Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Clin Cases. Oct 26, 2023; 11(30): 7485-7491
Published online Oct 26, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i30.7485
Published online Oct 26, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i30.7485
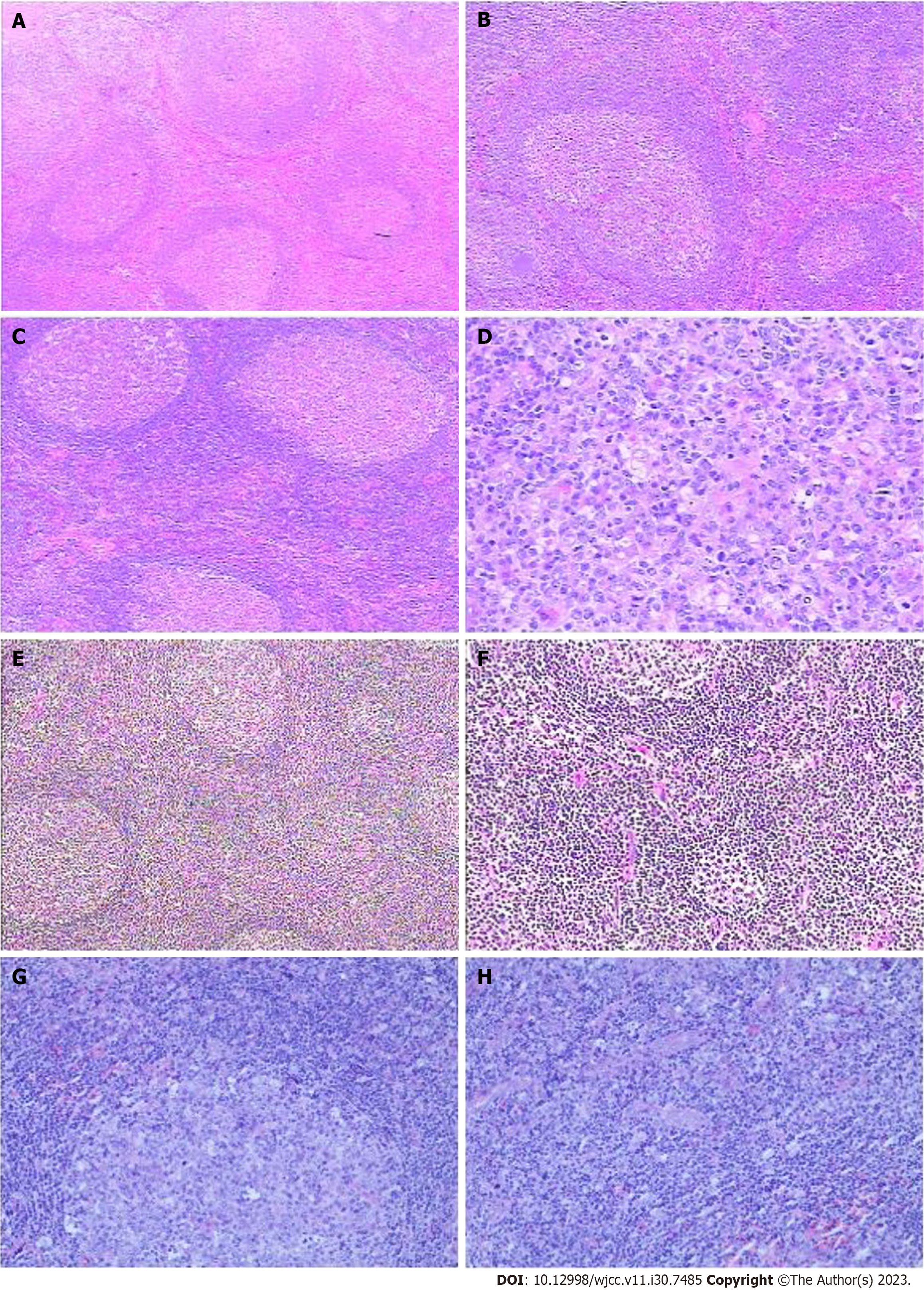
Figure 1 Hematoxylin and eosin staining and immunohistochemistry of lymph node biopsy.
A: The structure of lymph nodes is normal; the number of lymphoid follicles increased, and the volume of most follicles increased. The germinal center indicated proliferation and enlargement, and the germinal center cells were mixed; B: Macrophage phagocytosis was observed, and a few follicular cuff regions were pushed and thinned. A few follicular germinal centers shrank, and the sleeve area thickened. Lymph node follicular reactive hyperplasia; C: Most follicular germinal centers enlarged, and some showed apoptotic cells and nuclear fragments; D: A few follicular germinal centers shrank, and follicular epithelioid small vessel hyperplasia was observed. A few eosinophils proliferated; E: Some lymphoid follicles had atrophic with vitreous vessels in the center of the germinal center, onion skin-like structure in the covering area; F: and obvious proliferation of blood vessels with hyalinization in the paracentric region; G and H: Immunohistochemistry immunoglobulin G (IgG) and IgG4 (mostly located in the follicular germinal center, with a few located in the follicular area; IgG4/IgG4 > 40%) (G). Kappa and lambda plasmacytes (kappa plasmacytes > lambda plasmacytes). magnification, × 100 (H).
- Citation: Yu Y, Wang QQ, Jian L, Yang DC. Infrequent organ involvement in immunoglobulin G4-related prostate disease: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2023; 11(30): 7485-7491
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v11/i30/7485.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v11.i30.7485