Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Jun 16, 2022; 10(17): 5667-5679
Published online Jun 16, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i17.5667
Published online Jun 16, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i17.5667
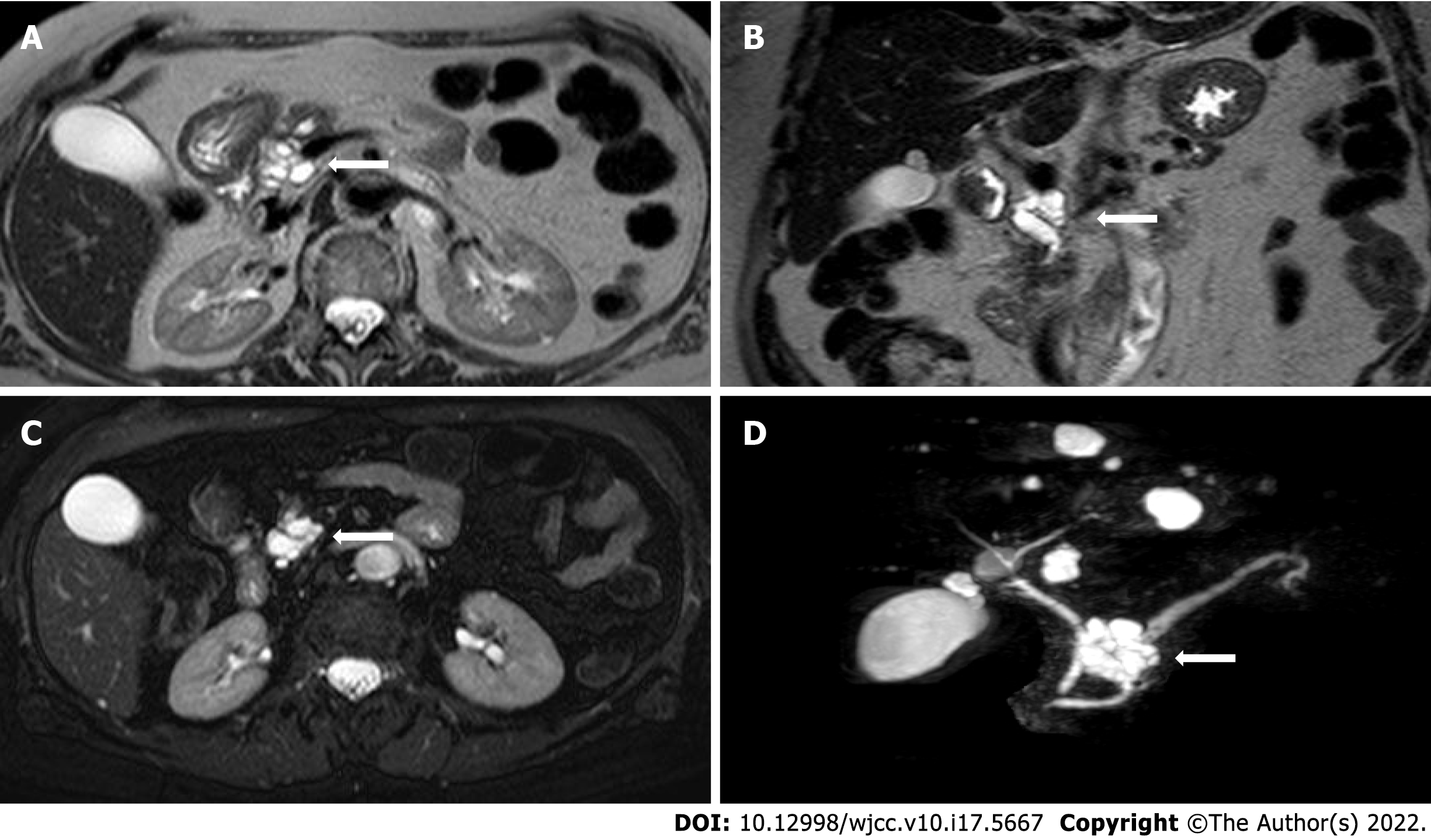
Figure 3 Non-contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance images of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms.
A: T2-weighted Turbo Spin Echo (TSE) axial image; B: T2-weighted TSE coronal image; C: T2-weighted TSE fat-sat axial image; and D: T2-weighted TSE volume (3D) TSE fat-sat sequences (with MIP reconstructions). The arrows indicate the location of the cyst.
- Citation: Innocenti T, Danti G, Lynch EN, Dragoni G, Gottin M, Fedeli F, Palatresi D, Biagini MR, Milani S, Miele V, Galli A. Higher volume growth rate is associated with development of worrisome features in patients with branch duct-intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(17): 5667-5679
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i17/5667.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i17.5667