Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Aug 6, 2022; 10(22): 8009-8017
Published online Aug 6, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i22.8009
Published online Aug 6, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i22.8009
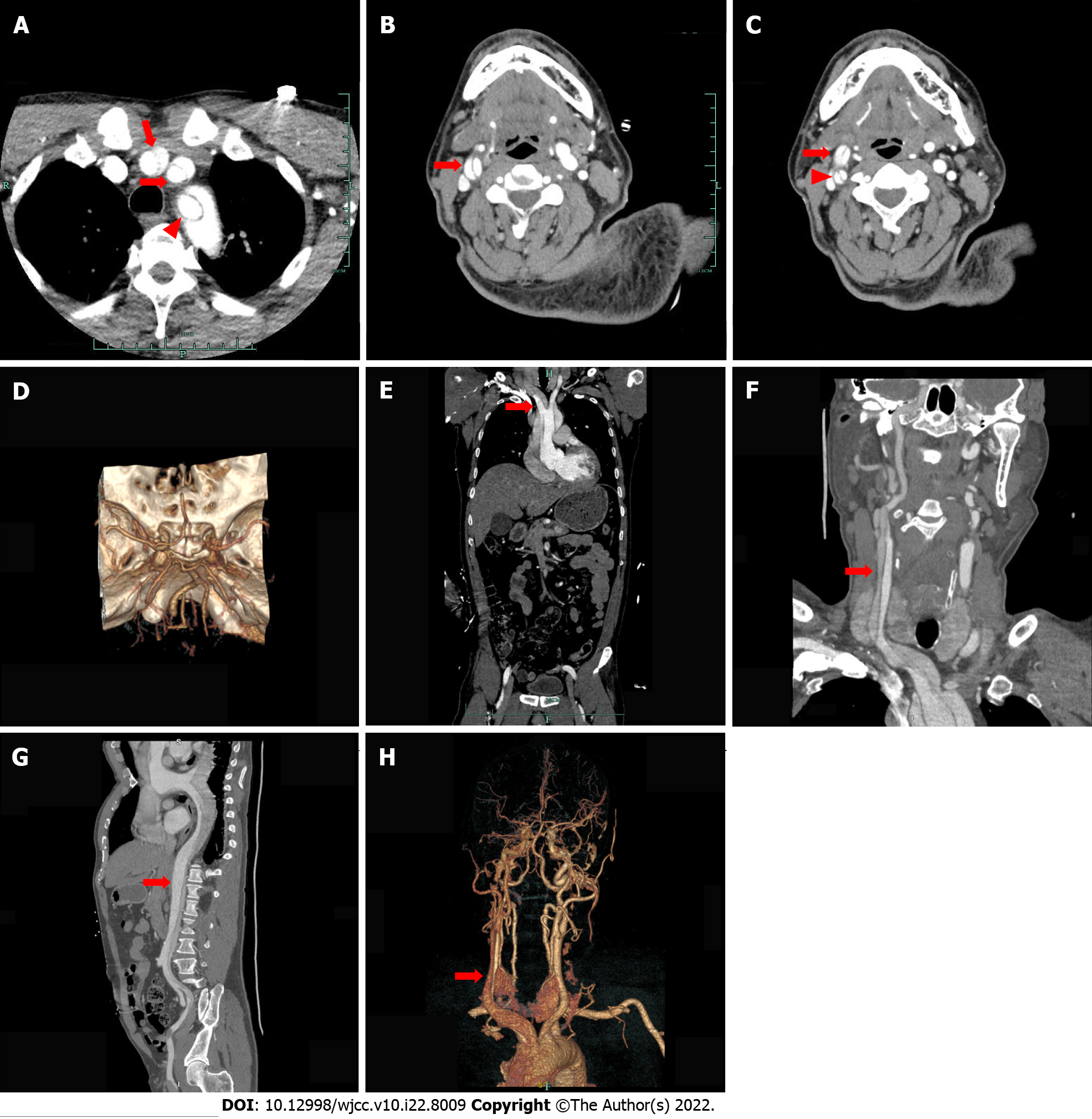
Figure 4 Enhanced computed tomography the day after thrombolytic therapy.
A: Axial enhanced computed tomography (CT) showing type A thoracic aortic dissection and an intimal flap within the innominate artery (long red arrow), left common carotid artery (short red arrow) and left subclavian artery (red triangle); B: Axial enhanced CT showing an intimal flap (red arrow) separating the right common carotid artery into two channels; C: Axial enhanced CT showing carotid artery dissection of the right external carotid artery (red arrow) and the right internal carotid artery (red triangle); D: Intracranial reconstruction CT angiography (CTA) did not show abnormalities; E: Coronal enhanced CT showing an intimal flap (red arrow) within the innominate artery; F: Coronal enhanced CT showing aortic dissection extending from the aortic root to the right common carotid artery (red arrow); G: Sagittal enhanced CT showing an intimal flap (red arrow) within the ascending aorta extending to the left external iliac artery; H: Reconstructive CTA of the head showing aortic dissection involving the innominate artery and the right common carotid artery.
- Citation: He ZY, Yao LP, Wang XK, Chen NY, Zhao JJ, Zhou Q, Yang XF. Acute ischemic Stroke combined with Stanford type A aortic dissection: A case report and literature review. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(22): 8009-8017
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i22/8009.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i22.8009