Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Dec 6, 2022; 10(34): 12500-12514
Published online Dec 6, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i34.12500
Published online Dec 6, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i34.12500
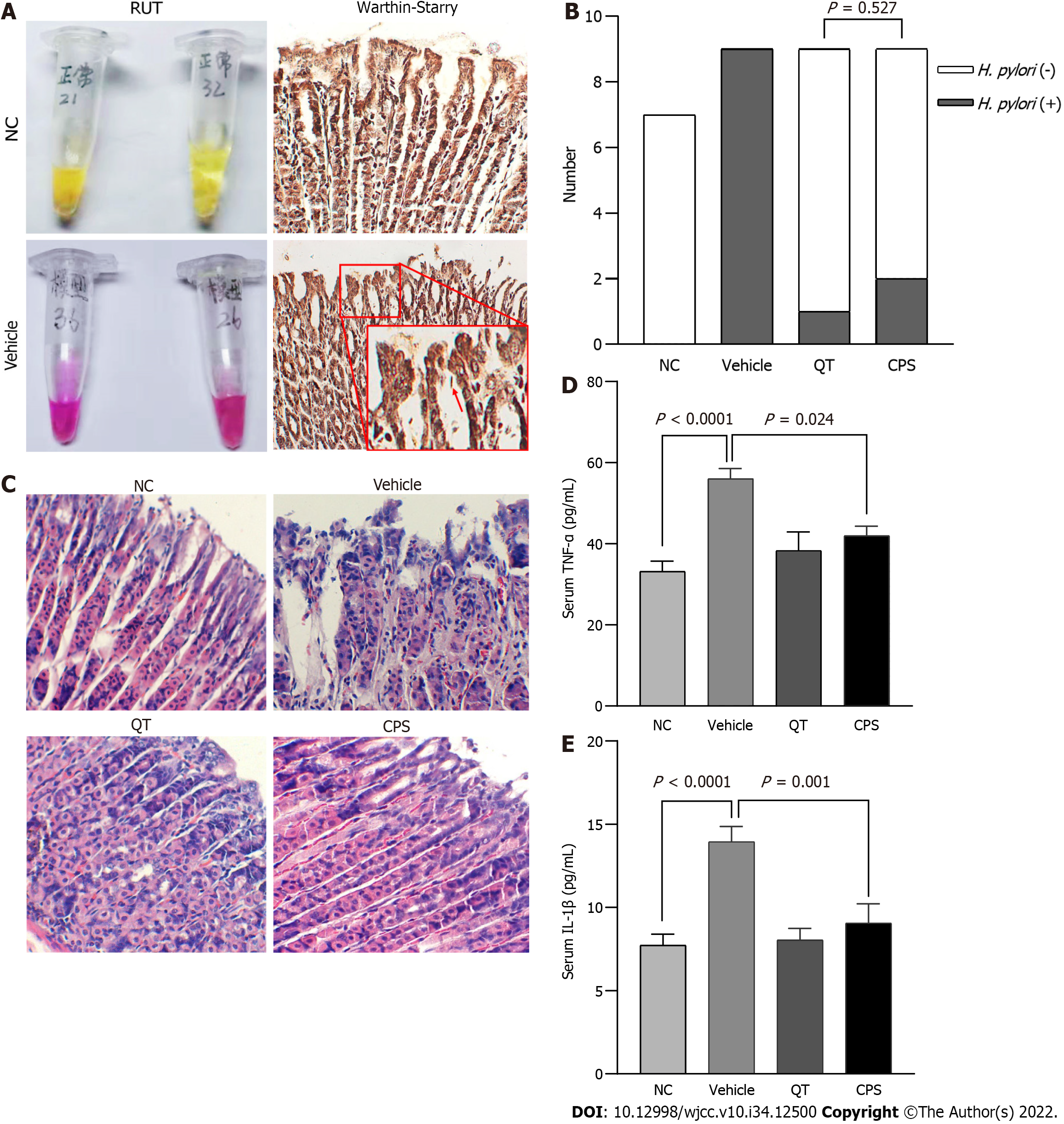
Figure 2 Coptis, Pinellia, and Scutellaria inhibit the inflammatory reaction.
A: Rapid urease test (RUT) and Warthin-Starry staining in mouse models of Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori)-associated gastritis; B: Effect of Coptis, Pinellia, and Scutellaria (CPS) on H. pylori infection. RUTs confirmed that the efficacy in the CPS and quadruple therapy groups was equal; C: Hematoxylin and eosin staining (200 ×); D and E: Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbnent Assay analysis of the serum levels of tumor necrosis factor-α and interleukin-1β in HAG mice. n = 7 per group or 9 per group (Vehicle, quadruple therapy, and CPS). Data are represented as the mean ± SD. RUT: Rapid urease test; HAG: Helicobacter pylori-associated gastritis; CPS: Coptis, Pinellia, and Scutellaria; NC: Negative control; QT: Quadruple therapy; IL-1β: Interleukin-1β; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α.
- Citation: Yu Z, Sheng WD, Yin X, Bin Y. Coptis, Pinellia, and Scutellaria as a promising new drug combination for treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection . World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(34): 12500-12514
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i34/12500.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i34.12500