Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Clin Cases. Apr 6, 2023; 11(10): 2290-2300
Published online Apr 6, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i10.2290
Published online Apr 6, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i10.2290
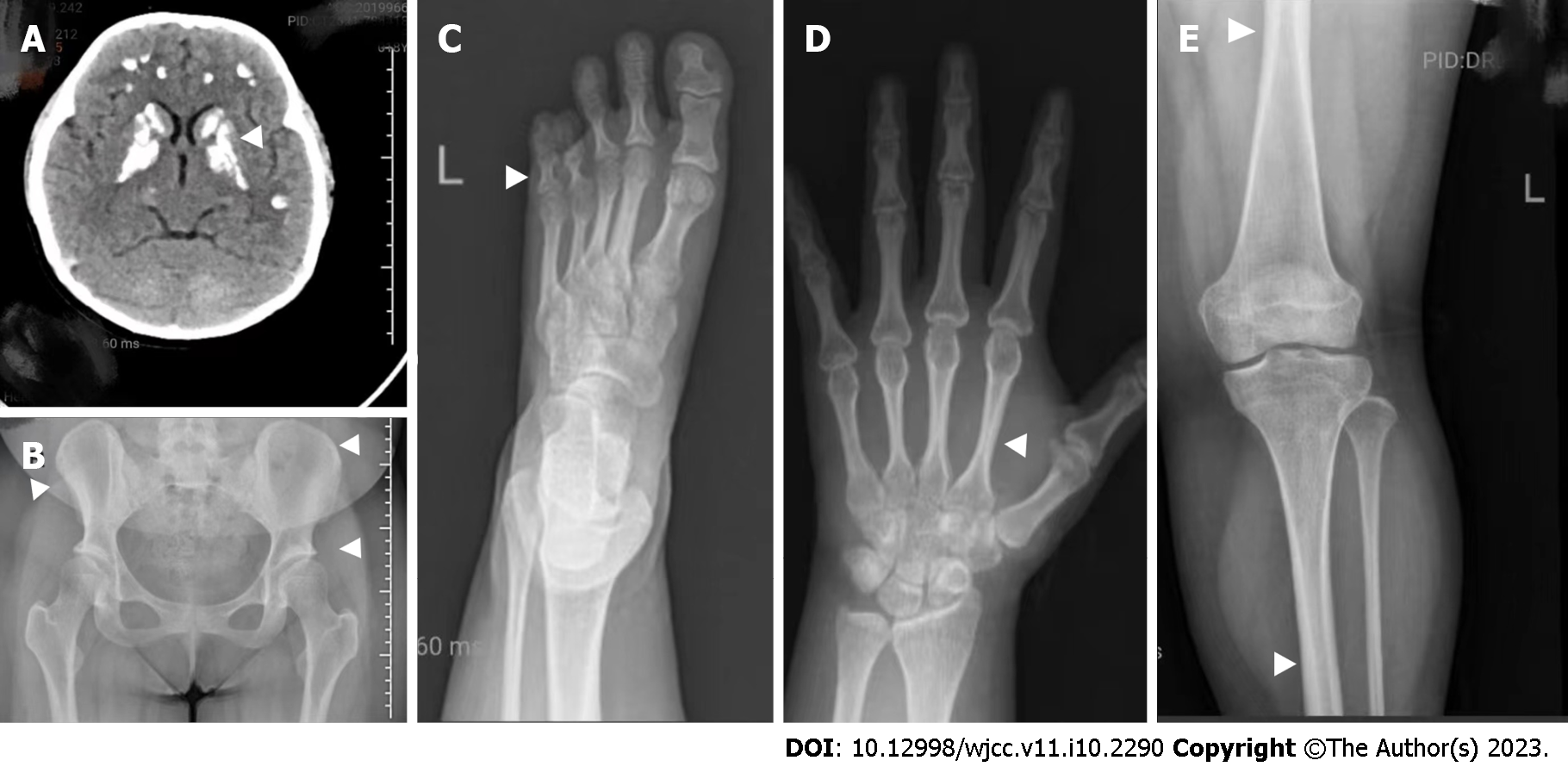
Figure 2 The head computed tomography and skeletal X-ray features of the patient are indicated by arrows A–E, respectively.
A: Head computed tomography (noncontrast) showing symmetrical calcifications in the cerebellar hemisphere, frontotemporal parietal lobe, basal ganglia, and thalamus; B: Digital radiography (DR) of the anteroposterior pelvis showing that the right ilium is smaller compared to the left side, as well as shallow acetabular fossa on both sides; C: DR of the left foot showing short and small 4th and 5th metatarsal bones and corresponding phalanges in both feet; D: The phalanges of the left little finger are short, with thickening of the cortex of the tubular bone and narrowing of the medulla; E: DR of the left lower limb showing thickening of the cortex of the tubular bone and narrowing of the medulla.
- Citation: Yuan N, Lu L, Xing XP, Wang O, Jiang Y, Wu J, He MH, Wang XJ, Cao LW. Clinical and genetic features of Kenny-Caffey syndrome type 2 with multiple electrolyte disturbances: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2023; 11(10): 2290-2300
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v11/i10/2290.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v11.i10.2290