Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Sep 6, 2022; 10(25): 8893-8905
Published online Sep 6, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i25.8893
Published online Sep 6, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i25.8893
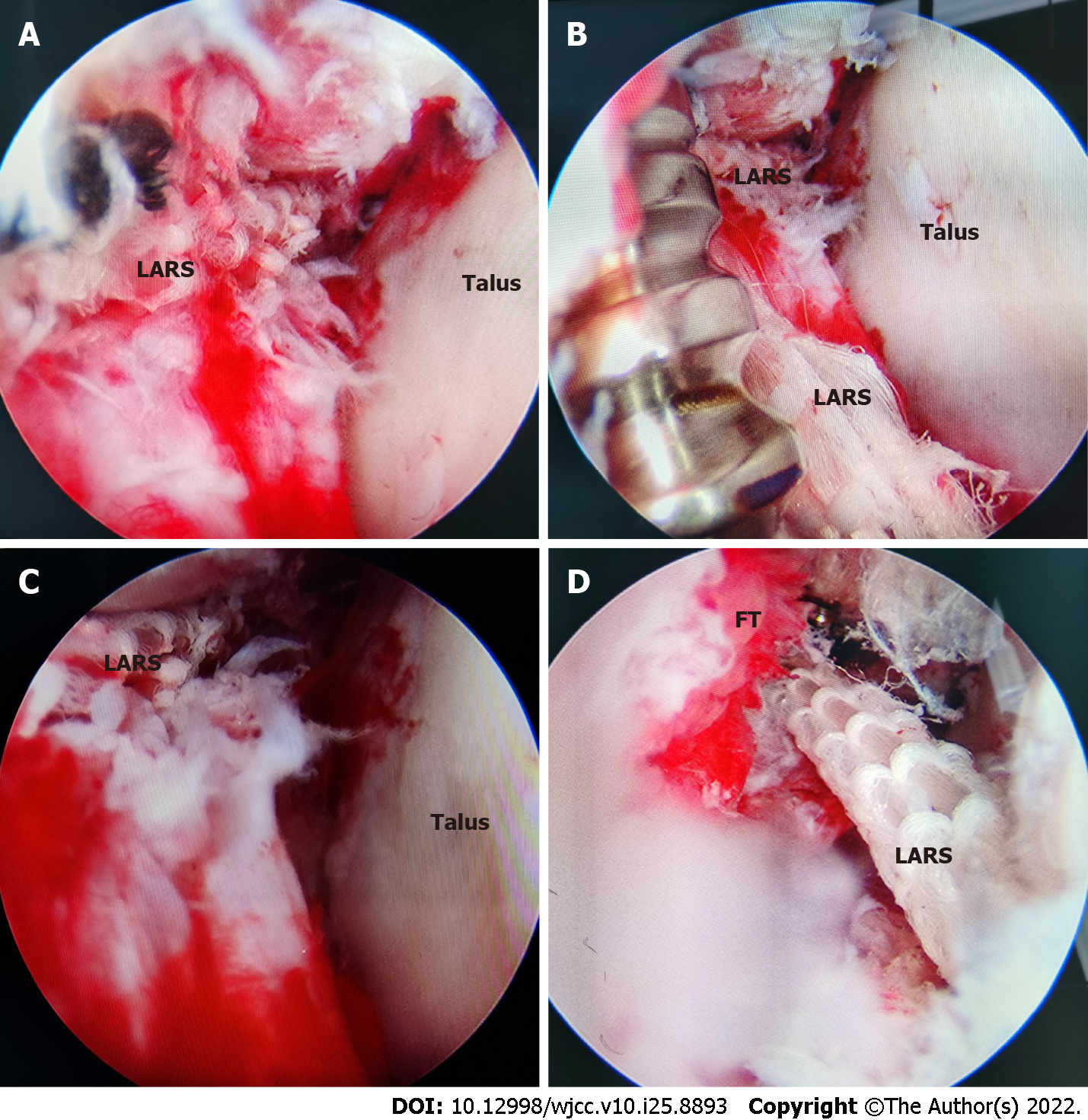
Figure 8 The last step corresponded to the positioning and fixation of the graft.
A: Through the lead through-line method, the high-strength suture of ligament advanced reinforcement system (LARS) was passed through the calcaneal tunnel, and the calcaneal stem of LARS was introduced, and the talar and fibular stems were also introduced into their respective bone tunnels; B: The fibular stem of LARS was fixed with a metal extrusion screw; C: The suture of the calcaneal stem was stretched and tensioned in the neutral position of the ankle, and the LARS of the calcaneal stem was fixed with a metal extrusion screw through the calcaneal incision; D: The suture of the talar stem was tensioned in the mild valgus position of the ankle, and the LARS of the talar stem was fixed with a metal extrusion screw through the lateral incision. FT: Fibular bone tunnel.
- Citation: Wang Y, Zhu JX. Arthroscopic anatomical reconstruction of lateral collateral ligaments with ligament advanced reinforcement system artificial ligament for chronic ankle instability. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(25): 8893-8905
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i25/8893.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i25.8893