Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Aug 6, 2022; 10(22): 7994-8002
Published online Aug 6, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i22.7994
Published online Aug 6, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i22.7994
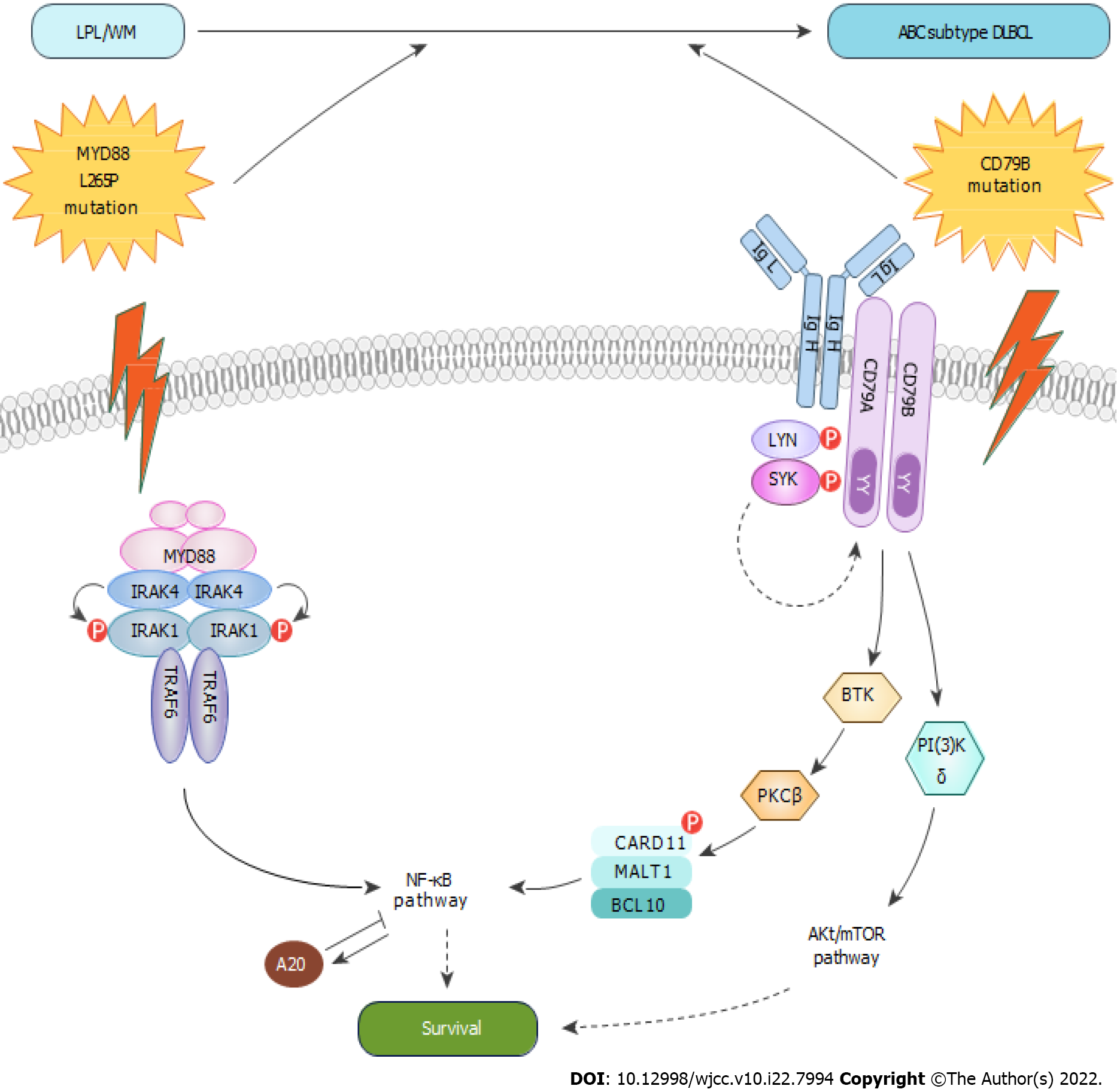
Figure 5 Nuclear factor-κB activation through the classical pathway is a hallmark of the ABC diffuse large B cell lymphoma subtype.
MYD88 is an adapter protein that couples TIR-containing receptors, regulating downstream signaling circuits, including the nuclear factor (NF)-κB. MYD88 coordinates the IRAK family kinases into a helical signaling complex through the interaction with the IRAK kinase. Phosphorylation of IRAK1 by IRAK4 will allow for the recruitment of the ubiquitin ligase TRAF6 and the activation of the downstream pathways. The mutation in MYD88L265P forms a stable, phosphorylated form of IRAK1, which upregulates gene expression signatures of NF-κB. The BCR consists of IgL and IgH chains that are noncovalently coupled to the CD79B (Ig-β) and CD79A (Ig-α) subunits, which regulate BCR surface trafficking, internalization, and expression. Upon antigen encounter, the BCR, CD79A and CD79B transmit signals to multiple downstream signaling pathways. Once BTK is recruited to the BCR signaling complex, LYN or SYK can phosphorylate and activate BTK. In turn activate PKCβ, leading to phosphorylation of CARD11 and activation of NF-κB. CBM complex, a signaling hub consisting of CARD11, BCL10, MALT1, and other proteins, which is required for the activation of classical NF-κB pathway in lymphocytes.
- Citation: Huang WY, Weng ZY. Occurrence of MYD88L265P and CD79B mutations in diffuse large b cell lymphoma with bone marrow infiltration: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(22): 7994-8002
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i22/7994.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i22.7994