Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Clin Cases. Jul 6, 2023; 11(19): 4713-4722
Published online Jul 6, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i19.4713
Published online Jul 6, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i19.4713
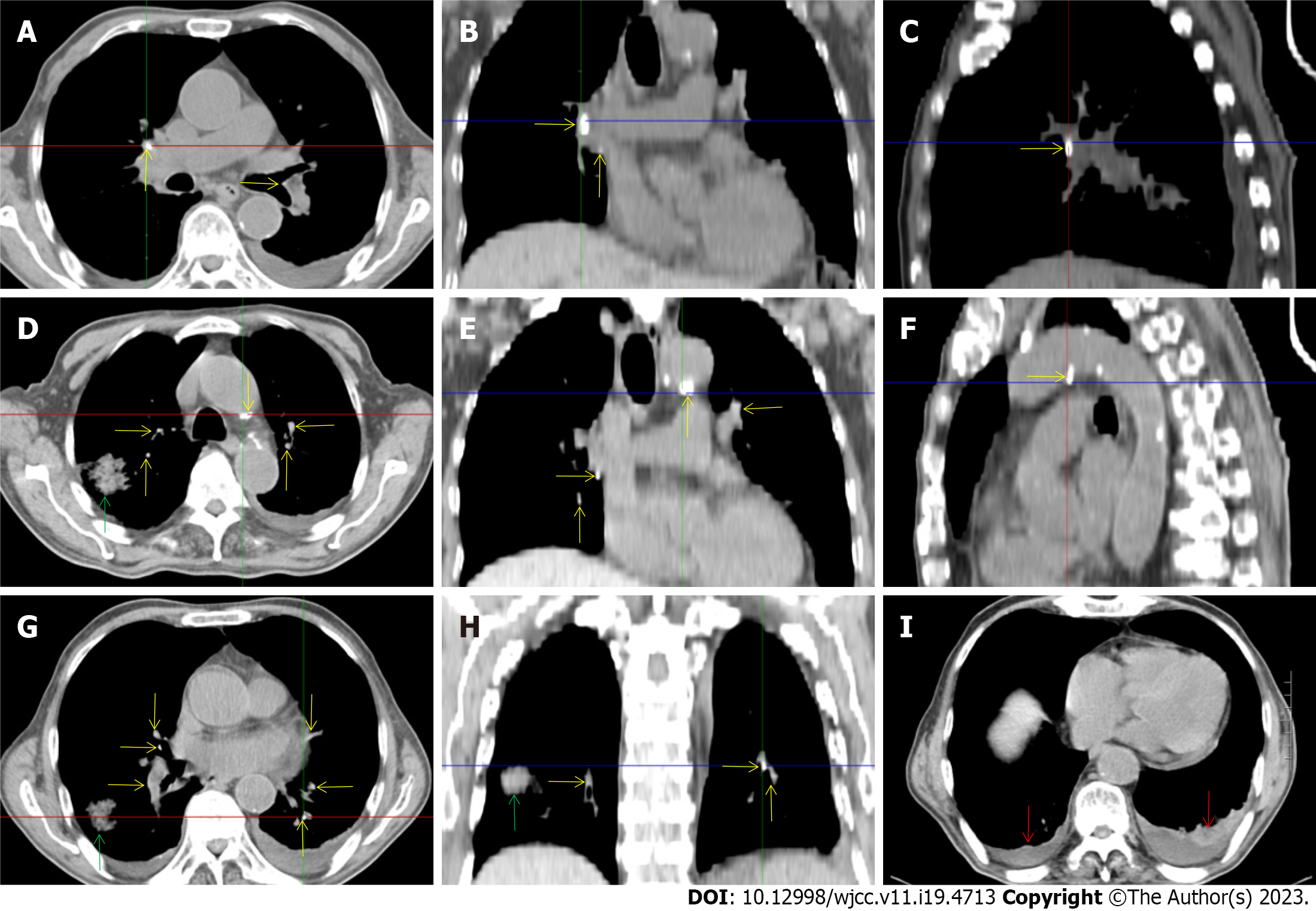
Figure 2 Chest computed tomography during aplastic crisis.
A-H: Multiple calcified lesions were present in the lungs, hilum and mediastinum (yellow arrows), indicating the existence of old tuberculosis. The adjacent exudative lesions indicated reactivation of the old tuberculosis condition. A massive exudative lesion was present in the right lung (green arrows), and there was a similar exudative lesion on the pleuron adjacent to the massive exudative lesion; I: Hypertrophic lesions with pleural effusion were present in the bilateral pleura (red arrows), indicating pleural involvement of the tuberculosis infection. The pleural effusion was bloody, with an elevated level of adenosine deaminase, which was detected in aspirates and reinforced the diagnosis of tuberculosis.
- Citation: Sun XY, Yang XD, Xu J, Xiu NN, Ju B, Zhao XC. Tuberculosis-induced aplastic crisis and atypical lymphocyte expansion in advanced myelodysplastic syndrome: A case report and review of literature. World J Clin Cases 2023; 11(19): 4713-4722
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v11/i19/4713.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v11.i19.4713