Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Aug 16, 2022; 10(23): 8304-8311
Published online Aug 16, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i23.8304
Published online Aug 16, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i23.8304
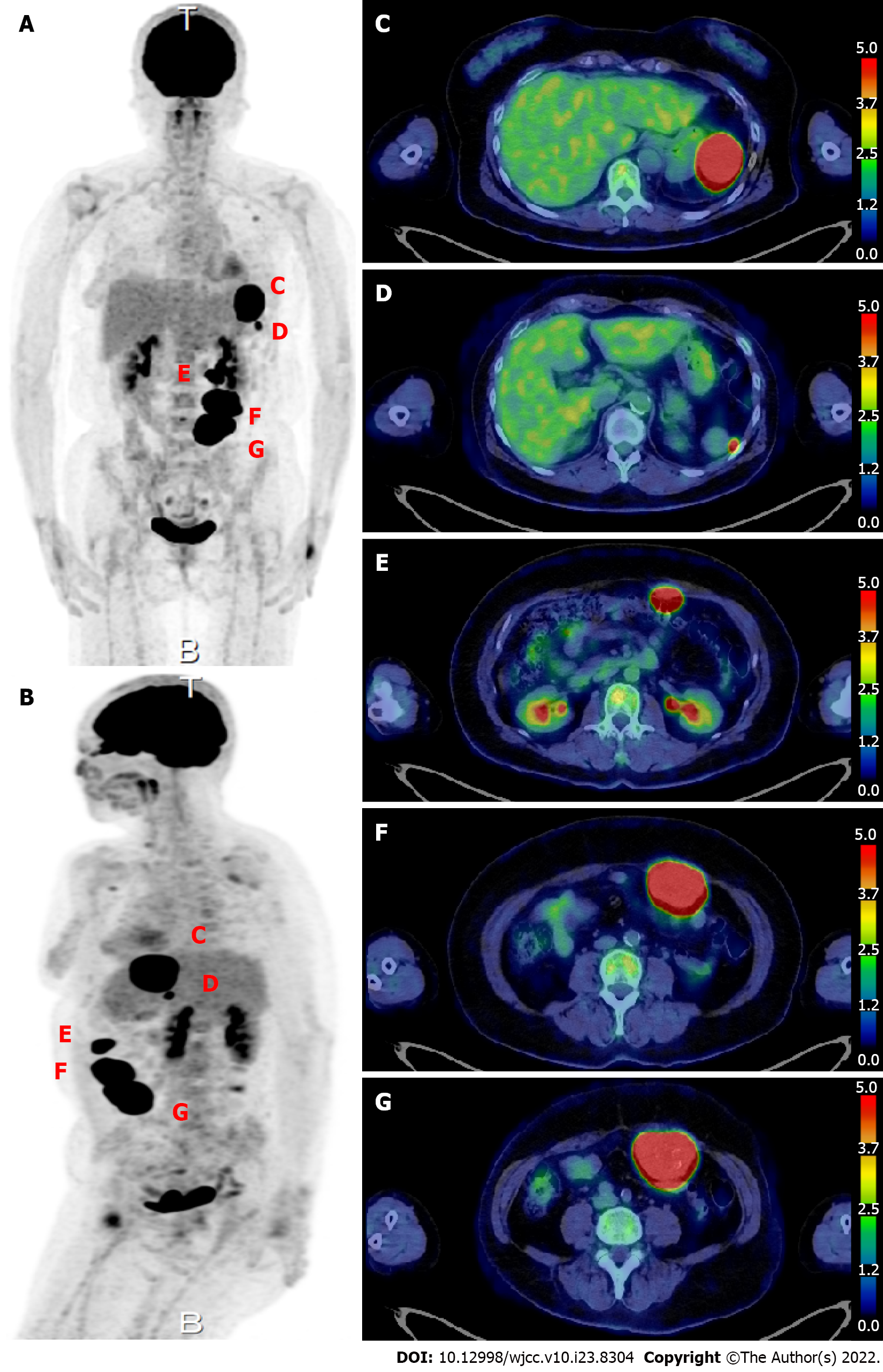
Figure 2 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography.
A and B: Scan image; C: A 50-mm mass with high fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) uptake [maximum standardized uptake value (SUVmax) 34.19] is seen protruding toward the serosa at the greater curvature of the stomach. A 50-mm intraperitoneal mass compressing the stomach is observed at the site of the previous splenectomy; D: A nodule about 7 mm in size with high FDG uptake (SUVmax 11.29) is observed near the accessory spleen; E: The most cranial abdominal wall mass shows high FDG uptake (SUVmax: 37.71); F: The middle abdominal wall mass shows high FDG uptake (SUVmax: 37.71); G: The most caudal abdominal wall mass shows high FDG uptake (SUVmax: 37.71).
- Citation: Ohkura Y, Uruga H, Shiiba M, Ito S, Shimoyama H, Ishihara M, Ueno M, Udagawa H. Phosphoglyceride crystal deposition disease requiring differential diagnosis from malignant tumors and confirmed by Raman spectroscopy: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(23): 8304-8311
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i23/8304.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i23.8304