Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Clin Cases. Sep 16, 2023; 11(26): 6091-6104
Published online Sep 16, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i26.6091
Published online Sep 16, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i26.6091
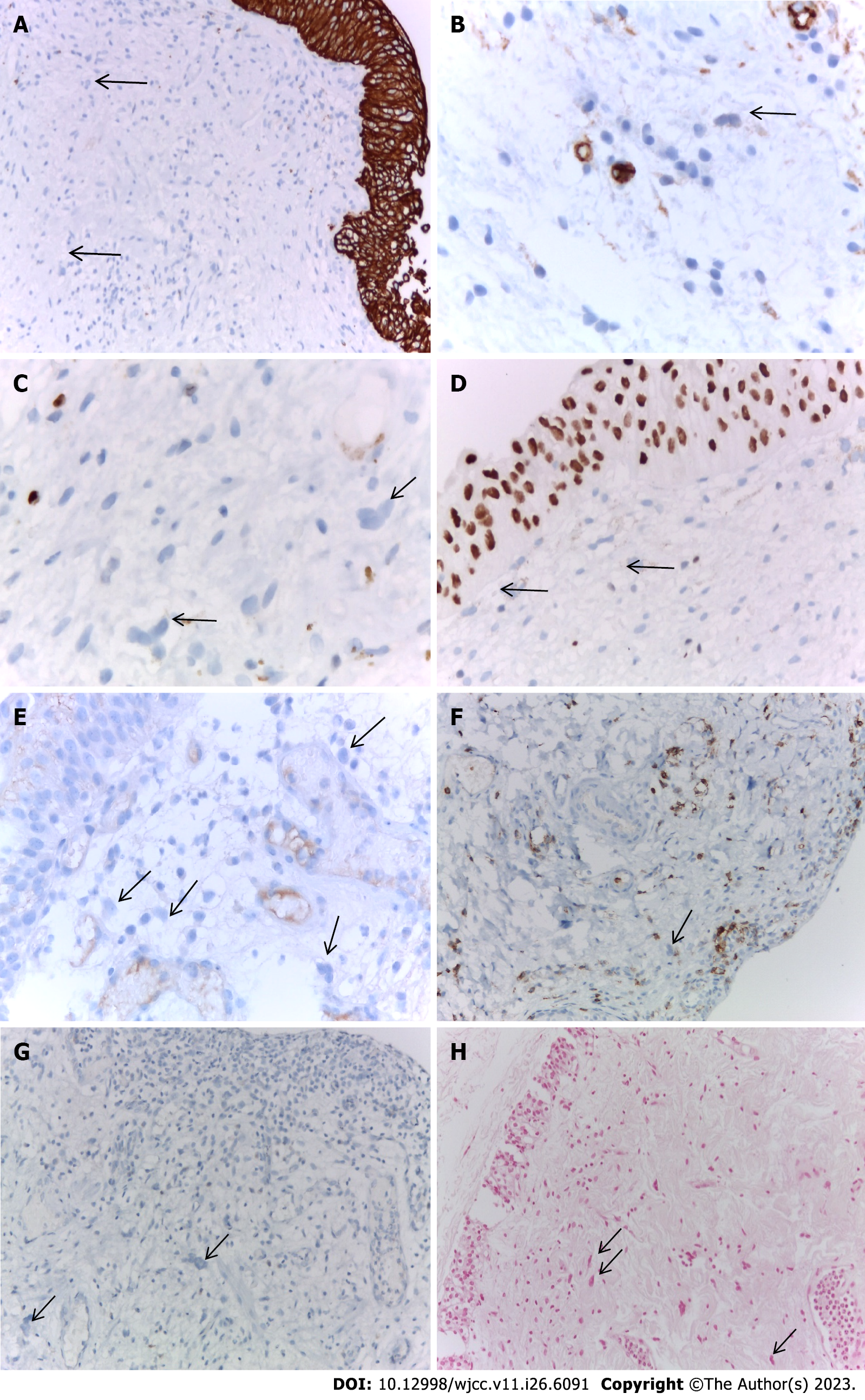
Figure 6 Immunohistochemical examination of urothelial carcinoma of the bladder.
A: Multinucleated giant cells (MGCs) with a negative expression for CK AE1/AE3, a positively marked LG urothelial carcinoma served for internal positive control. immunohistochemical (IHC), CK AE1/AE3 × 200; B: MGCs lacking expression for CD34 blast- (arrow), the surrounding capillaries served as an internal positive control. IHC, CD34blast × 400; C: MGCs were negative for Ki-67- (arrow), mononuclear inflammatory cells served as an internal positive control. IHC, Ki-67 × 630; D: MGCs were negative for GATA3- (arrow), for internal positive control serves the surrounding urothelial mucosa. IHC, anti-GATA3 × 400; E: MGCs with negative expression for PD-L1 (arrow). IHC, anti-PD-L1 × 400; F: MGC was negative for CD45 (arrow). IHC, CD45 × 200; G: MGCs were negative for CD1A (arrow). IHC, CD1A, × 200; H: Giant cells were negative for Perls staining (arrow). Perls, × 200.
- Citation: Gulinac M, Velikova T, Dikov D. Multinucleated giant cells of bladder mucosa are modified telocytes: Diagnostic and immunohistochemistry algorithm and relation to PD-L1 expression score. World J Clin Cases 2023; 11(26): 6091-6104
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v11/i26/6091.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v11.i26.6091