Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Clin Cases. Jul 6, 2023; 11(19): 4458-4476
Published online Jul 6, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i19.4458
Published online Jul 6, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i19.4458
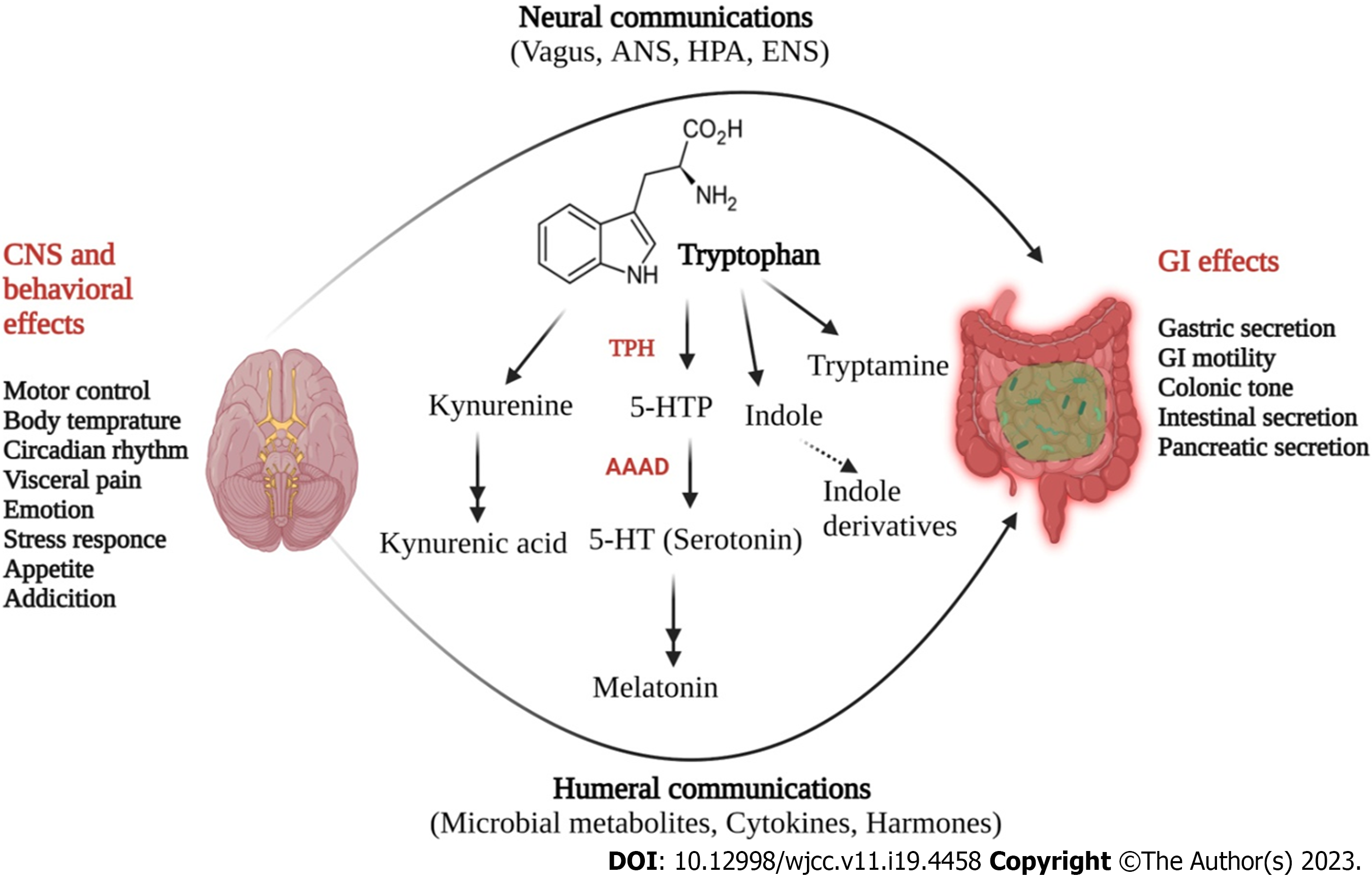
Figure 4 Tryptophan derived serotonergic metabolism in gut brain axis cross talk.
Upon absorption in the gut, L-tryptophan is metabolized through three pathways, particular to bacterial cells (indole pathway) of gut microbiota and mammalian cells (kynurenine and serotonin pathways). Tryptophan is converted to 5-hydoxytryptophan (5-HTP) by tryptophan hydroxylase and thereafter converted to -5-HT by the enzyme aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase. In addition to this, tryptophan is also metabolized to indole derivatives and kynurenine, which also perform various biological functions. Tryptophan derived 5-HT regulates various functions in central nervous system (including emotion, cognition, stress, and visceral perception) and in enteric nervous system (gastrointestinal motility and secretion). CRF: Corticotropin-releasing factor; ANS: Autonomic nervous system; CNS: Central nervous system; GI: Gastrointestinal; 5-HT: 5-Hydroxytryptamine; HPA: Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal.
- Citation: Singh SV, Ganguly R, Jaiswal K, Yadav AK, Kumar R, Pandey AK. Molecular signalling during cross talk between gut brain axis regulation and progression of irritable bowel syndrome: A comprehensive review. World J Clin Cases 2023; 11(19): 4458-4476
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v11/i19/4458.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v11.i19.4458