Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Sep 26, 2022; 10(27): 9619-9627
Published online Sep 26, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i27.9619
Published online Sep 26, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i27.9619
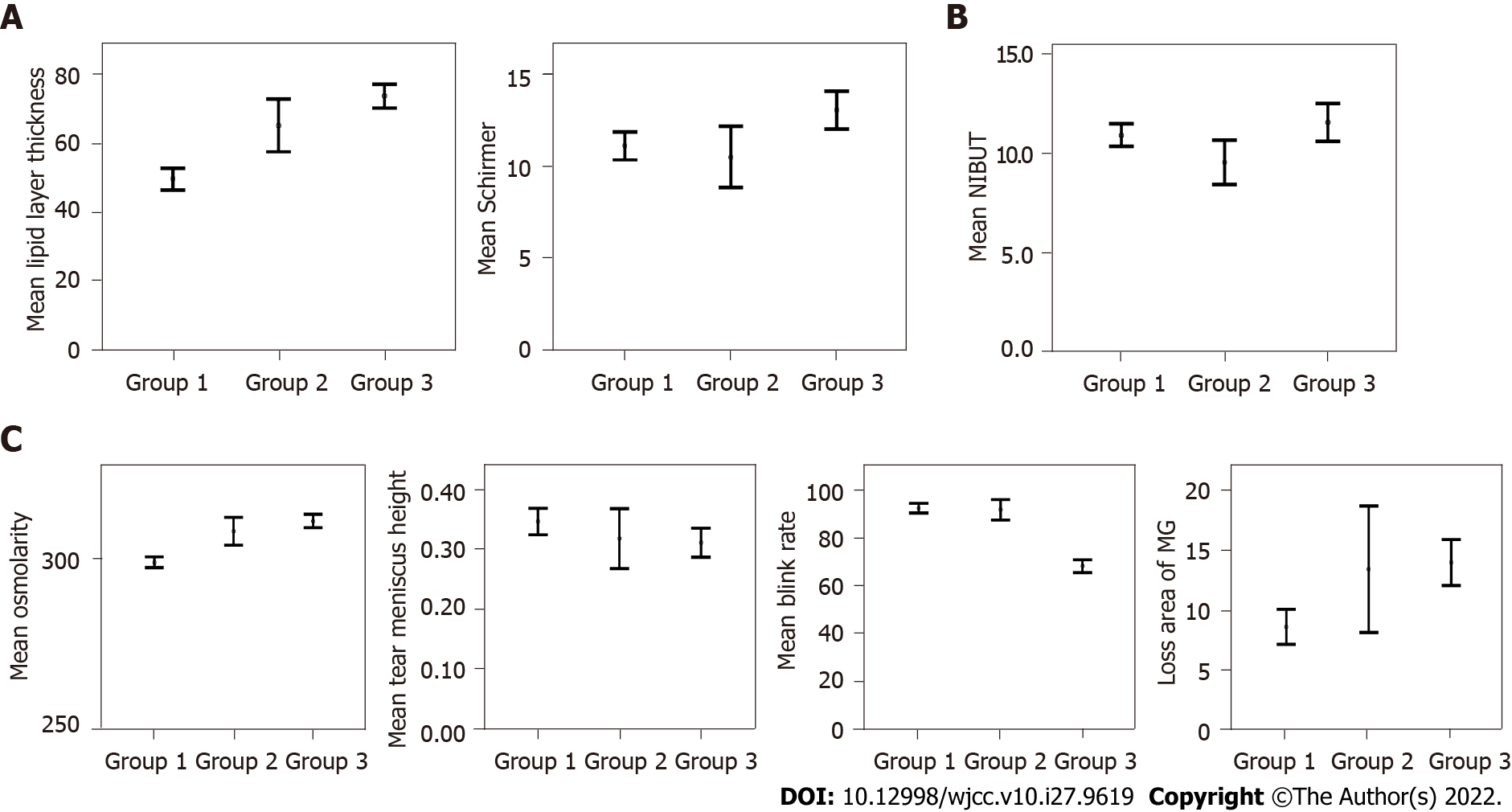
Figure 1 Lipid layer thickness, Schirmer test, non-invasive break-up time, osmolarity, tear meniscus height, blink rate, and loss area of meibomian gland means before lockdown (from August 2019 to March 2020 - group 1), after lockdown without mask mandate (from April 2020 to October 2020 - group 2), and after lockdown with mask mandate (from November 2020 to April 2021 - group 3).
A: Variables that improved after lockdown with mask mandate included: Lipid layer thickness (P < 0.001) and Schirmer test (P = 0.002); B: Variable that did not change after lockdown with mask mandate included: Non-invasive break-up time (P = 0.263); C: Variables that worsened after lockdown with mask mandate included: Osmolarity (P < 0.001), tear meniscus height (P = 0.038), blink rate (P < 0.001), and loss area of meibomian gland (P < 0.001). NIBUT: Non-invasive break-up time; MG: Meibomian gland.
- Citation: Marta A, Marques JH, Almeida D, José D, Sousa P, Barbosa I. Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on the ocular surface. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(27): 9619-9627
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i27/9619.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i27.9619