Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Jun 16, 2022; 10(17): 5634-5645
Published online Jun 16, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i17.5634
Published online Jun 16, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i17.5634
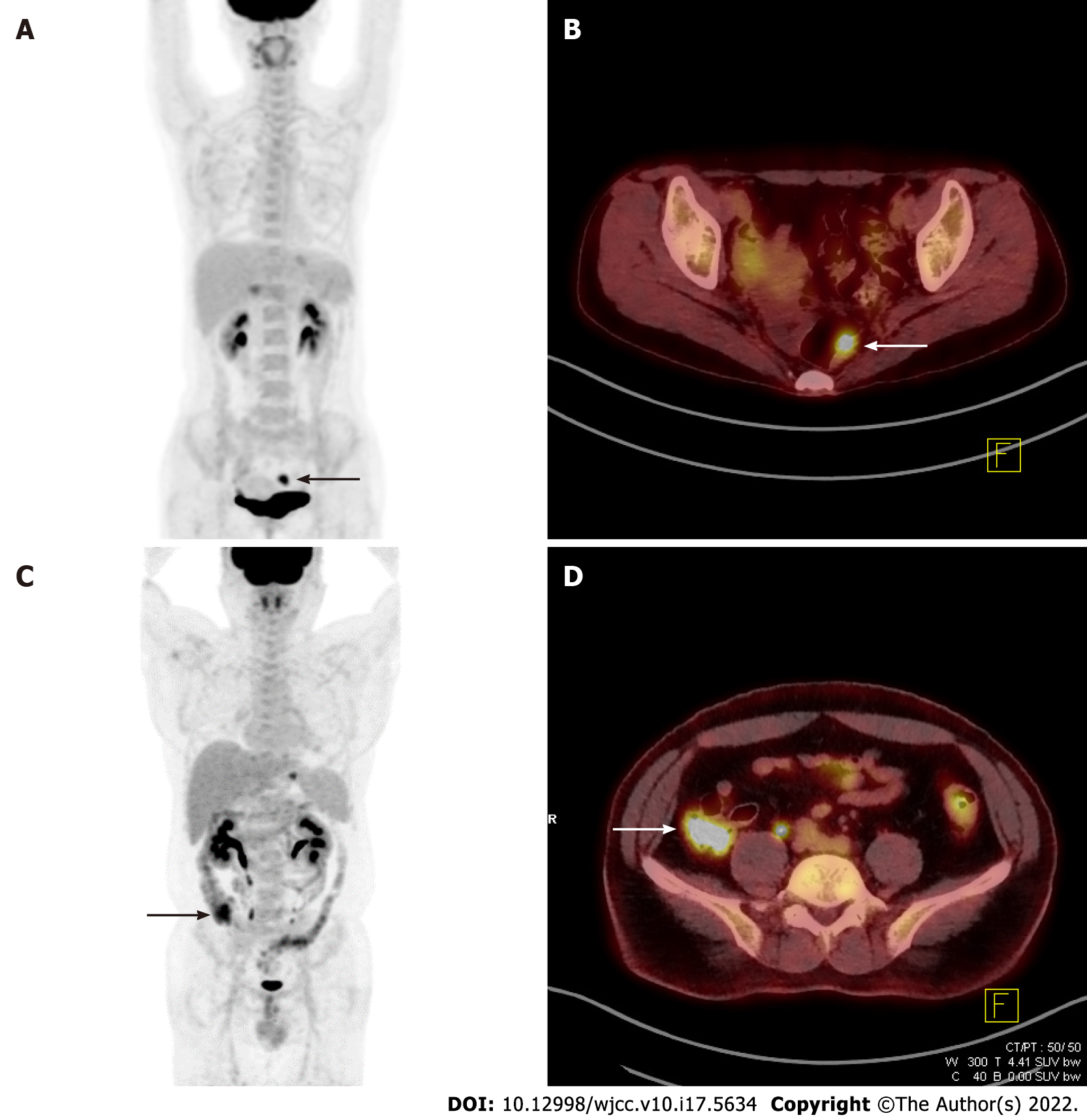
Figure 2 Cases with premalignant and benign incidental focal colorectal fluorine-18 fluorodeoxyglucose uptake.
A: Focal uptake (black arrow) in the lower abdomen on the maximum intensity projection (MIP) image of a 41-year-old woman diagnosed with stomach cancer; B: Axial view showing a hypermetabolic rectal lesion (white arrow, SUVmax 10.1) diagnosed as rectal villous adenoma; C: Focal uptake (black arrow) in the right lower abdomen on the MIP image of a 42-year-old man diagnosed with stomach cancer; D: Axial view showing hypermetabolism (white arrow, maximum standardized uptake value 8.6) with a final colonoscopy report of “No remarkable mucosal lesion”.
- Citation: Lee H, Hwang KH, Kwon KA. Assessment of incidental focal colorectal uptake by analysis of fluorine-18 fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography parameters. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(17): 5634-5645
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i17/5634.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i17.5634