Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Clin Cases. Jul 16, 2023; 11(20): 4912-4919
Published online Jul 16, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i20.4912
Published online Jul 16, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i20.4912
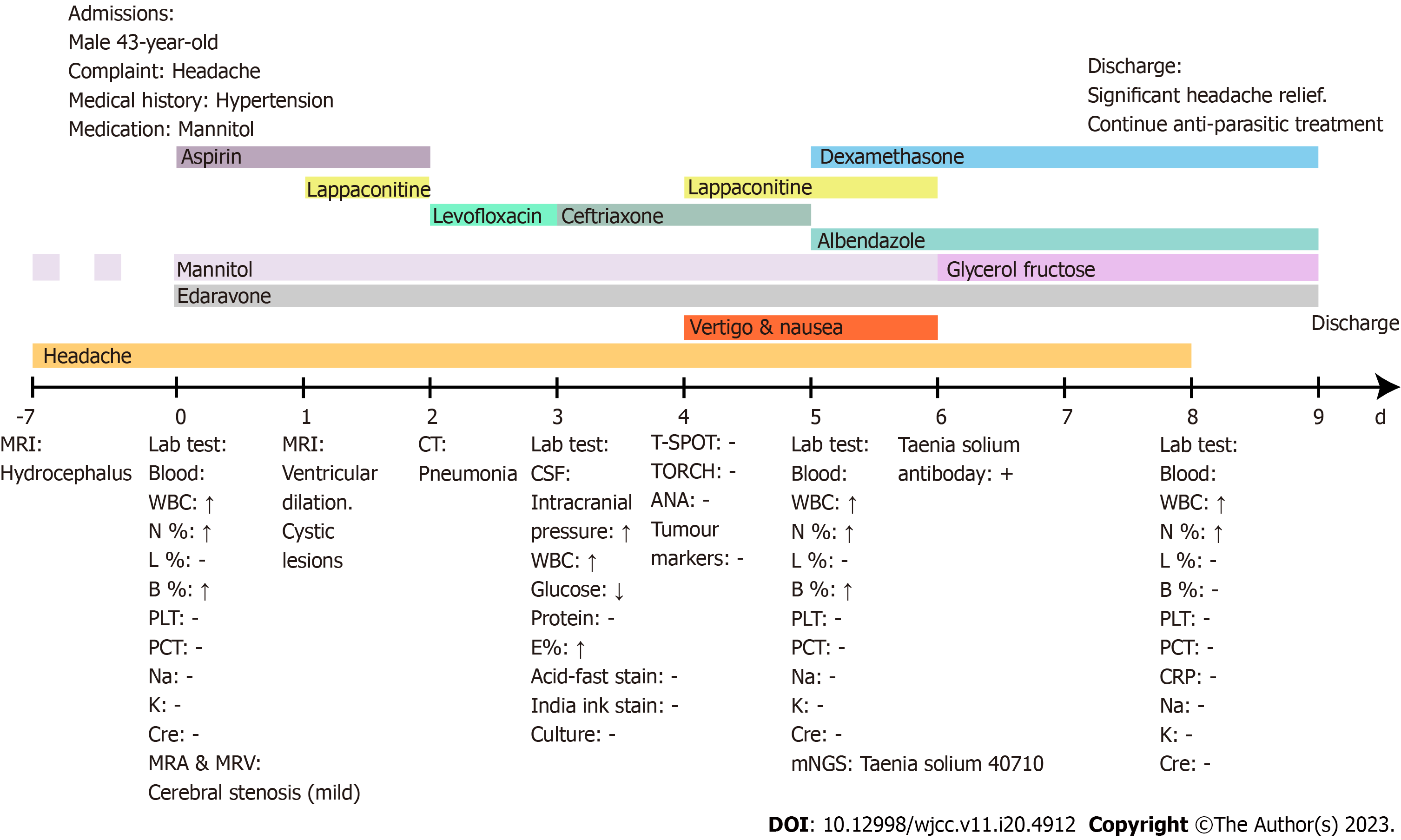
Figure 3 The timeline of clinical events.
Imaging examinations from the local hospital, taken seven days before admission, showing hydrocephalus. The patient was treated with mannitol. Before metagenomic next-generation sequencing (mNGS) was conducted (the first five days of the hospital stay), we considered this to be a central nervous system infection case. On the fifth day of the hospital stay, we obtained the mNGS results which showed high Taenia solium reads. Symptomatic treatments were carried out combining dexamethasone and albendazole; meanwhile, glycerol fructose and lappaconitine were used to relieve the symptoms. Blood means the Blood specimen. CSF means the cerebrospinal fluid specimen. MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging; WBC: White blood cell; N: Neutrophils; L: Lymphocyte; B: Basophilic granulocyte; E: Eosinophilic granulocyte; PLT: Platelets; PCT: Procalcitonin; CRP: C-reactive protein; Na: Sodium; K: Potassium; Cre: Creatinine; TORCH: Antibody test for Toxoplasma, Herpes virus, Cytomegalovirus, and Rubella virus; CSF: Cerebrospinal fluid; mNGS: Metagenomic next-generation sequencing; ANA: Antinuclear antibody. -: Normal; ↑: Above normal; ↓: Below normal.
- Citation: Xu WB, Fu JJ, Yuan XJ, Xian QJ, Zhang LJ, Song PP, You ZQ, Wang CT, Zhao QG, Pang F. Metagenomic next-generation sequencing in the diagnosis of neurocysticercosis: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2023; 11(20): 4912-4919
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v11/i20/4912.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v11.i20.4912