Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Nov 6, 2022; 10(31): 11625-11629
Published online Nov 6, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i31.11625
Published online Nov 6, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i31.11625
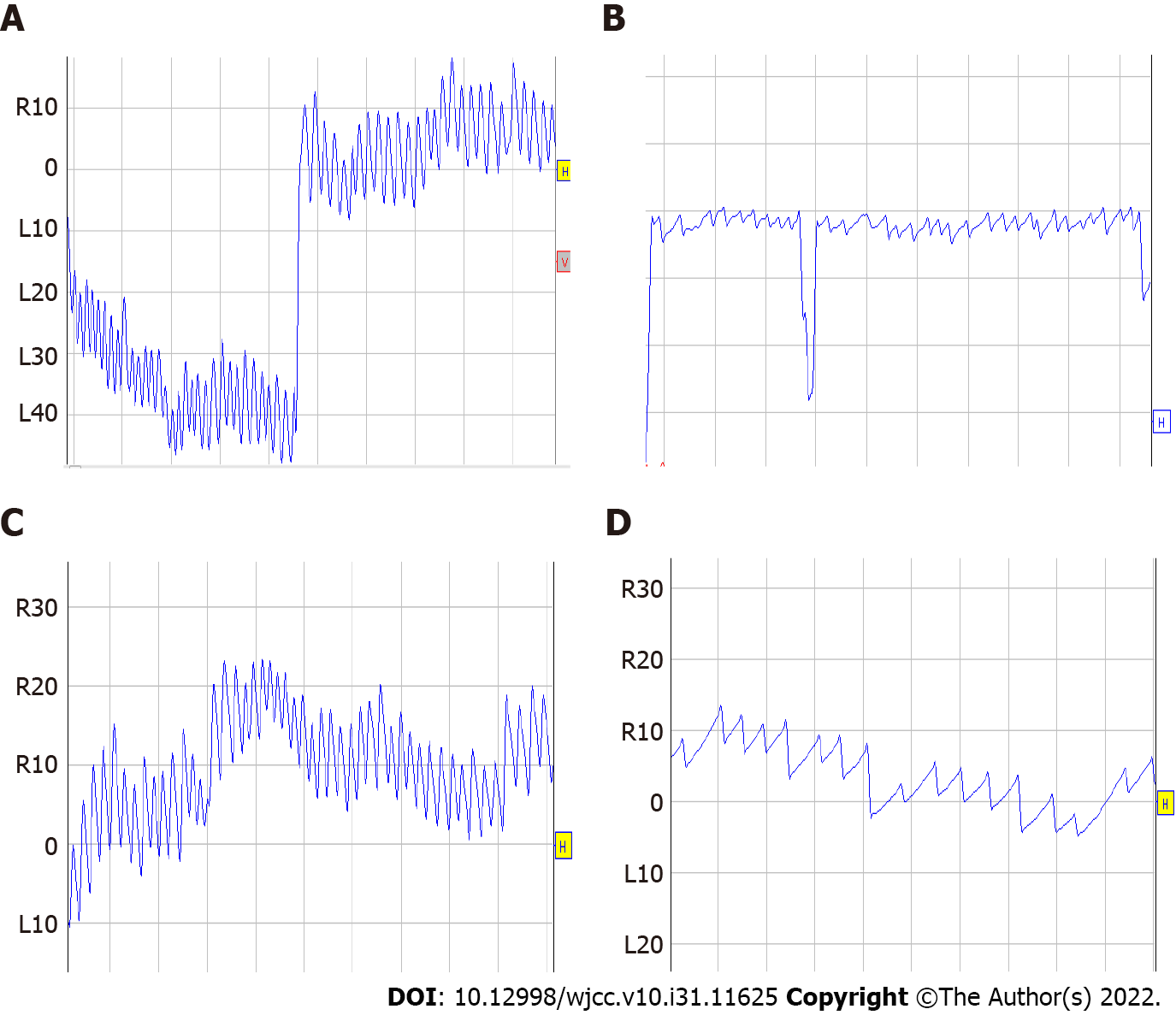
Figure 1 Nystagmus in the roll test.
A and B: When the head was to the right, intensive nystagmus occurred between 13 s and 32 s with dizziness and nausea; the highest slow phase velocity (SPV) was 162°/s and then weakened gradually to 8°/s, and vertigo disappeared; C and D: When the head was to the left, the intensive nystagmus occurred between 9 s and 30 s with dizziness; the highest SPV was 62°/s and then weakened gradually to 9°/s, and vertigo disappeared.
- Citation: Li GF, Wang YT, Lu XG, Liu M, Liu CB, Wang CH. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo with congenital nystagmus: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(31): 11625-11629
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i31/11625.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i31.11625