Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Clin Cases. Oct 26, 2023; 11(30): 7318-7328
Published online Oct 26, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i30.7318
Published online Oct 26, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i30.7318
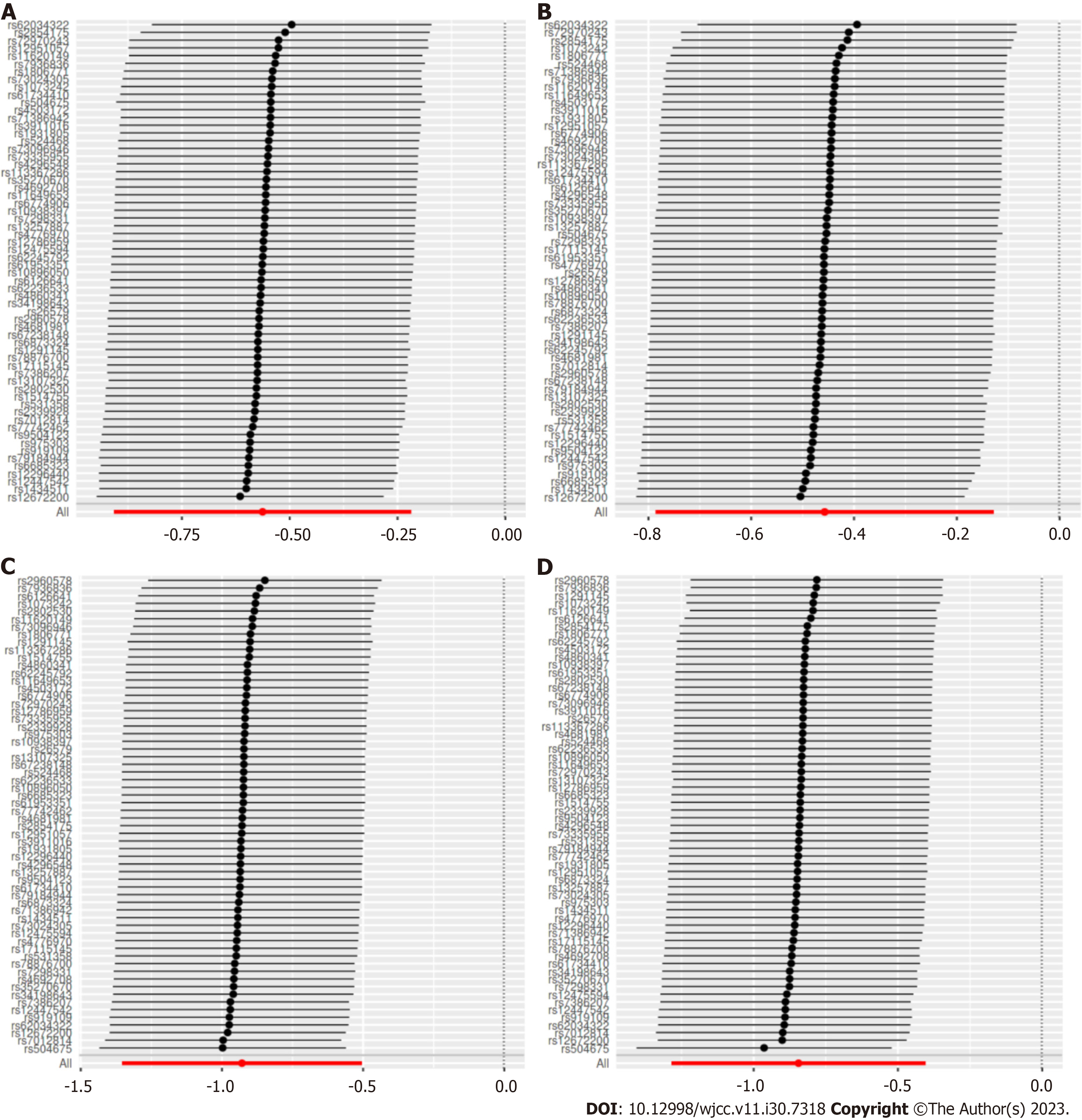
Figure 4 Leave-one-out of each single nucleotide polymorphisms associated of cheese intake with gestational hypertension and gestational diabetes risk.
Each black point represents result of the inverse variance weighted (IVW) Mendelian randomization method applied to estimate the causal effect of cheese intake on gestational hypertension and gestational diabetes excluding particular single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) from the analysis. Each red point depicts the IVW estimate using all SNPs. A: Mendelian randomization (MR) leave-one-out sensitivity analysis of gestational hypertension risk in FinnGen Biobank database; B: MR leave-one-out sensitivity analysis of gestational hypertension in FinnGen Biobank database; C: MR leave-one-out sensitivity analysis of gestational diabetes in FinnGen Biobank database; D: MR leave-one-out sensitivity analysis of gestational diabetes in FinnGen Biobank database.
- Citation: Zhong T, Huang YQ, Wang GM. Causal relationship association of cheese intake with gestational hypertension and diabetes result from a Mendelian randomization study. World J Clin Cases 2023; 11(30): 7318-7328
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v11/i30/7318.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v11.i30.7318