Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Clin Cases. Sep 16, 2024; 12(26): 5952-5959
Published online Sep 16, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i26.5952
Published online Sep 16, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i26.5952
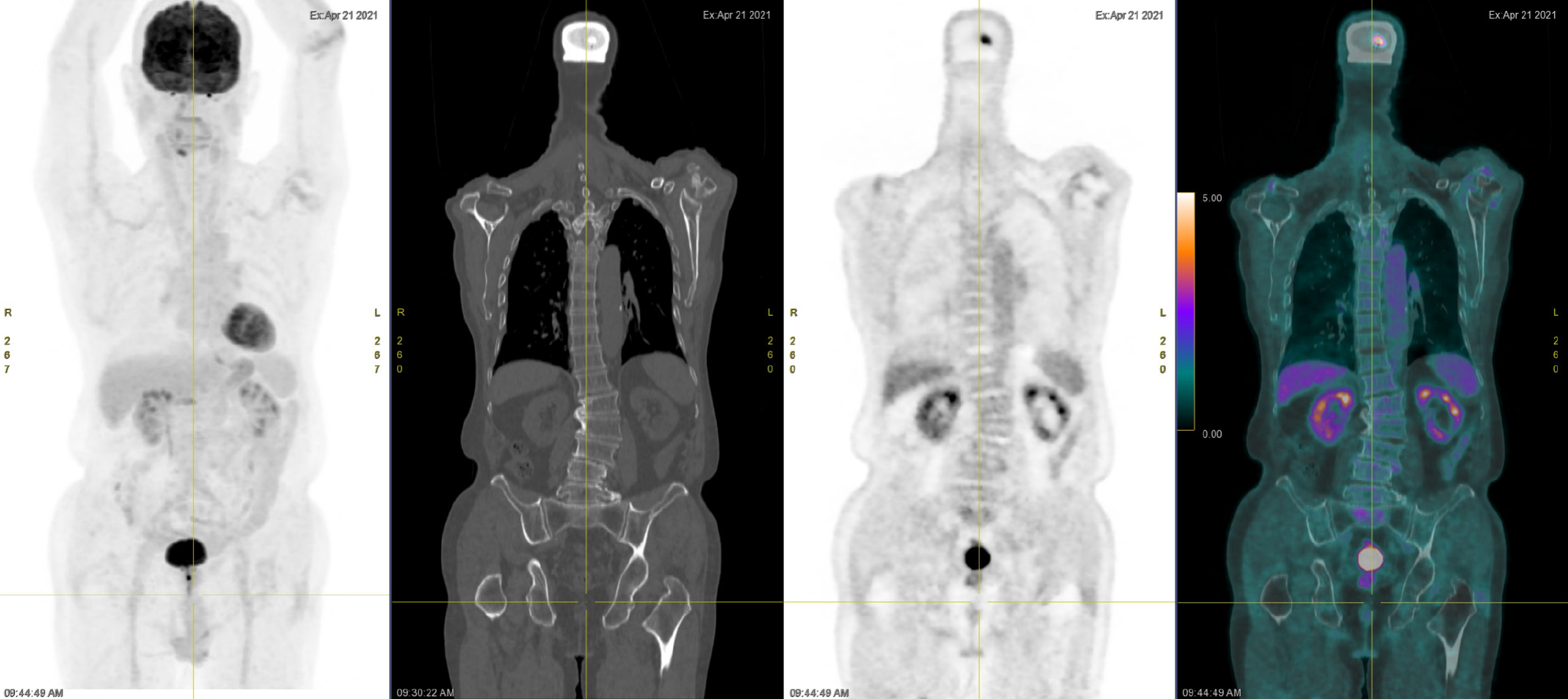
Figure 4 Images obtained during an 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography evaluation of the region comprising the head to the upper thigh.
From left to right: Ill-defined fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) avidity is observed in the prostate; No FDG-avid regional or distant lymph nodes are apparent; Ill-defined FDG avidity is noted in the right buccal region after the dental prosthesis; and Ill-defined FDG avidity in the right T1, T4, T8, T12, and left upper ilia with sclerotic changes, suggesting a benign etiology.
- Citation: Hsu JY, Lin YS, Huang LH, Tsao TY, Hsu CY, Ou YC, Tung MC. Concurrent occurrence of adenocarcinoma and urothelial carcinoma of the prostate gland: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2024; 12(26): 5952-5959
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v12/i26/5952.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v12.i26.5952