Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Clin Cases. Jul 26, 2024; 12(21): 4748-4754
Published online Jul 26, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i21.4748
Published online Jul 26, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i21.4748
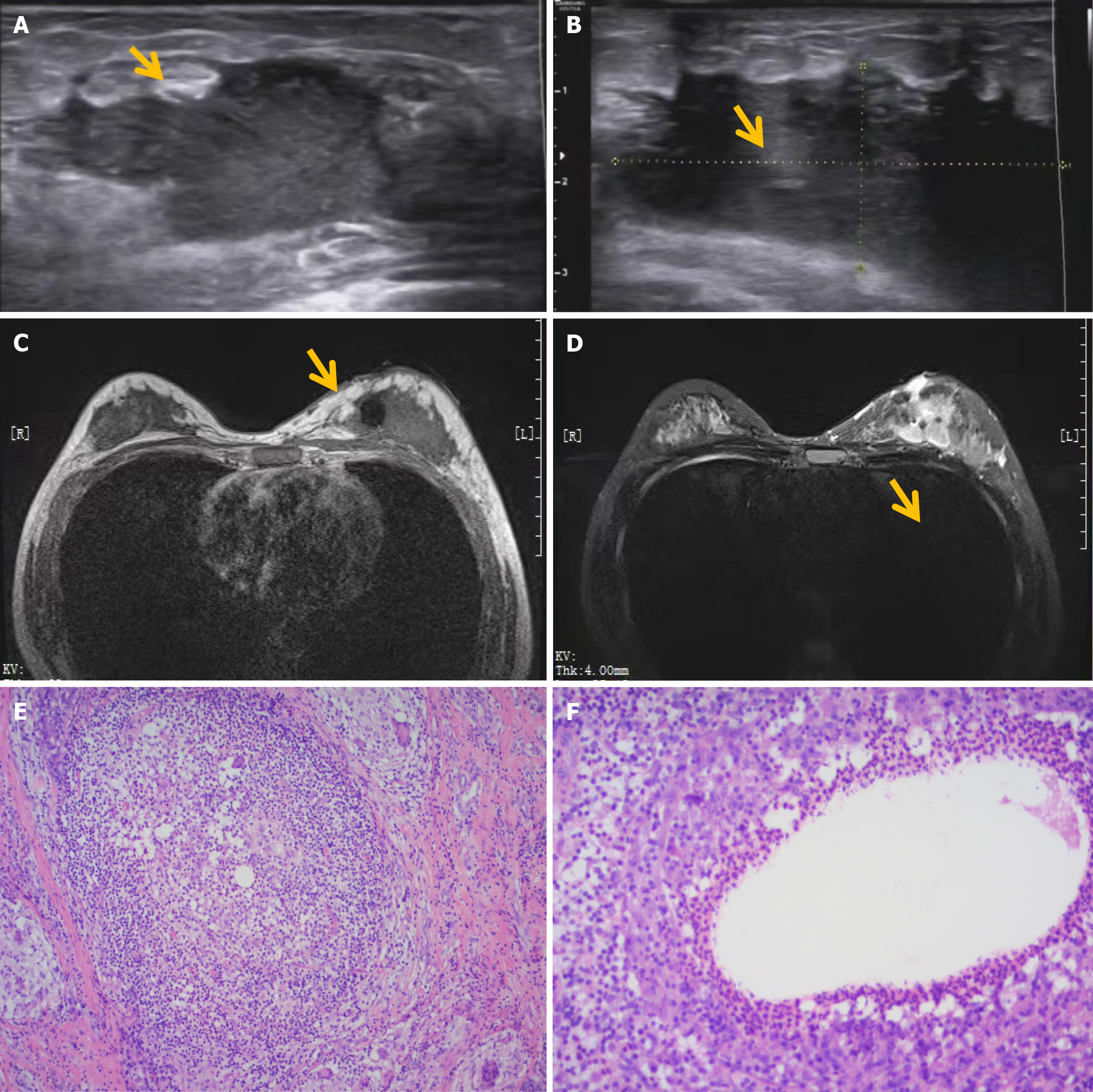
Figure 2 Granulomatous mastitis of the left breast.
A and B: Ultrasound images (outer lower quadrant of the left breast: 50 mm × 24 mm, below the left nipple: 46 mm × 22 mm); C and D: Magnetic resonance imaging images, manifesting non-mass enhancement lesions in multiple areas of the left breast, with irregular shape, "grid and burr" signals at the edges, surrounding skin edema, and skin fistula formation in the inner and lower quadrants; E and F: Pathological images (hematoxylin and eosin staining; original magnification, × 200), showing squamous epithelial hyperplasia, interstitial acute and chronic inflammatory cell infiltration, local abscess and granuloma formation, with vacuoles in the center, surrounded by layers of inflammatory cells, such as neutrophils and multinucleated giant cells.
- Citation: Meng T, Chu ML, Wang B, Ye MN, Cheng YQ, Chen HF. Granulomatous lobular mastitis treated by a combined internal and external treatment of traditional Chinese medicine: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2024; 12(21): 4748-4754
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v12/i21/4748.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v12.i21.4748