Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Clin Cases. Mar 6, 2023; 11(7): 1528-1548
Published online Mar 6, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i7.1528
Published online Mar 6, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i7.1528
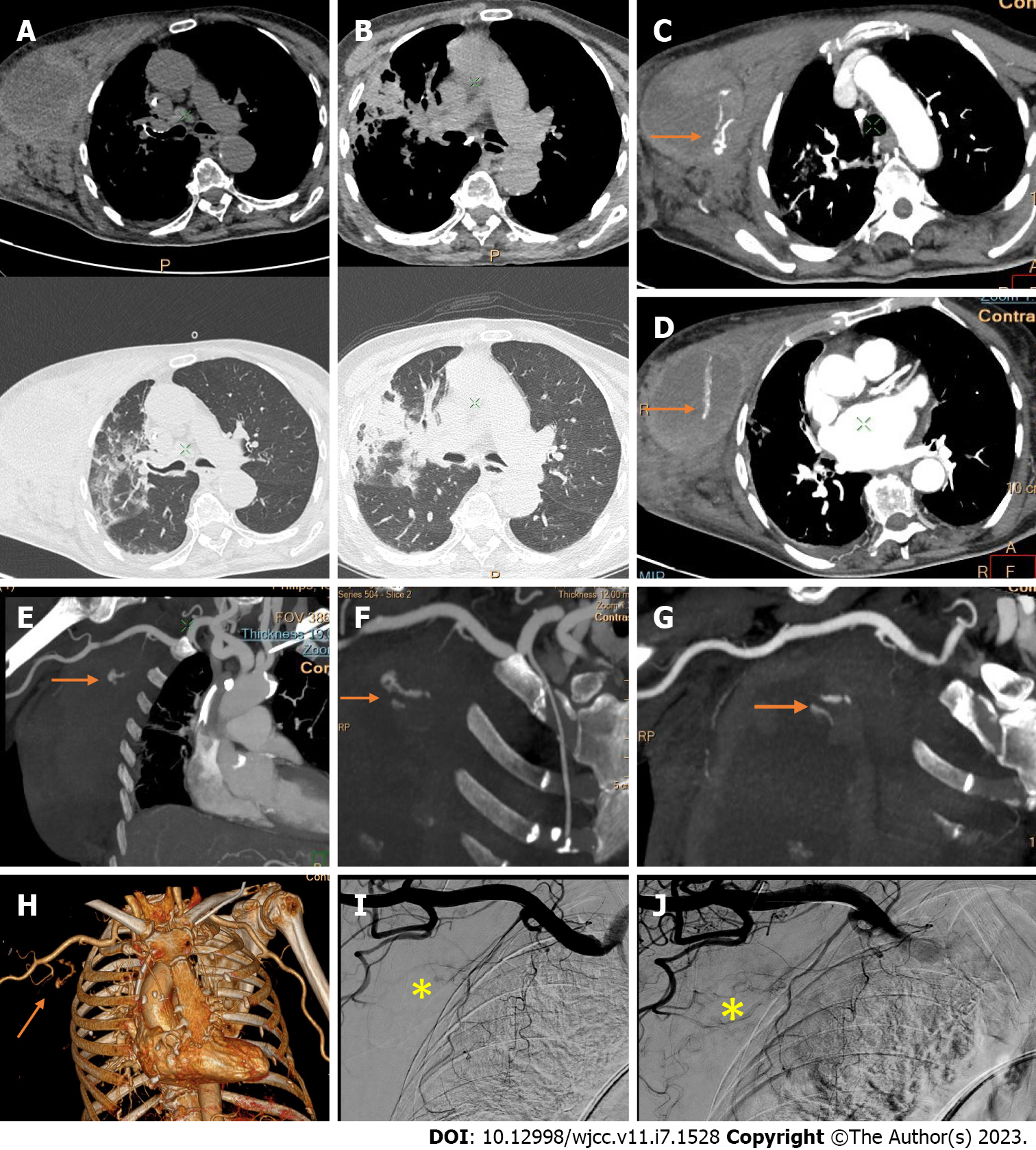
Figure 11 Computed tomography angiography and digital subtraction angiography of a giant right-sided chest wall hematoma in a patient with coronavirus disease 2019 pneumonia.
A-D: Hematoma arising from and infiltrating between the pectoral muscles, with “crazy paving” interstitial inflammatory changes in the right lung; C and D: Post-contrast axial images and coronal reconstructions with two pooling sites of extravasated contrast material within the hematoma (arrows); E-G: Computed tomography angiography maximum intensity projection images; H: Volume rendering three-dimensional reconstructions enable the visualization of a jet from the bleeding vessels (terminal branches of the superior and lateral thoracic artery (arrows). No bleeding from the pectoral branch of the thoracoacromial artery is evident; I and J: Digital subtraction angiograms confirm the predefined sites of bleeding without need of embolization due to bleeding reduction by the compression of those small vessels by the giant hematoma (asterisk).
- Citation: Evrev D, Sekulovski M, Gulinac M, Dobrev H, Velikova T, Hadjidekov G. Retroperitoneal and abdominal bleeding in anticoagulated COVID-19 hospitalized patients: Case series and brief literature review. World J Clin Cases 2023; 11(7): 1528-1548
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v11/i7/1528.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v11.i7.1528