Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Sep 26, 2022; 10(27): 9897-9903
Published online Sep 26, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i27.9897
Published online Sep 26, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i27.9897
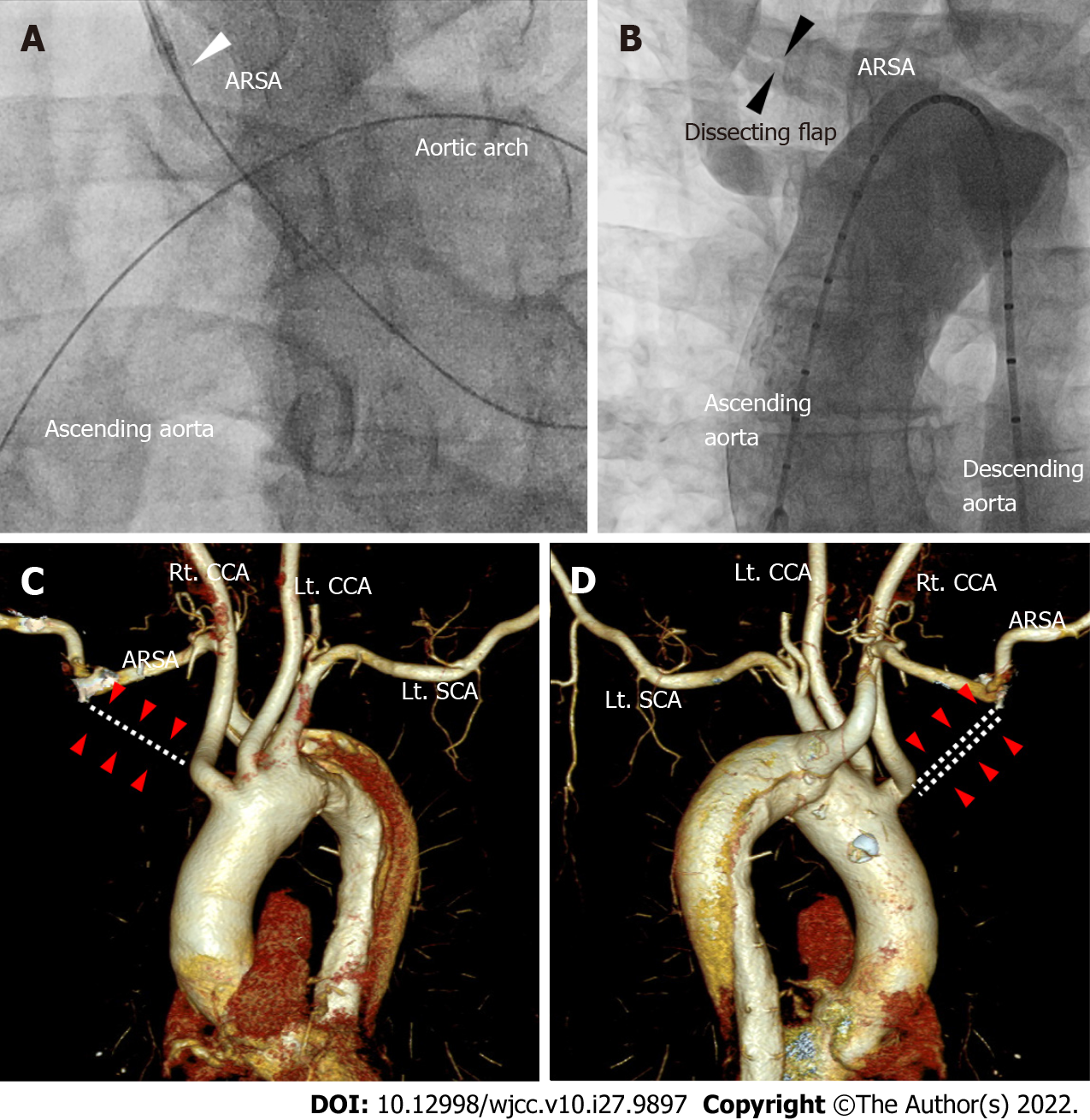
Figure 1 Aortography and computed tomography of aorta and aberrant right subclavian artery.
A: The guidewire reached the ascending aorta after forming a large loop in the left anterior oblique 30° view of coronary angiography. We were unable to advance the guiding catheter past the ostium of the right subclavian artery (white arrowhead); B: The aortogram using a 5Fr pigtail catheter via the right femoral artery shows a dissection flap of the right subclavian artery in the AP view (black arrowheads); C and D: The right subclavian artery did not originate from the right innominate artery (white dotted lines and red arrow heads in C and D). Instead, aberrant right subclavian artery emerged from the descending aorta. ARSA: Aberrant right subclavian artery; SCA: Subclavian artery; CCA: Common carotid artery.
- Citation: Ha K, Jang AY, Shin YH, Lee J, Seo J, Lee SI, Kang WC, Suh SY. Iatrogenic aortic dissection during right transradial intervention in a patient with aberrant right subclavian artery: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(27): 9897-9903
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i27/9897.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i27.9897