Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Clin Cases. Jan 26, 2023; 11(3): 598-609
Published online Jan 26, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i3.598
Published online Jan 26, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i3.598
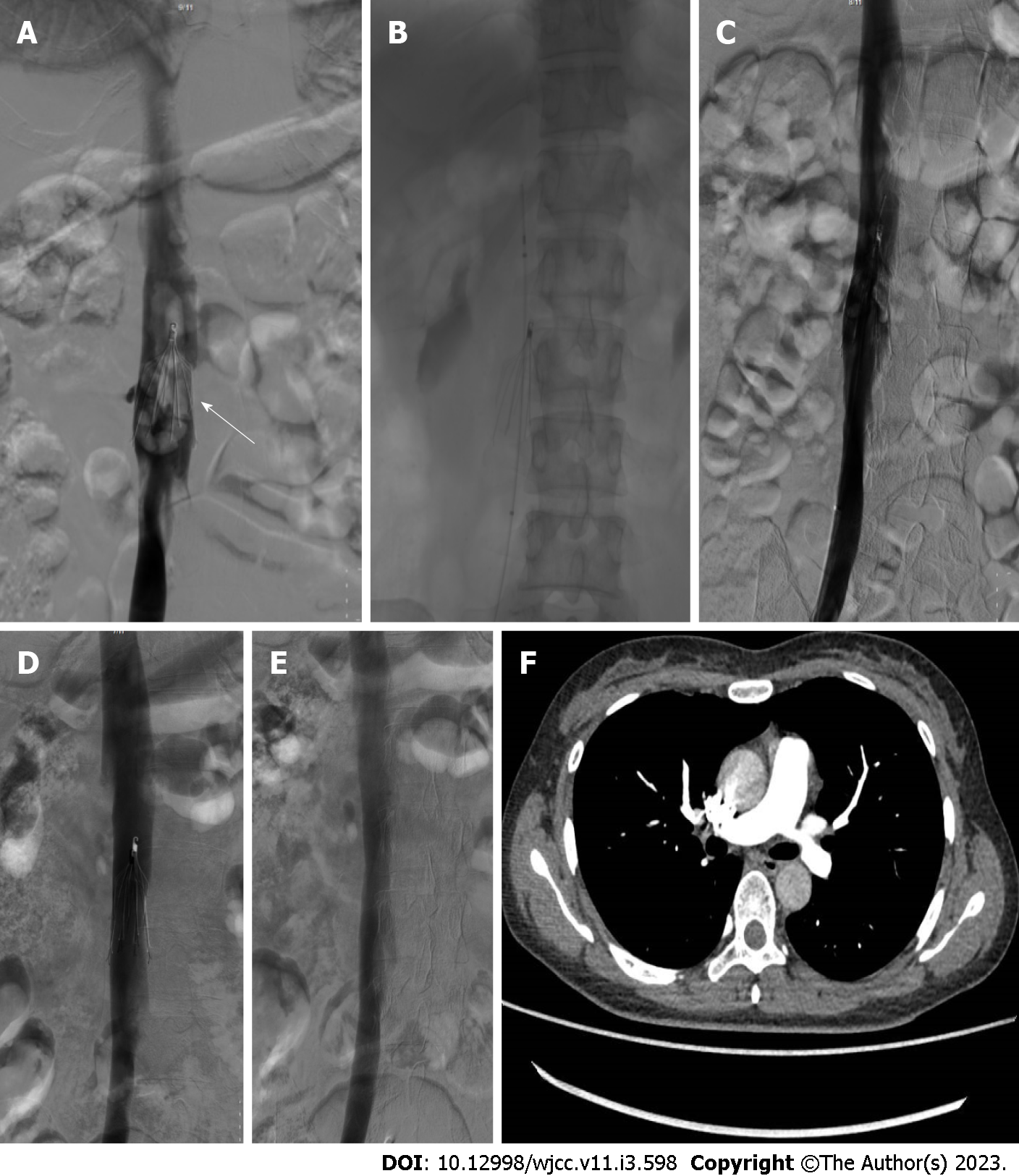
Figure 3 Angiography was implemented to assess the thrombus clearance of catheter-directed thrombolysis.
A: A 36-year-old male patient with acute traumatic lower-limb fracture and simultaneous deep venous thrombosis received an inferior vena cava (IVC) filter before surgical fixation. Filter removal was attempted within 2 wk after fracture surgery, and venography showed IVC-related caval thrombosis; B: A thrombolytic catheter was placed in the thrombosed segment via the right femoral vein, and urokinase was continuously injected; C: The venography showed that the most clearance thrombus of filter-related thrombosis; D: The patient was given anticoagulation therapy with rivaroxaban 20 mg daily after catheter-directed thrombolysis. The venography showed that the complete thrombus clearance of filter-related thrombosis 7 wk later; E: The venography showed that the IVC vein was unobstructed after the filter removal; F: Computed tomography angiopulmonography did not show pulmonary embolism after intervention.
- Citation: Li JY, Liu JL, Tian X, Jia W, Jiang P, Cheng ZY, Zhang YX, Liu X, Zhou M. Clinical outcomes of AngioJet pharmacomechanical thrombectomy versus catheter-directed thrombolysis for the treatment of filter-related caval thrombosis. World J Clin Cases 2023; 11(3): 598-609
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v11/i3/598.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v11.i3.598