Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Dec 26, 2022; 10(36): 13148-13156
Published online Dec 26, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i36.13148
Published online Dec 26, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i36.13148
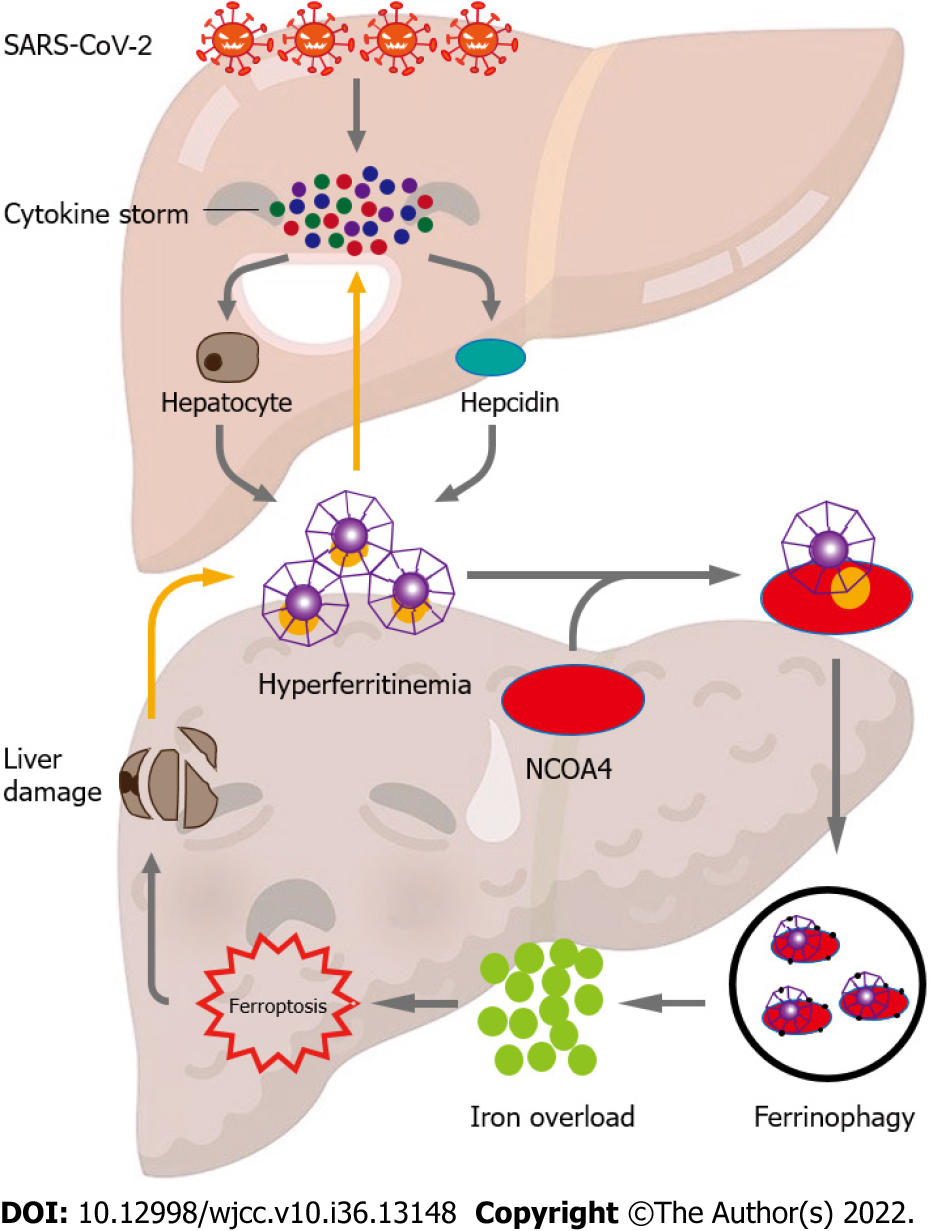
Figure 1 Proposed mechanism of ferritinophagy-mediated ferroptosis in severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection-induced liver injury.
High levels of inflammation characterized by cytokine storms are caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection. These cytokine storms cause hyper-ferritinemia by stimulating hepatocytes to secrete ferritin and upregulate hepcidin levels, which further amplifies inflammation. The nuclear receptor coactivator 4 binds to ferritin and delivers it to autophagosomes for ferritin degradation and iron release. Ferroptosis is generated by the excess of intracellular iron, consequently resulting in liver injury. The death of hepatocytes further releases ferritin. Thus, the mutual promotion of ferritin and hepatocyte damage generates a vicious loop that constantly heightens liver injury.
- Citation: Jia FJ, Han J. Liver injury in COVID-19: Holds ferritinophagy-mediated ferroptosis accountable. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(36): 13148-13156
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i36/13148.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i36.13148