Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Clin Cases. Aug 6, 2023; 11(22): 5224-5235
Published online Aug 6, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i22.5224
Published online Aug 6, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i22.5224
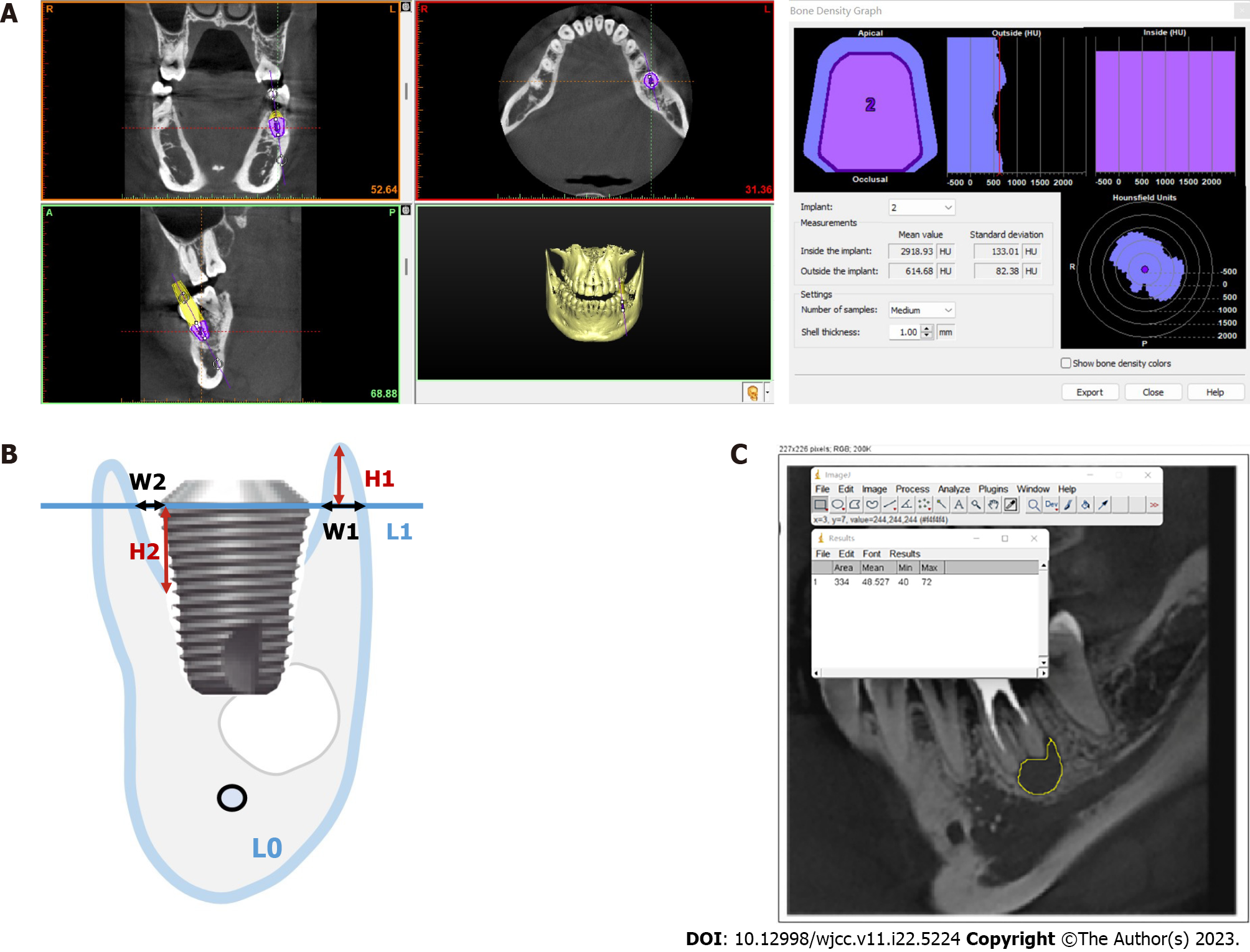
Figure 4 Method for measuring changes in bone tissue around implants.
A: The peri-implant bone mineral density was measured using Simplant software; B: Schemas of marginal bone resorption and jump gap measurements. L0 is the long axis of the implant. L1 is perpendicular to L0. H1 is the vertical distance from the crest of the alveolar bone to L1. W1 is the horizontal distance from the most lateral side of the alveolar bone wall to the edge of the implant. H2 is the vertical distance from the highest point of contact between the implant and the bone to L1. W2 is the width of the jump gap. C: Image J software was used to measure the gray value of the bone destruction area at the root apex of the affected tooth (the gray value of alveolar bone cone-beam computed tomography can reflect its bone mineral density).
- Citation: Yang H, Luo D, Yuan MJ, Yang JJ, Wang DS. Five-year outcomes of immediate implant placement for mandibular molars with and without chronic apical periodontitis: A retrospective study. World J Clin Cases 2023; 11(22): 5224-5235
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v11/i22/5224.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v11.i22.5224