Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Clin Cases. Jun 26, 2023; 11(18): 4446-4453
Published online Jun 26, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i18.4446
Published online Jun 26, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i18.4446
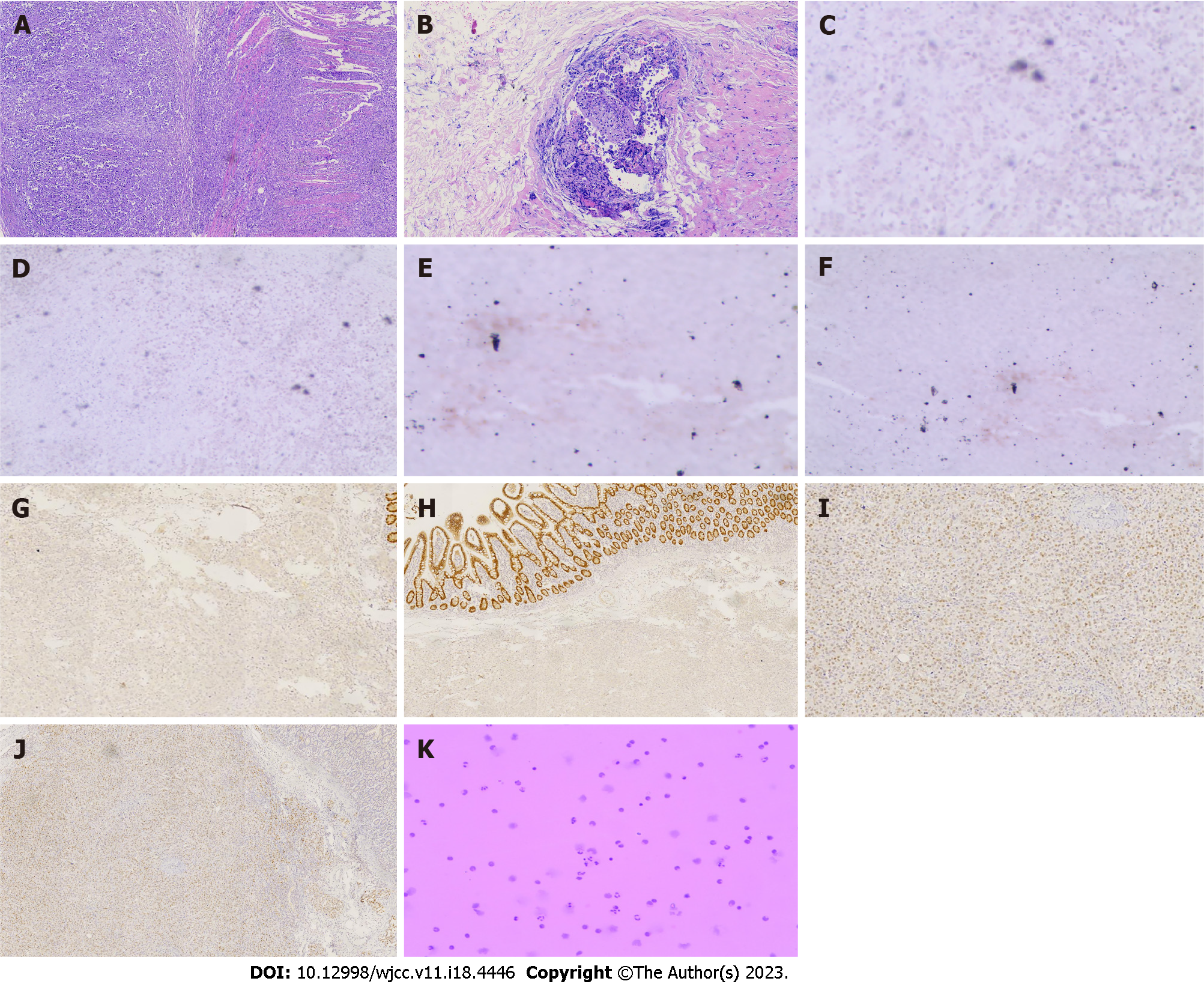
Figure 2 Immunohistochemical and histological features of metastatic cholangiocarcinoma and small intestine cancer from breast cancer.
A: Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining showed that cancer cells infiltrated the entire intestinal wall, (40 ×); B: H&E staining showed that cancer cells infiltrated the glandular duct of the bile duct (100 ×); C-J: Immunohistochemical staining showed negative expression of caudal-related homeobox transcription factor 2 (CDX-2) (C) and villin (E) in metastatic cholangiocarcinoma. Immunohistochemical staining showed negative expression of CDX-2 (D) and villin (F) in the metastatic small intestine tumor. Immunohistochemical staining showed positive gross cystic disease fluid protein 15 (GCDFP-15) (G) and expression of GATA binding protein-3 (GATA3) (I) in metastatic cholangiocarcinoma. Immunohistochemical staining showed positive GCDFP-15 (H) and expression of GATA3 (J) in the metastatic small intestine tumor; K: Tumor cells were detected in the hydrothorax and ascites.
- Citation: Jiao X, Zhai MM, Xing FZ, Wang XL. Simultaneously metastatic cholangiocarcinoma and small intestine cancer from breast cancer misdiagnosed as primary cholangiocarcinoma: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2023; 11(18): 4446-4453
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v11/i18/4446.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v11.i18.4446