Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Clin Cases. Sep 6, 2023; 11(25): 5840-5856
Published online Sep 6, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i25.5840
Published online Sep 6, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i25.5840
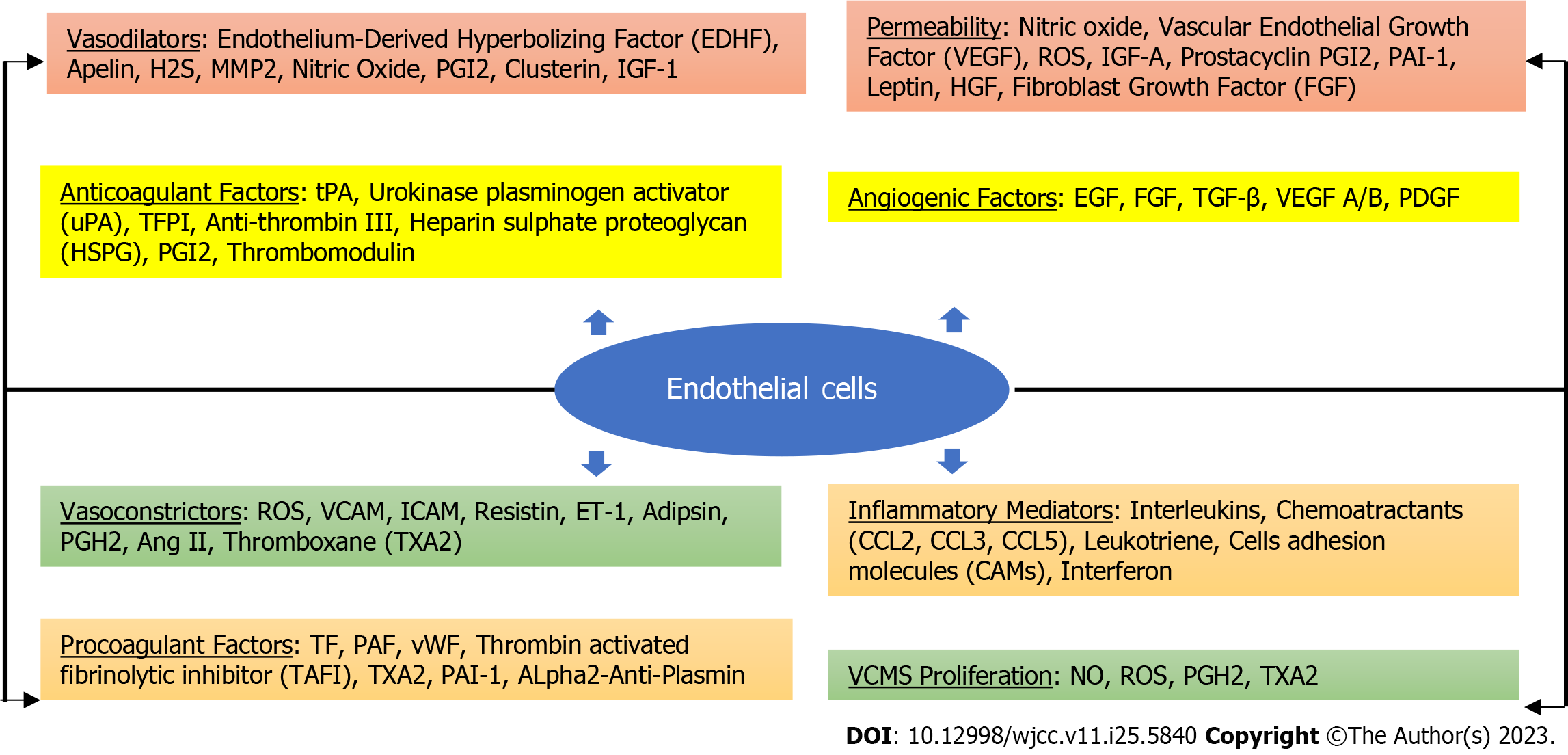
Figure 3 Important molecular functions of endothelial cells and the link between obesity-induced inflammation and endothelial dysfunction[74].
MMP2: Matrix metalloproteinase 2; PGI2: Prostacyclin; IGF-1: Insulin-like growth factor-1;ROS: Reactive oxygen species; FGF: Fibroblast growth factor; tPA: Tissue plasminogen activator; TFPI: Tissue factor pathway inhibitor; EGF: Epidermal growth factor; TGF-β: Transforming growth factor-β; PDGF: Platelet-derived growth factor; VCAM: Vascular cell adhesion molecule; ICAM: Intercellular adhesion molecule; ET-1: Endothelin-1; PAF: Platelet activating factor; vWF: von Willebrand factor; TXA2: Thromboxane A2; NO: Nitric oxide.
- Citation: Kumar S, Senapati S, Bhattacharya N, Bhattacharya A, Maurya SK, Husain H, Bhatti JS, Pandey AK. Mechanism and recent updates on insulin-related disorders. World J Clin Cases 2023; 11(25): 5840-5856
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v11/i25/5840.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v11.i25.5840