Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Oct 6, 2022; 10(28): 9985-10003
Published online Oct 6, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i28.9985
Published online Oct 6, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i28.9985
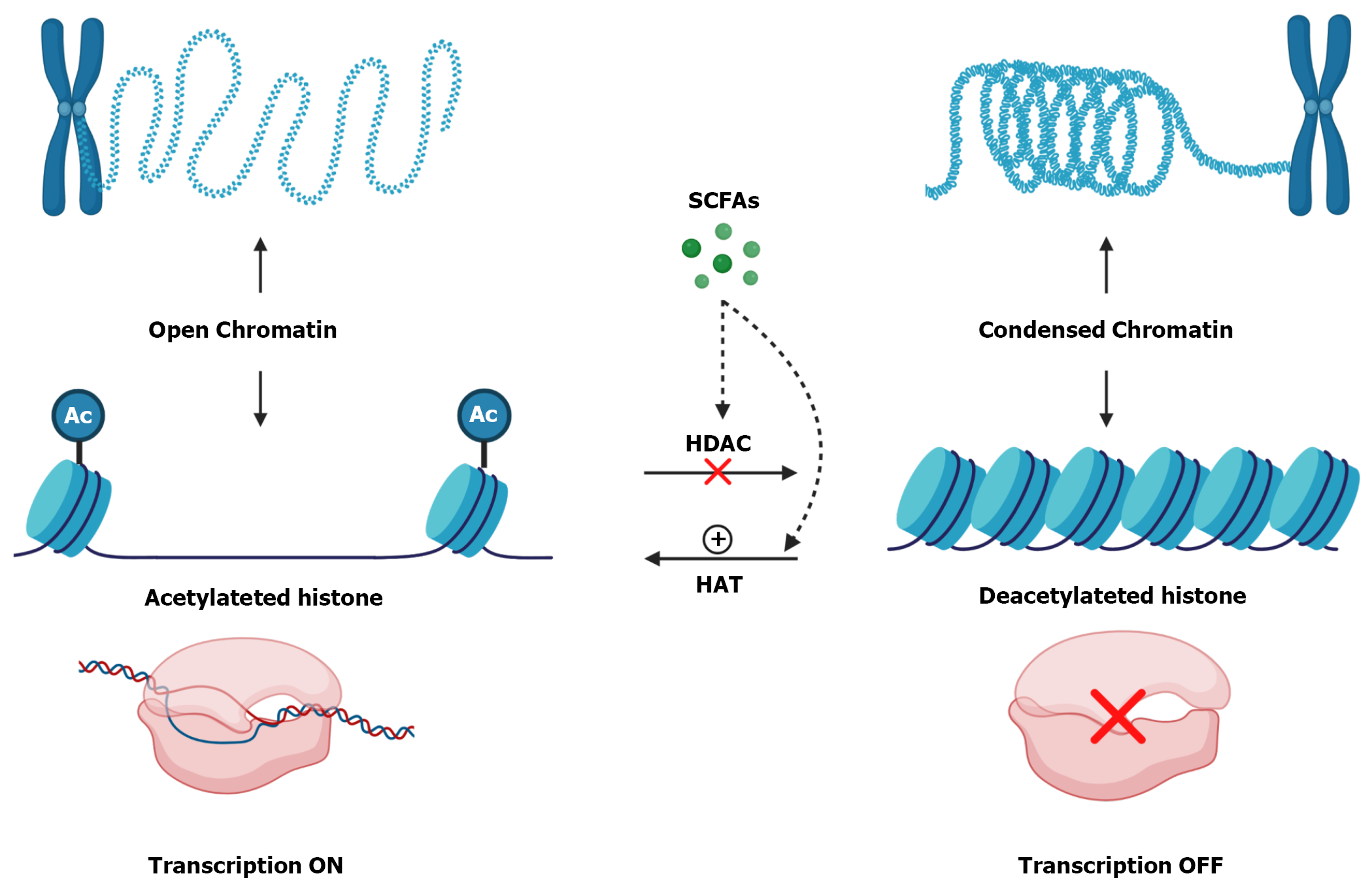
Figure 4 Histone modifications and short-chain fatty acids influence.
Histones are proteins that interacts with DNA and play an important role in organizing the double strand. When histones contain acetyl (Ac) groups they become acetylated and there is a repulsion between these groups, so histone becomes more distant from each other, causing chromatin to become decondensed and, consequently, more accessible which activate transcription. Otherwise, when histones are deacetylated, without Ac groups, DNA becomes more tangled which makes chromatin more condensed and promotes gene silencing. Histone Deacetylases (HDAC) are enzymes that remove Ac groups from Histones making them deacetylated. Otherwise, Histone Acetylases (HAT) are enzymes that insert Ac groups in Histones making them acetylated. Short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), mainly Butyrate, inhibit HDAC and increase HAT activity. The authors have obtained the permission for figure using from the BioRender.com (Supplementary material).
- Citation: Caetano MAF, Castelucci P. Role of short chain fatty acids in gut health and possible therapeutic approaches in inflammatory bowel diseases. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(28): 9985-10003
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i28/9985.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i28.9985