Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Clin Cases. Aug 16, 2023; 11(23): 5602-5609
Published online Aug 16, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i23.5602
Published online Aug 16, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i23.5602
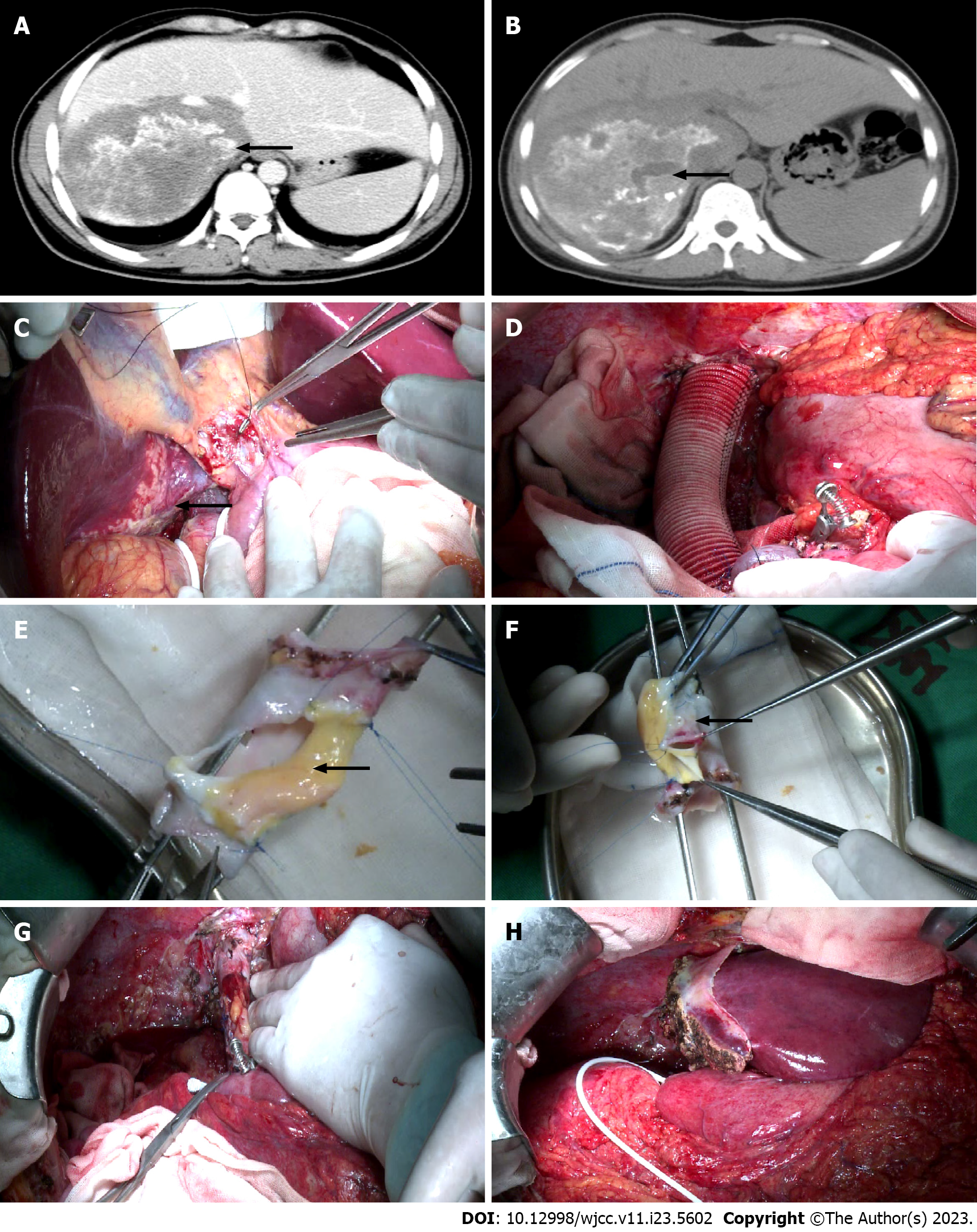
Figure 1 Preoperative imaging examination and surgical procedure.
A: Preoperative enhanced computed tomography (CT) scan shows the inferior vena cava (IVC) invaded by the lesion. The black arrow indicates IVC; B: A Preoperative enhanced CT scan shows the hepatic alveolar echinococcosis (AE) lesion located in the right posterior lobe and the caudate lobe of the liver. The black arrow indicates a hepatic AE lesion; C: Ex vivo liver resection and autotransplantation (ELRA) for the treatment of hepatic end-stage AE. The black arrow indicates the lesion; D: Reconstruct the hepatic IVC with artificial vessels to perform a temporary portal shunt; E: Using disease-free IVC and the umbilical vein within the ligamentum teres hepatis (LTH) to reconstruct the IVC. The black arrow indicates the umbilical vein within the LTH; F: Using disease-free IVC and part of the portal vein (PV) to reconstruct the IVC. The black arrow indicates the PV; G: The IVC was replanted back into the abdominal cavity after complex reconstruction; H: After meticulous dissection, the left lateral lobes were replanted back into the abdominal cavity.
- Citation: Humaerhan J, Jiang TM, Aji T, Shao YM, Wen H. Complex inferior vena cava reconstruction during ex vivo liver resection and autotransplantation: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2023; 11(23): 5602-5609
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v11/i23/5602.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v11.i23.5602