Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Clin Cases. May 26, 2024; 12(15): 2606-2613
Published online May 26, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i15.2606
Published online May 26, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i15.2606
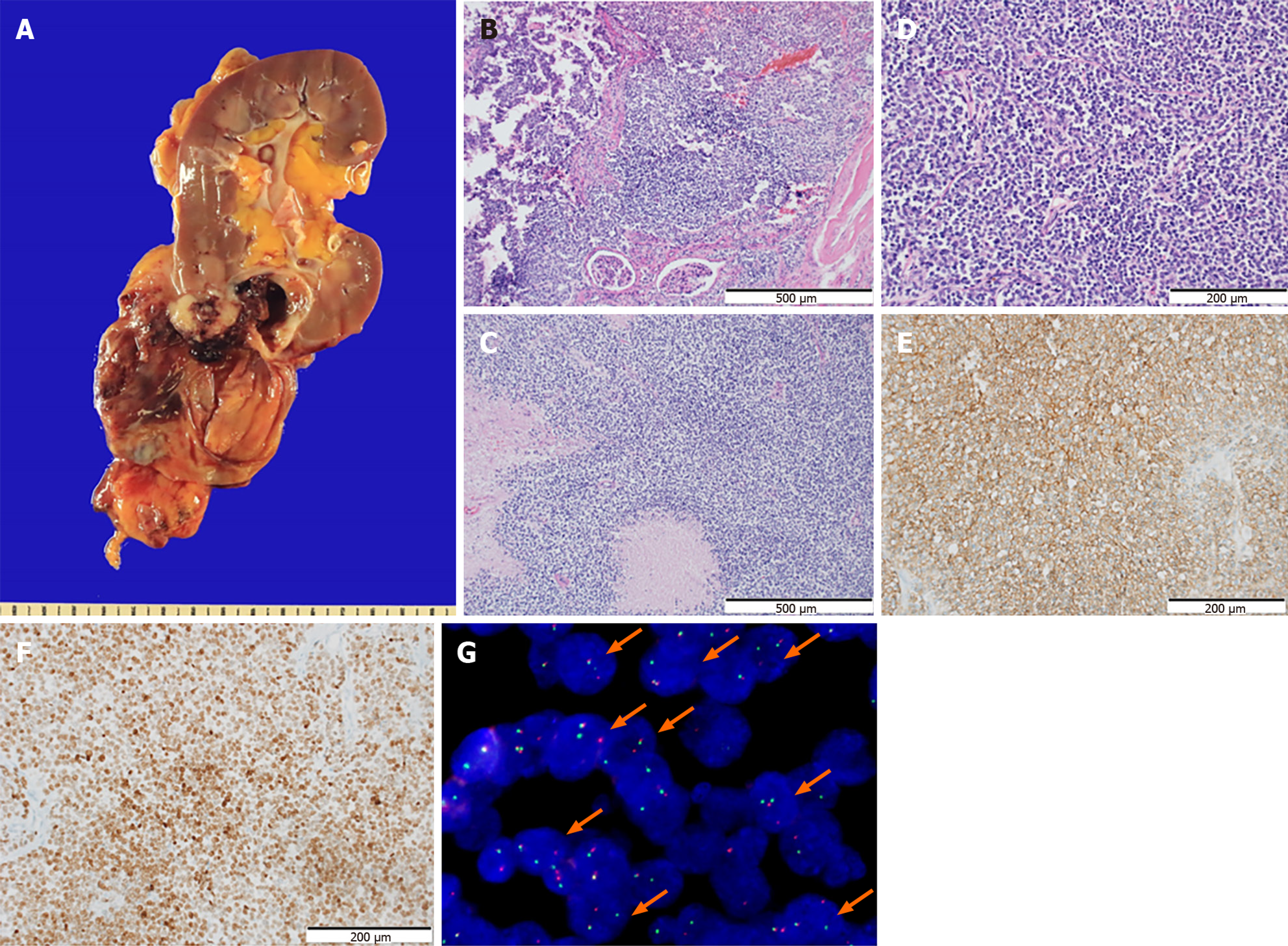
Figure 2 Morphological features and immunostaining results of the tumor.
A: A huge cystic mass in the lower pole of the right kidney without rupture. Most parts of the tumor consisted of cystic lesions, while the solid area showed infiltration into the renal parenchyma grossly; B: The border of the tumor infiltrating into the renal parenchyma is also identified on the hematoxylin and eosin (HE) sections (× 100). Staining method: HE staining; C: Frequent necrosis is observed (× 100). Staining method: HE staining; D: The section shows a relatively diffuse sheet pattern composed of small round tumor cells. The tumor cells show no glandular or squamous differentiation and present moderate pleomorphism (× 200). The nuclei are monotonous with inconspicuous nucleoli. The tumor has scanty or clear cytoplasm (× 200). Staining method: HE staining; E and F: The tumor cells exhibit diffuse membranous stain for CD99 (E, × 200) and nuclear stain for NK2 Homeobox 2 (F, × 200). Staining method: Polymer method; G: Fluorescence in situ hybridization exhibits the diagnostic t (11; 22) EWSR1 translocation (orange arrows).
- Citation: Kim S, Park J, Ko YH, Kwon HJ. Primary Ewing sarcoma of the kidney mimicking cystic papillary renal cell carcinoma in an older patient: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2024; 12(15): 2606-2613
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v12/i15/2606.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v12.i15.2606