Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Clin Cases. Jun 16, 2024; 12(17): 2921-2924
Published online Jun 16, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i17.2921
Published online Jun 16, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i17.2921
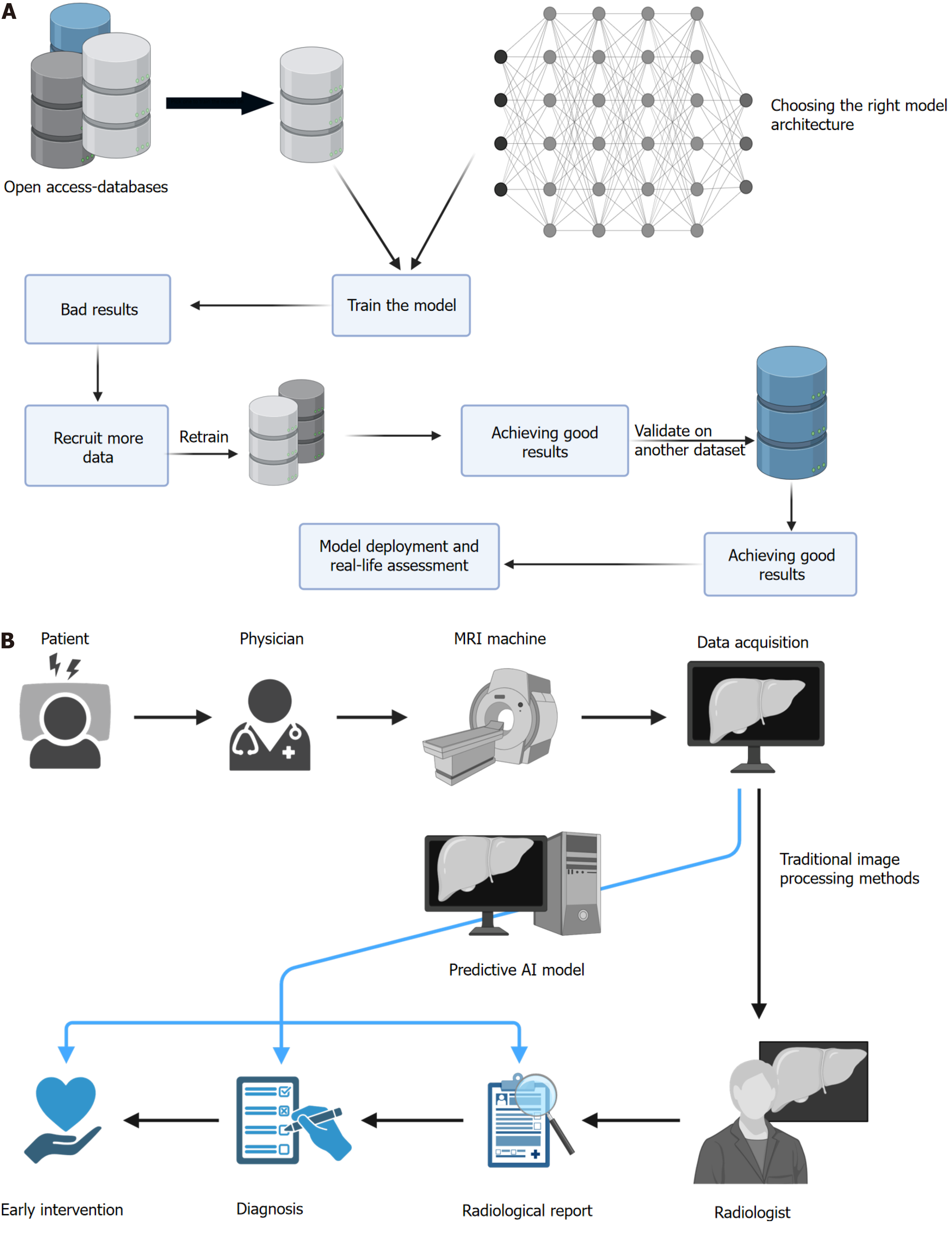
Figure 1 Illustrates the general benefits of utilizing open-access datasets.
A: Initially, we had multiple datasets (three datasets in total); however, using the first dataset alone proved to be insufficient for training a satisfactory model, therefore, we incorporated another dataset into the training data. Following this, we evaluated the model on an external dataset to confirm the efficacy of the model, yielding a good result. The model is then transferred to the deployment stage; B: Clinical testing of the model and if proven to be effective, it is started to be tested on a larger scale, and lastly used in the computer-aided-diagnosis. MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging; AI: Artificial intelligence. This figure was created with BioRender.com.
- Citation: Jaradat JH, Nashwan AJ. Revolutionizing disease diagnosis and management: Open-access magnetic resonance imaging datasets a challenge for artificial intelligence driven liver iron quantification. World J Clin Cases 2024; 12(17): 2921-2924
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v12/i17/2921.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v12.i17.2921