Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Jun 26, 2022; 10(18): 6136-6140
Published online Jun 26, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i18.6136
Published online Jun 26, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i18.6136
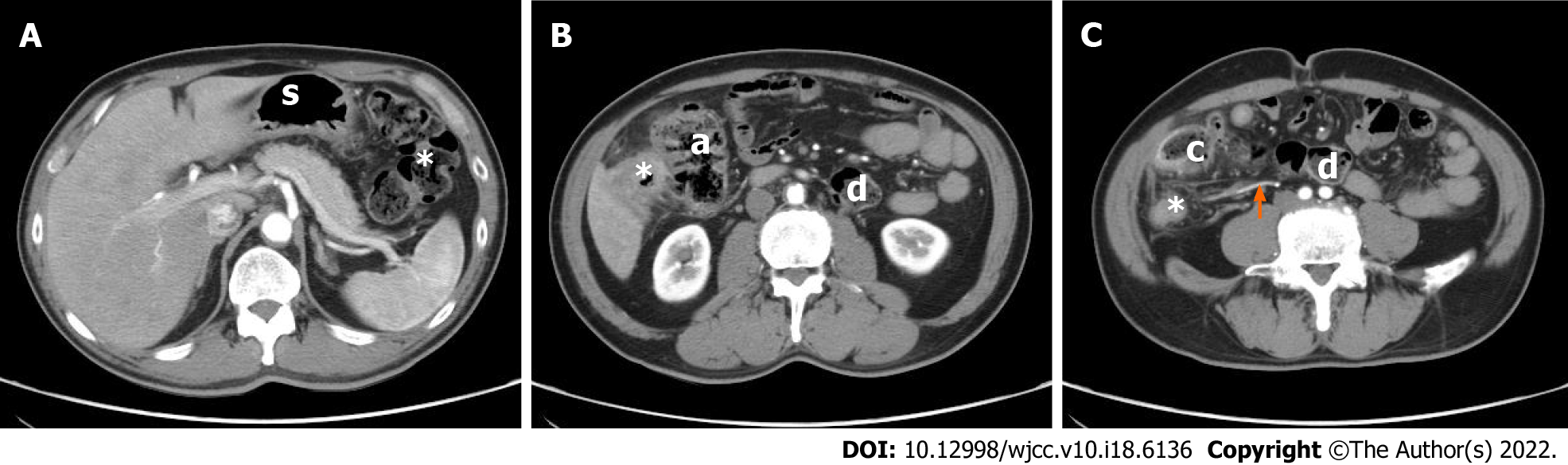
Figure 1 A 56-year-old man with right-sided sigmoid colon carcinoma.
A: Axial post-contrast computed tomography (CT) scan in the arterial phase demonstrates that the stomach (s) and splenic flexure of colon are normal (*); B: Axial post-contrast CT scan in the arterial phase shows the descending colon entering the peritoneum. The sigmoid colon with the tumor (*) is located on the right side of the ascending colon (a); C: Axial post-contrast CT scan in the arterial phase shows the descending colon (d) crossing to the right at the level of the L4 vertebra and continuing as the sigmoid colon (s) on the right. The tumor (*) is located in a redundant right-sided sigmoid colon. The cecum (c) is displaced toward the left at the level of the L4 transverse process instead of the right pelvic region. The inferior mesenteric artery (arrows) is shown running to the right instead of its normal left-sided course.
- Citation: Lyu LJ, Yao WW. Carcinoma located in a right-sided sigmoid colon: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(18): 6136-6140
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i18/6136.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i18.6136