Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Mar 26, 2022; 10(9): 2743-2750
Published online Mar 26, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i9.2743
Published online Mar 26, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i9.2743
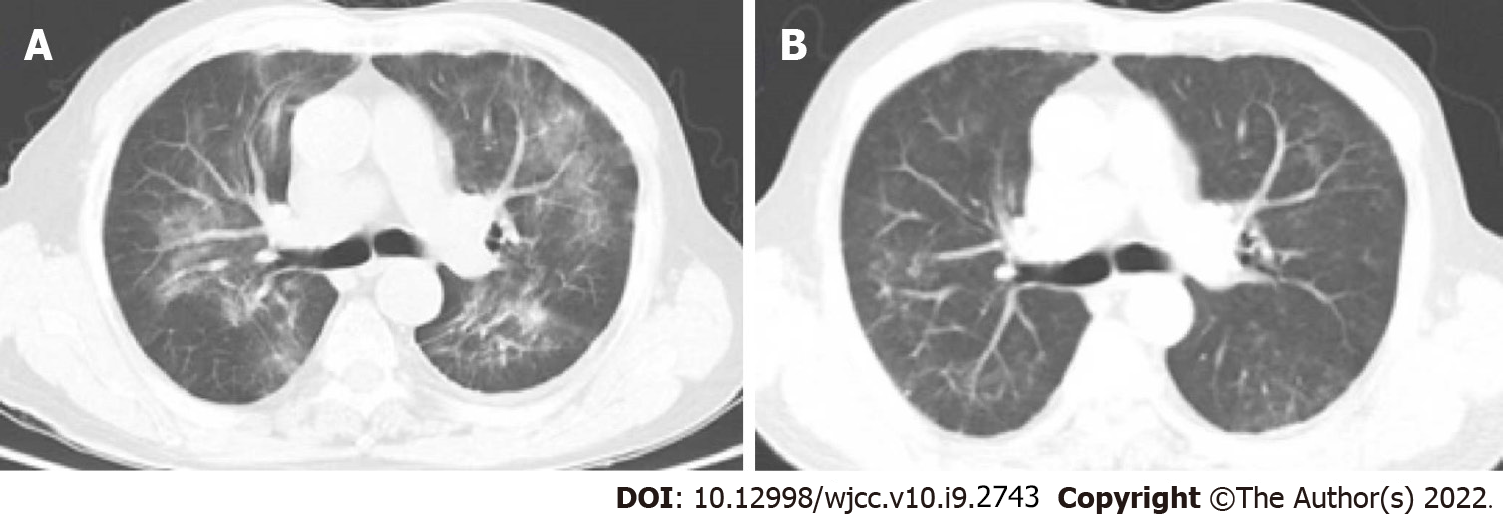
Figure 1 A 76-year-old man with rheumatic polymyalgia who under 8 mg/wk methotrexate treatment attended our hospital with complaints of cough and fever.
A: The patient presented with respiratory failure and received 3 L/min oxygen therapy nasally. Computed tomography (CT) indicated bilateral infiltration dominantly in the hilum. The patient received bronchoscopy the day after admission. Next-generation sequencing analysis of the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid was positive for Pneumocystis jirovecii. The patient was diagnosed with severe non-human immunodeficiency virus-infected Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia. Daily oral administration of 12 mg/kg trimethoprim (TMP) and 60 mg/kg sulfamethoxazole (SMX) [oral administration of two tablets of TMP (80 mg) and SMX (400 mg), four times daily] and caspofungin (intravenous administration of 70 mg QD for the first day and 50 mg QD for maintenance) was initiated and continued for 14 d without any adverse events; B: The respiratory status of the patient improved gradually. CT at 14 d after start of treatment showed restoration of respiration. The patient was discharged on day 18 of hospitalization.
- Citation: Wu HH, Fang SY, Chen YX, Feng LF. Treatment of Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia in non-human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients using a combination of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole and caspofungin. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(9): 2743-2750
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i9/2743.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i9.2743