Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Clin Cases. Jun 6, 2023; 11(16): 3714-3724
Published online Jun 6, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i16.3714
Published online Jun 6, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i16.3714
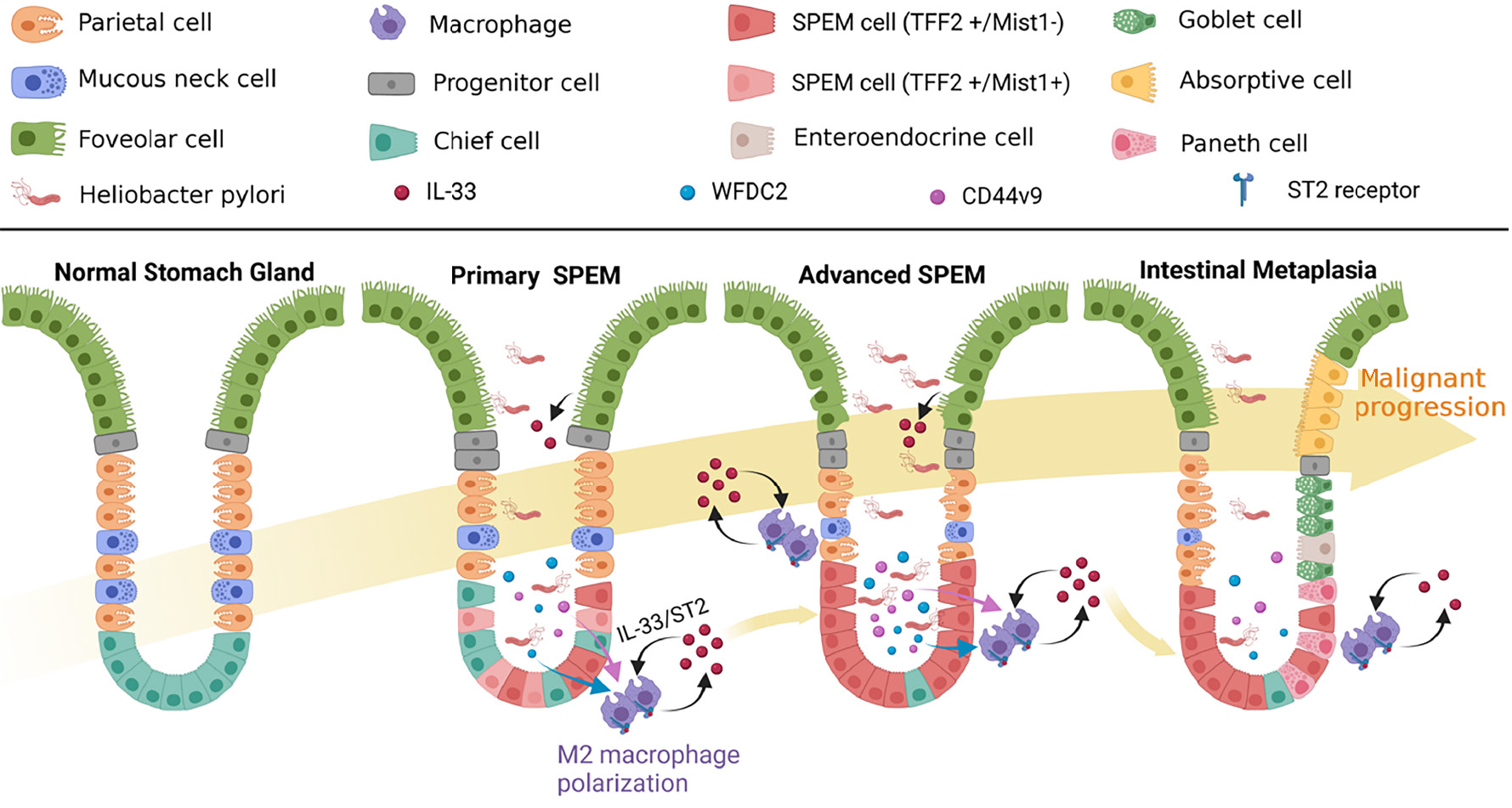
Figure 1 Alteration of glandular cells during spasmolytic polypeptide-expressing metaplasia malignant progression due to Heliobacter pylori infection.
Under the influences of chronic inflammation, CD44 variant 9, and whey acidic protein 4-disulfide core domain protein 2 produced by spasmolytic polypeptide-expressing metaplasia (SPEM) malignant cells, M1 and M2 polarization is induced in local macrophages, after which M1 polarized macrophages will secrete interferon-γ, which is one of the important inflammatory factors that aggravate local inflammation. M2 polarization causes macrophages to secrete large amounts of interleukin-33, which aggravates the transdifferentiation of mature master cells and promotes the malignant progression of SPEM. Citation: Created with BioRender.com. (Supplementary material). SPEM: Spasmolytic polypeptide-expressing metaplasia; IL: Interleukin; WFDC: Whey acidic protein 4-disulfide core domain protein 2; CD44v9: CD44 variant isoform 9.
- Citation: Li ML, Hong XX, Zhang WJ, Liang YZ, Cai TT, Xu YF, Pan HF, Kang JY, Guo SJ, Li HW. Helicobacter pylori plays a key role in gastric adenocarcinoma induced by spasmolytic polypeptide-expressing metaplasia. World J Clin Cases 2023; 11(16): 3714-3724
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v11/i16/3714.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v11.i16.3714