Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Clin Cases. Sep 26, 2024; 12(27): 6045-6056
Published online Sep 26, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i27.6045
Published online Sep 26, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i27.6045
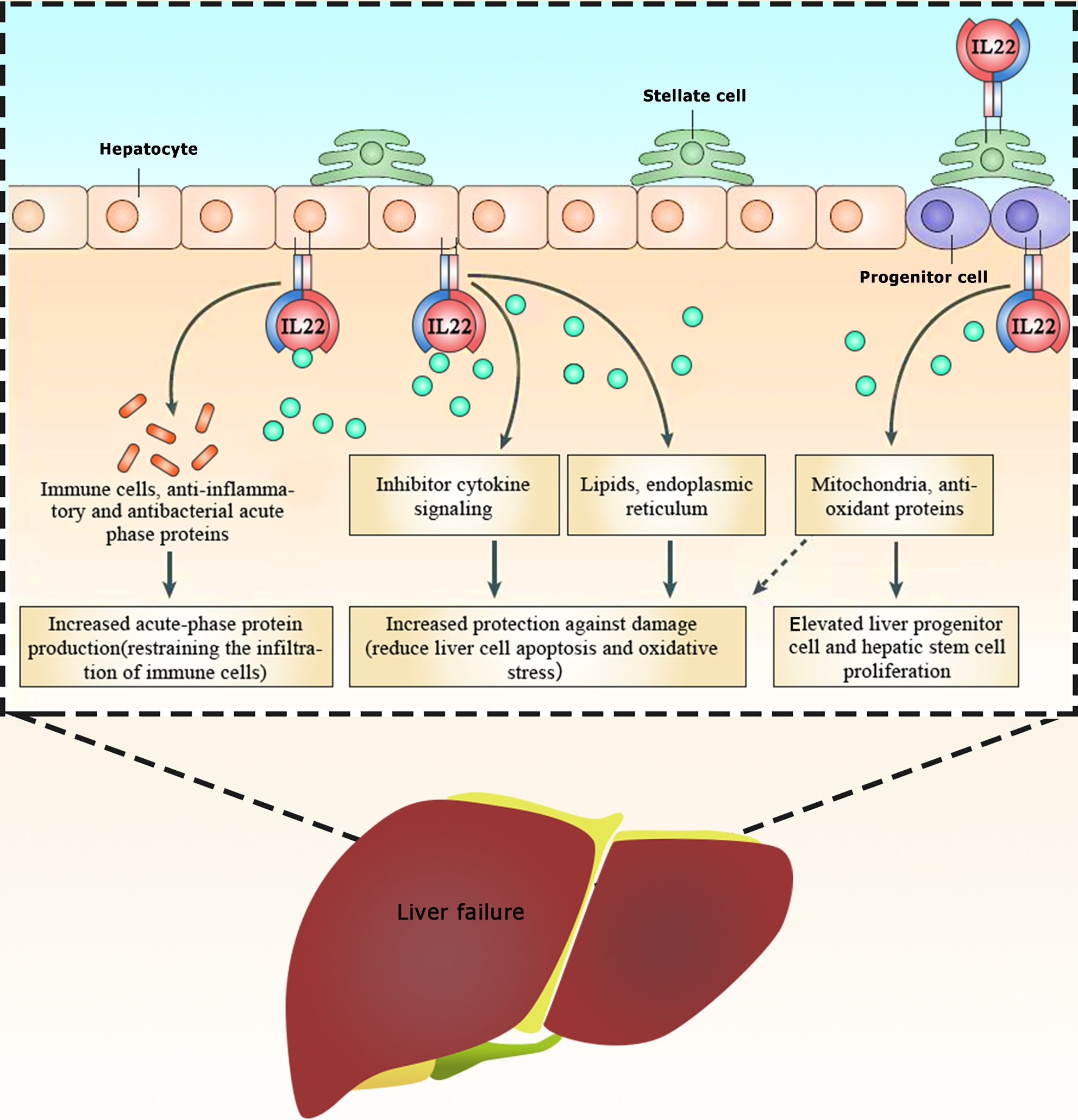
Figure 3 Mechanism of interleukin 22 (IL-22) in liver failure (diagram illustrates the protective role of IL-22 in liver health and its potential benefits in preventing liver failure).
Interleukin 22 (IL-22) is secreted by immune cells, specifically progenitor cells, and binds to receptors on the surface of hepatocytes, stellate cells, and progenitor cells. This binding triggers a series of downstream effects: (1) Hepatocytes: IL-22 acts on hepatocytes by increasing the production of acute-phase proteins, which help fight infection and inflammation. This, in turn, helps restrain the infiltration of immune cells, reducing inflammation and protecting the liver from damage; (2) Stellate cells: IL-22's interaction with stellate cells increases protection against damage and reduces liver cell apoptosis (cell death) and oxidative stress; (3) Progenitor cells: IL-22 stimulates the production of mitochondria and antioxidant proteins in progenitor cells. This promotes the proliferation of liver progenitor cells and hepatic stem cells, which are crucial for liver regeneration).
- Citation: Lin Y, Yan GJ, Liu MY, Cao Y, Zhang K, Wang N, Long FL, Mao DW. Review of the potential value of serum interleukin levels as prognostic biomarkers of liver failure. World J Clin Cases 2024; 12(27): 6045-6056
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v12/i27/6045.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v12.i27.6045