Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Oct 6, 2022; 10(28): 9985-10003
Published online Oct 6, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i28.9985
Published online Oct 6, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i28.9985
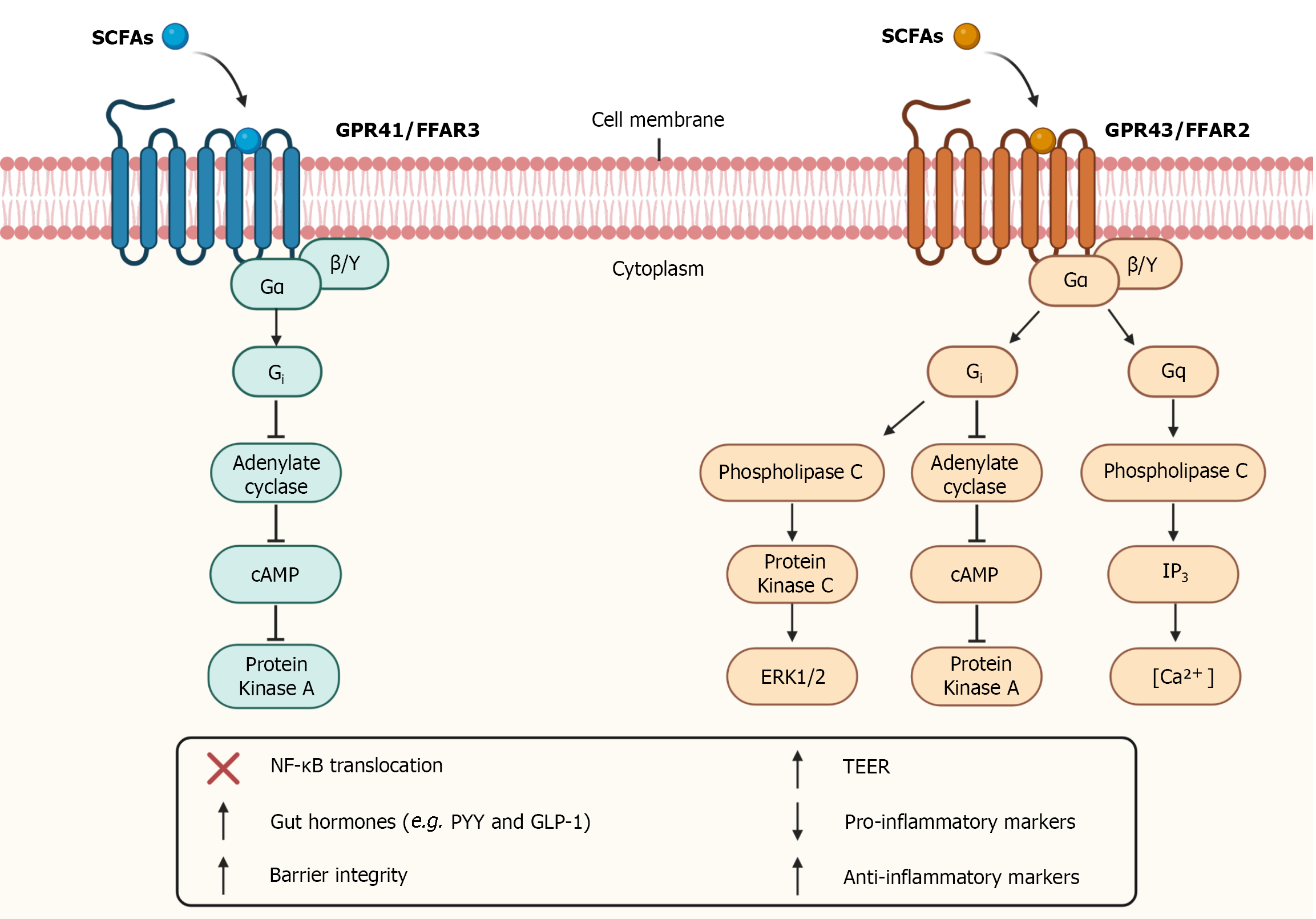
Figure 2 Short-chain fatty receptors and intracellular signaling.
Short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) binds to G-protein coupled receptors such as GPR41 and GPR43 receptors also known as free fatty acid receptors (FFAR) 3 and FFAR2, respectively. The activation of GPR41 and GPR43 receptors through Gi subunit promotes inhibition of adenylate cyclase which inhibit cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) that inhibit protein kinase A. GPR43 receptor activation through Gq subunit promotes activation of phospholipase C which activate inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3) leading to the elevation of intracellular calcium levels. GPR43 receptor activation through Gq subunit also promotes activation of phospholipase C which activate protein kinase C leading to activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) cascade. The activation of these receptors inhibits translocation of nuclear factor kappa B (NF- ΚB), altering the expression of certain proteins, promotes an increase in the release of gut hormones such as Peptide YY (PYY) and Glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1), increase intestinal barrier integrity and Transepithelial Electrical Resistance (TEER), reduce pro-inflammatory markers levels, and increase anti-inflammatory markers levels. The authors have obtained the permission for figure using from the BioRender.com (Supplementary material).
- Citation: Caetano MAF, Castelucci P. Role of short chain fatty acids in gut health and possible therapeutic approaches in inflammatory bowel diseases. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(28): 9985-10003
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i28/9985.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i28.9985