Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Mar 26, 2022; 10(9): 2751-2763
Published online Mar 26, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i9.2751
Published online Mar 26, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i9.2751
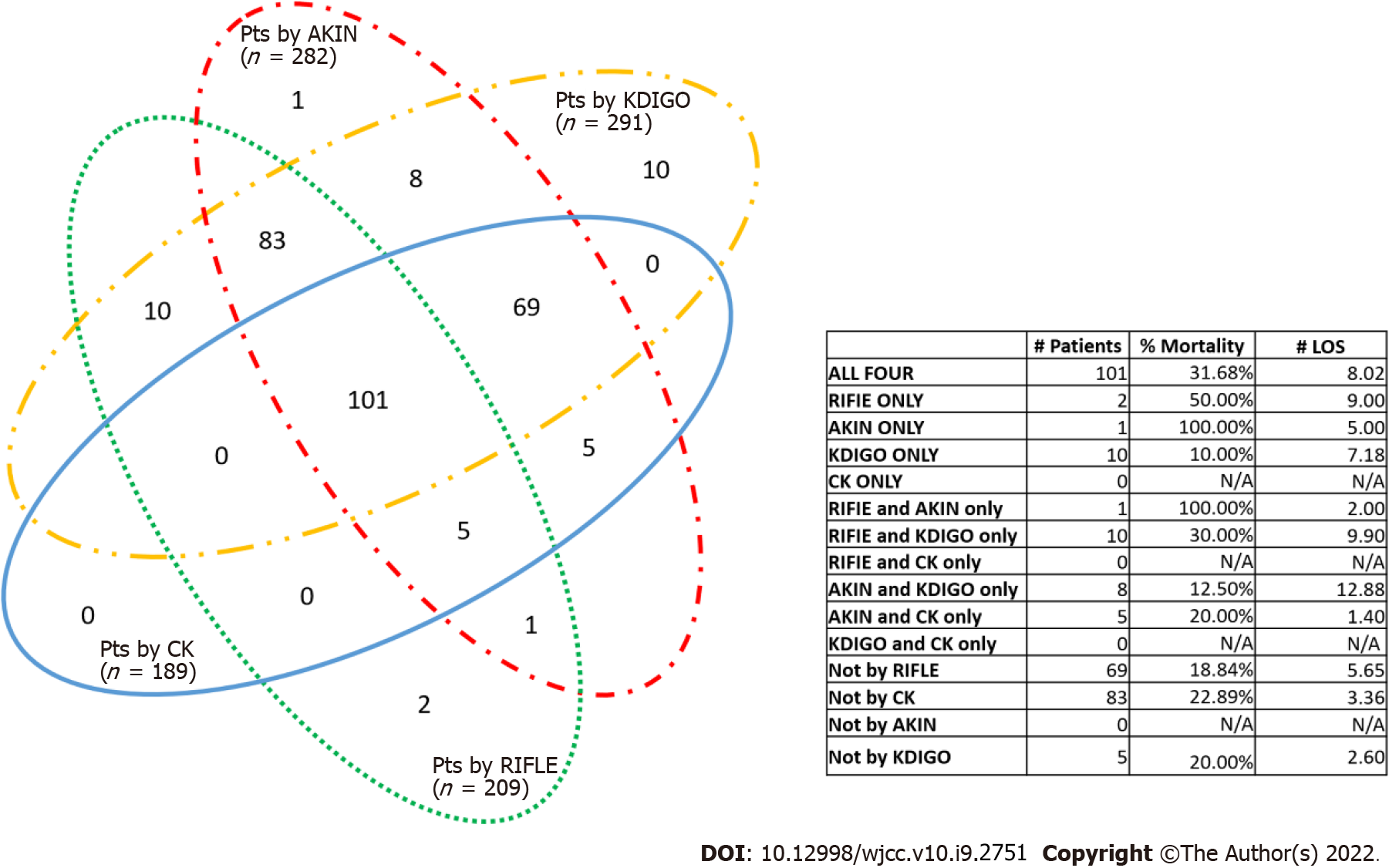
Figure 2 Definition overlap and in-hospital mortality of patients diagnosed by Creatinine kinetics, “Risk, Injury, Failure, Loss of kidney function, and End-stage kidney disease”, Acute Kidney Injury Network, and Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes.
Each number in the figure represents the number of patients correctly identified with acute kidney injury by the different definitions represented by the colored circles. For example, 101 patients are included in all four circles, meaning that they have been correctly classified by all four definitions, while 83 patients were correctly identified by “Risk, Injury, Failure, Loss of kidney function, and End-stage kidney disease” (RIFLE), Acute Kidney Injury Network (AKIN), and Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO). KDIGO was shown in yellow; AKIN in red; RIFLE in green; and Creatinine kinetics in blue. LOS: Length of stay (day); CK: Creatinine kinetics; RIFLE: Risk, Injury, Failure, Loss of kidney function, and End-stage kidney disease; AKIN: Acute Kidney Injury Network; KDIGO: Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes.
- Citation: Huang ZY, Liu Y, Huang HF, Huang SH, Wang JX, Tian JF, Zeng WX, Lv RG, Jiang S, Gao JL, Gao Y, Yu XX. Acute kidney injury in traumatic brain injury intensive care unit patients. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(9): 2751-2763
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i9/2751.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i9.2751