Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Nov 16, 2022; 10(32): 12036-12044
Published online Nov 16, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i32.12036
Published online Nov 16, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i32.12036
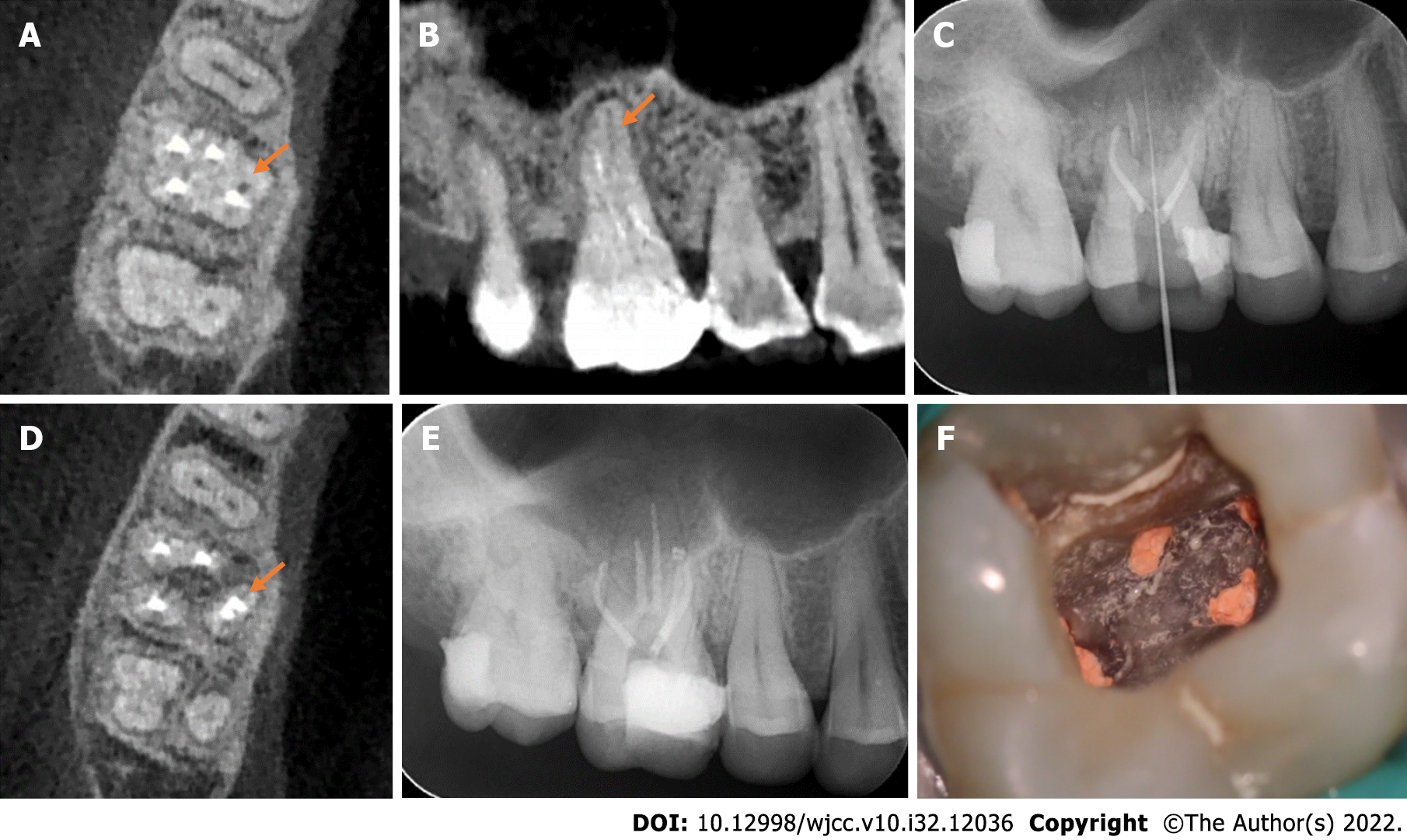
Figure 2 X-ray and an intraoral photograph showing the treatment process of the mesiopalatal canal.
A: The cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) image reveals that the maxillary first molar contains three roots, and the mesiopalatal (MP) canal has not been filled (orange arrow); B: The CBCT image reveals an unfilled MP canal in the palatal root (orange arrow); C: The X-ray demonstrates the measurement of the working length of the MP canal; D: The axial sectional CBCT image reveals that the MP canal is tightly obturated (orange arrow); E: The X-ray reveals that five canals of the tooth are well obturated; F: The intraoral photograph reveals that the mesiobuccal (MB), MB2, distobuccal, MP, and distopalatal canals are obturated with gutta-percha.
- Citation: Chen K, Ran X, Wang Y. Endodontic treatment of the maxillary first molar with palatal canal variations: A case report and review of literature. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(32): 12036-12044
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i32/12036.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i32.12036