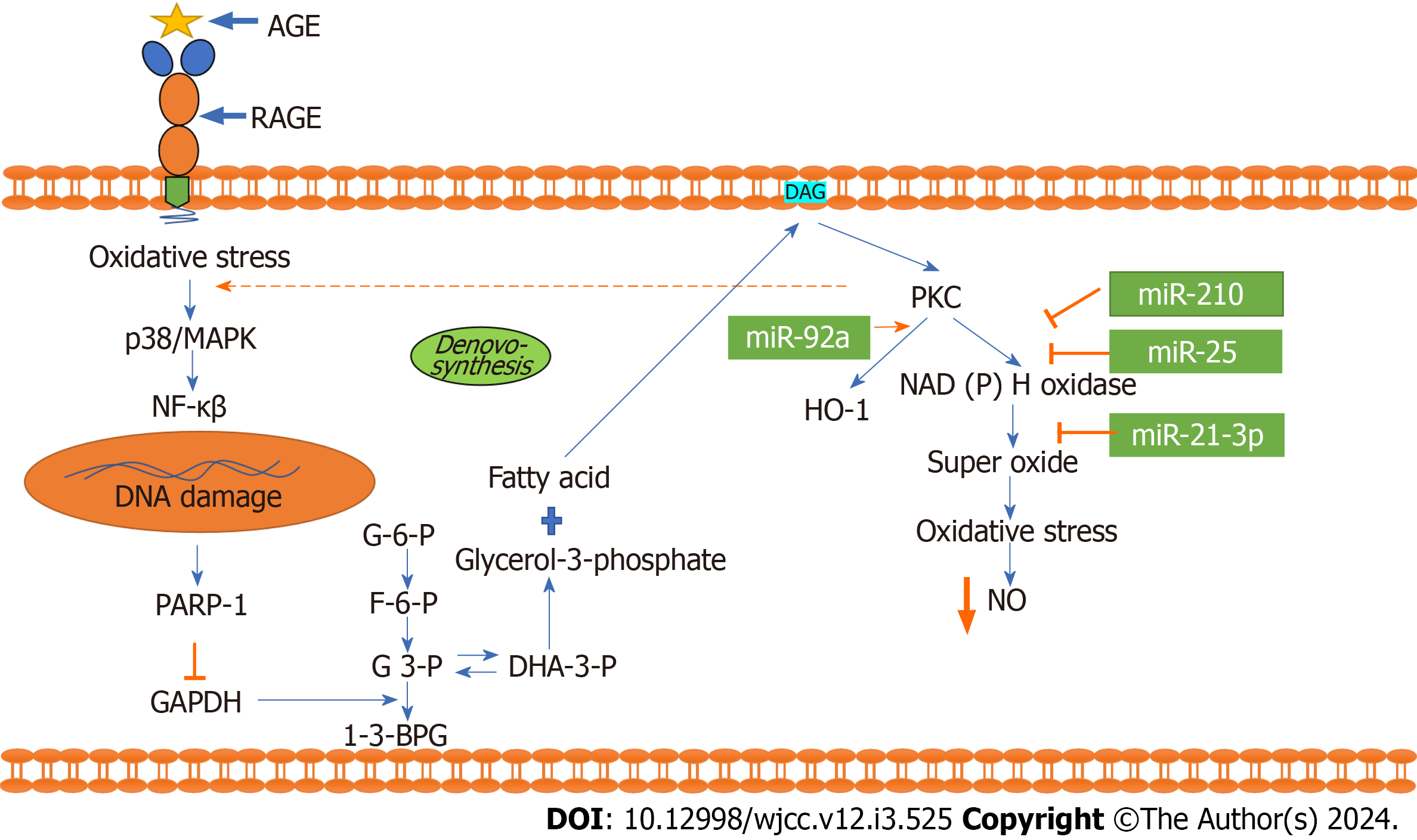
Figure 4 Interaction of advanced glycation end product and receptor of advanced glycation end product activates the protein kinase C pathway: The interaction of advanced glycation end product and advanced glycation end product activates the nuclear factor pathway and damages DNA, causing PARP-1 to be released and GAPDH to be inhibited.
The inhibition of GAPDH affects the glycolysis pathway and increases fatty acid synthesis. This increased synthesis of fatty acids activates diacyl glycerol in the cell membrane, which is a potent activator of protein kinase C (PKC). Increased PKC promotes synthesis of NADPH oxidase, super oxide and oxidative stress and ultimately decreases cellular nitric oxide. In this pathway, miRNA 210, miR-25, and miR-21-3p inhibit NADPH oxidase and oxidative stress. Apart from that, miR 92a promotes the expression of the antioxidant HO-1. AGE: Advanced glycation end product; RAGE: Receptor of advanced glycation end product; NF-κB: Nuclear factor kappa beta.
- Citation: Shrivastav D, Singh DD. Emerging roles of microRNAs as diagnostics and potential therapeutic interest in type 2 diabetes mellitus. World J Clin Cases 2024; 12(3): 525-537
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v12/i3/525.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v12.i3.525