Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Clin Cases. Jul 26, 2023; 11(21): 5047-5055
Published online Jul 26, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i21.5047
Published online Jul 26, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i21.5047
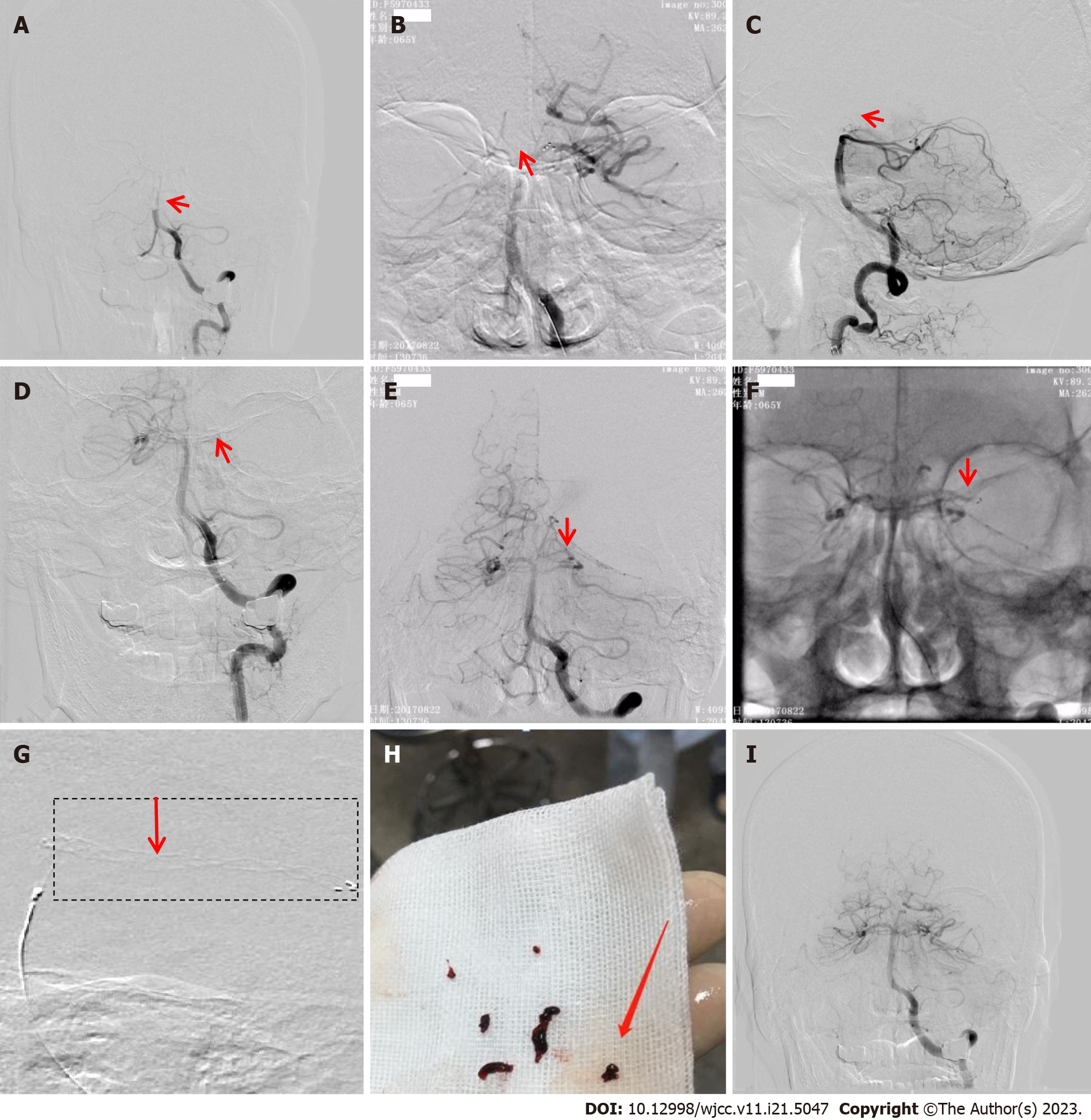
Figure 1 Operative procedure: Patient 1.
A: Digital subtraction angiography (DSA) revealing proximal basilar artery (BA) occlusion (arrow); B: Stent deployed at the left posterior cerebral artery (LPCA)-P1 segment and BA (without stent imaging, arrow); C: DSA revealing the upper part of the BA occlusion (arrow); D: Stent deployed in the proximal region of the right posterior cerebral artery (RPCA)-P1 segment to capture the thrombus; E: DSA revealing the RPCA and LPCA-P1 segment proximal occlusion (arrow); F: Stent placed in the distal LPCA-P1 segment (without stent imaging, arrow); it was unable to capture a thrombus; G: Stent deployed at the LPCA-P2 segment and stent imaging presenting a grid-form shadow; H: Stent capturing three fragmented thrombi; I: Repeat DSA revealing good recanalization.
- Citation: Yao QY, Fu ML, Zhao Q, Zheng XM, Tang K, Cao LM. Image-based visualization of stents in mechanical thrombectomy for acute ischemic stroke: Preliminary findings from a series of cases. World J Clin Cases 2023; 11(21): 5047-5055
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v11/i21/5047.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v11.i21.5047