Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Clin Cases. Jul 26, 2023; 11(21): 5136-5146
Published online Jul 26, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i21.5136
Published online Jul 26, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i21.5136
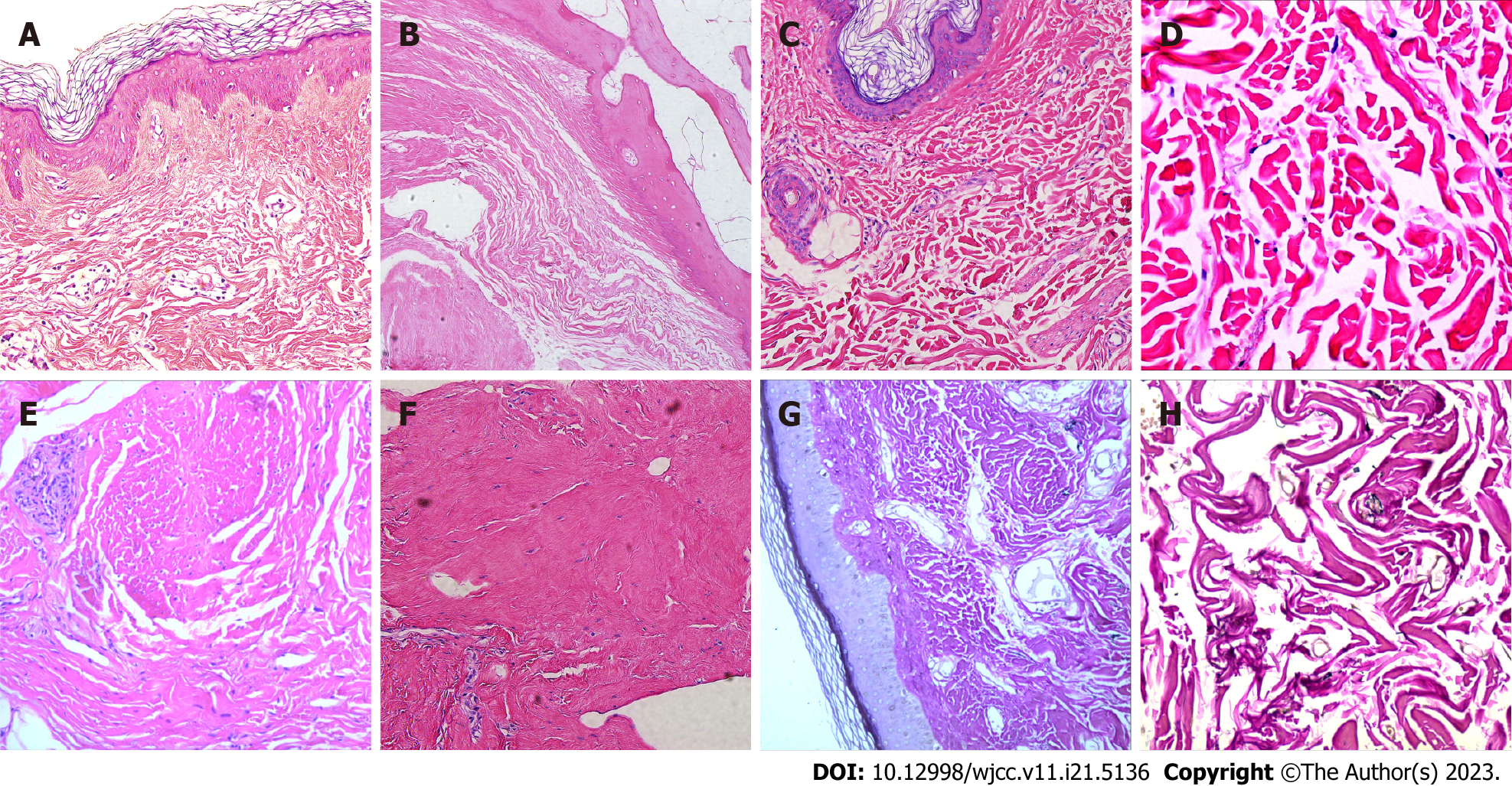
Figure 2 Typical pathological images of skin lesions in patients with fibroblast rheumatism.
A: Skin biopsy from the finger revealing dermal fibrous hyperplasia, elastic fiber disorder, skin hyperkeratosis, and irregular thickening of the spinous layer; B: Haematoxylin and eosin staining of left foot articular cartilage displaying central cartilage degeneration and necrosis with calcification, along with dermal collagen fiber hyperplasia and spindle cell proliferation; C and D: Histological examination of upper arm scar tissue and synovium, showing collagen fiber hyperplasia, elastic fiber disorder, and spindle cell proliferation; E and F: Palmar aponeurosis biopsy from the right arch demonstrating fibrous hyperplasia with localized spindle cell proliferation (Haematoxylin and eosin, original magnifications: (A: ×200; B: ×200; C: ×200; D: ×400; E: ×40; F: ×200); G and H: Elastica van Gieson staining revealing reduced elastic fibers in the dermis (G: ×200; H: ×400).
- Citation: Guo H, Liang Q, Dong C, Zhang Q, Gu ZF. Systematic review of fibroblastic rheumatism: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2023; 11(21): 5136-5146
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v11/i21/5136.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v11.i21.5136