Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Clin Cases. Feb 26, 2023; 11(6): 1224-1235
Published online Feb 26, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i6.1224
Published online Feb 26, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i6.1224
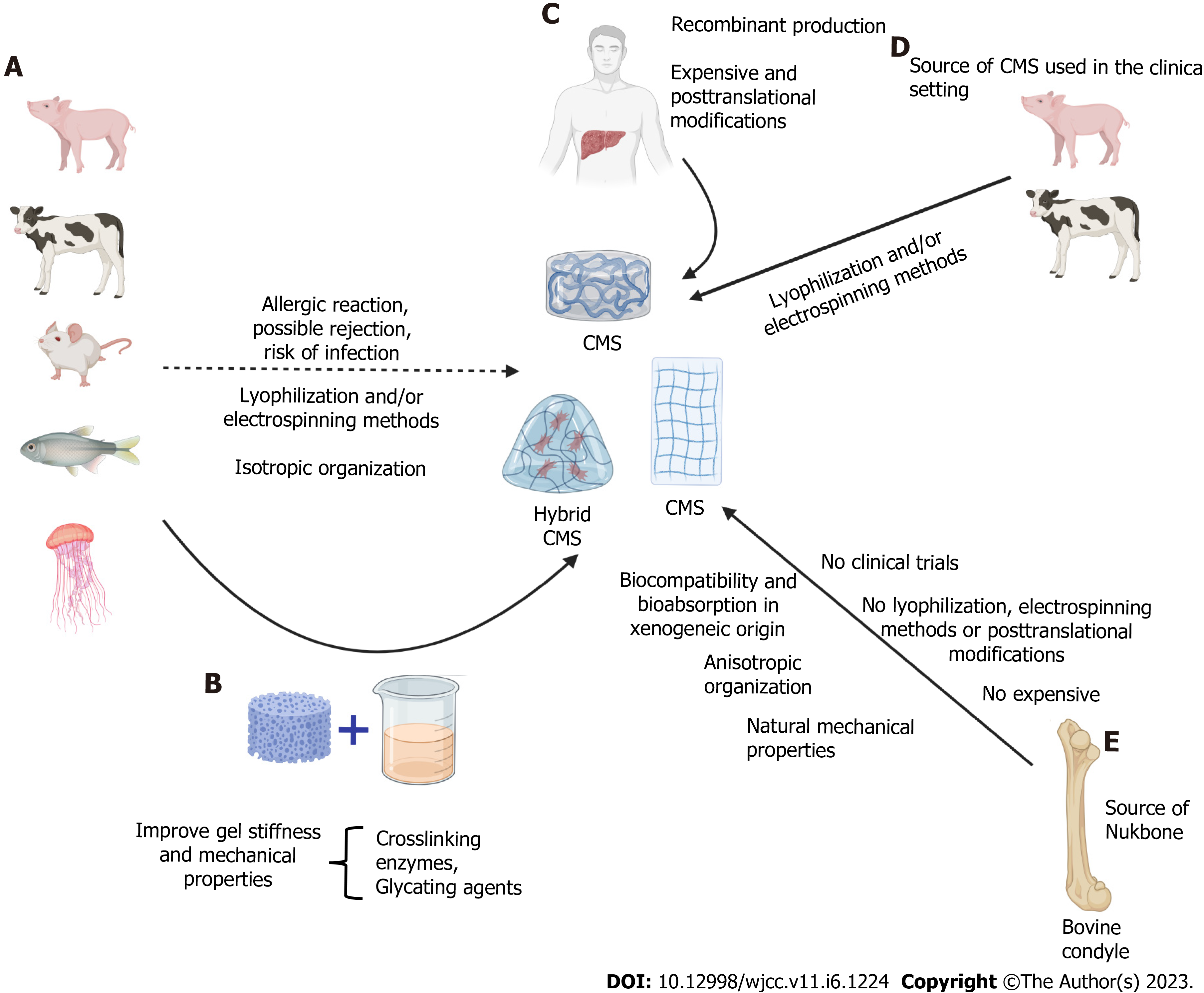
Figure 3 Challenges and limitations of collagen matrix scaffolds.
A: Xenogeneic sources of collagen promote allergic reactions, rejection or risk of infections (e.g., bovine spongiform encephalopathy). Lyophilization and/or electrospinning methods are used to obtain collagen matrix scaffold (CMS), which alter their natural properties, including isotropic organization; B: Hybrid collagen matrices using crosslinking enzymes (e.g., lysyl oxidase and transglutaminase) and glycating agents (high concentrations of ribose) to improve mechanical properties and stiffness; C: The production of human recombinant collagen is expensive, and current recombinant systems lack native prolyl 4-hydroxylase activity; D: The available sources of CMS are obtained from bovines and pigs using lyophilization and/or electrospinning methods; E: Nukbone obtained from bovine condyles as a CMS source showed great advantages; however, it is important to validate its use in clinical trials. The next step of CMS is explored in the context of the different stages of chronic liver disease induced by distinct liver insults.
- Citation: Martinez-Castillo M, Altamirano-Mendoza I, Zielinski R, Priebe W, Piña-Barba C, Gutierrez-Reyes G. Collagen matrix scaffolds: Future perspectives for the management of chronic liver diseases. World J Clin Cases 2023; 11(6): 1224-1235
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v11/i6/1224.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v11.i6.1224