Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Dec 16, 2022; 10(35): 13108-13114
Published online Dec 16, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i35.13108
Published online Dec 16, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i35.13108
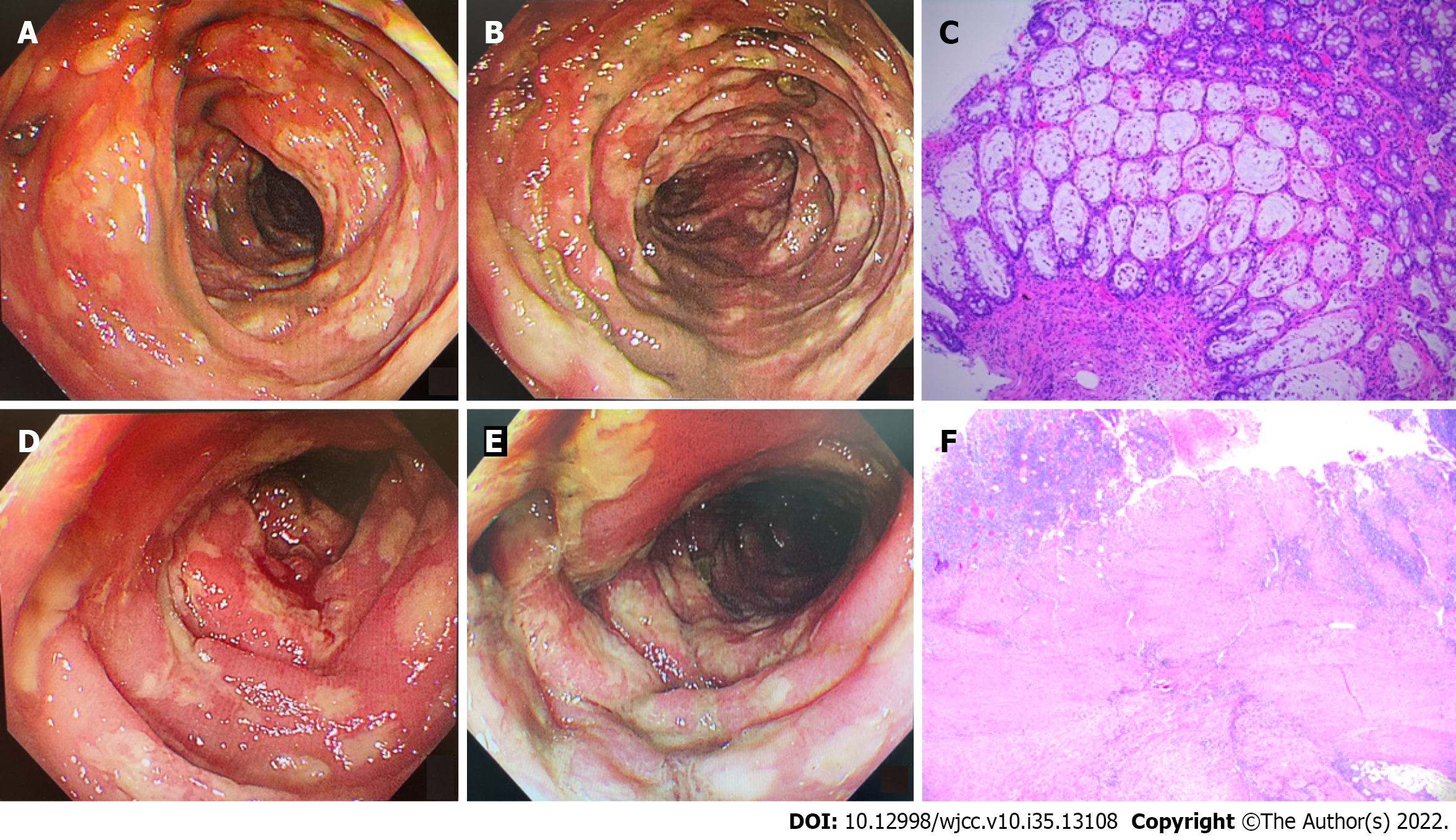
Figure 2 Colonoscopic findings and pathology.
A and B: Colonoscopic findings of descending colon (A) and sigmoid colon (B). A colonoscopy was performed on February 6, 2022. There were mucosal congestion, edema, and roughness, indistinct vascular texture, multiple diffuse superficial ulcers with purulent discharge, and a white moss adhering to the surface below the descending colon, 40 cm from the anus. The endoscopic diagnosis was multiple ulcers in the colon (nature pending pathology); C: Colonoscopic pathology (H&E staining) of the descending colon, sigmoid colon, and rectum. Multiple sites of the intestinal mucosa had localized purulent exudate and necrosis suggesting multifocal ulcer formation, surrounding mucosal erosion, marked interstitial hemorrhagic edema, and crypt atrophy (× 100). Immunohistochemistry: CMV (-), EBER (-); D and E: Colonoscopic findings of sigmoid colon (D) and rectum (E). A colonoscopy was performed on February 15, 2022. There were mucosal congestion, edema, and roughness; multiple diffuse superficial ulcers with purulent discharge, and white moss adhering to the surface were seen below the sigmoid colon, 20 cm from the anus; F: Postoperative pathology, H&E staining revealed a chronic ulcer and intestinal abscess formation in the colon (× 100).
- Citation: Lu L, Sha L, Feng Y, Yan L. Multidisciplinary treatment of a patient with severe immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced colitis: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(35): 13108-13114
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i35/13108.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i35.13108