Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. May 16, 2022; 10(14): 4436-4445
Published online May 16, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i14.4436
Published online May 16, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i14.4436
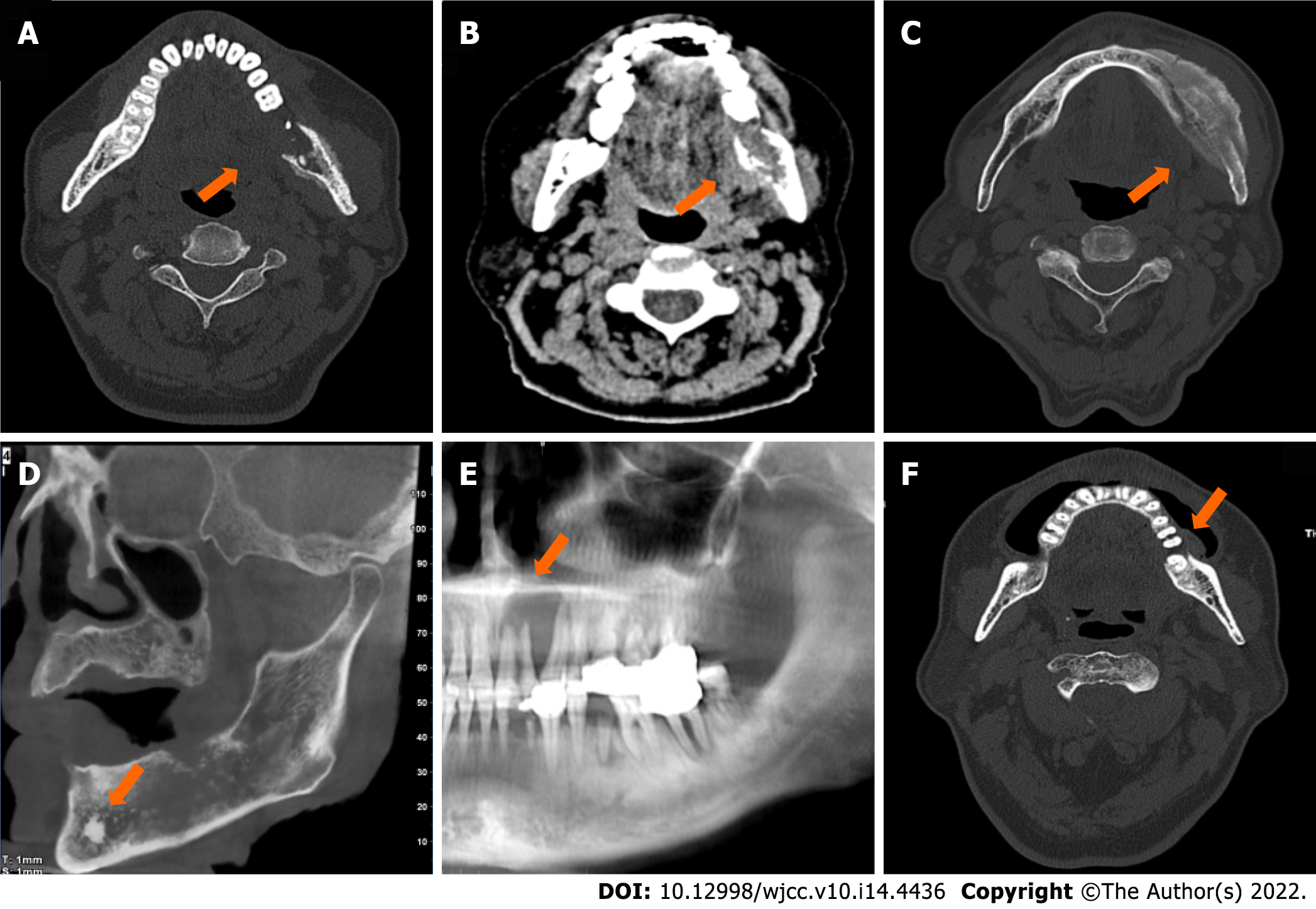
Figure 1 Five types of metastatic adenocarcinoma of the jaw.
A: Osteolytic type. Axial spiral-computed tomography (SCT) with bone window showed decreased radiodensity of the lesion (arrow) with a permeative margin. The multi-layered periosteal reaction was observed on the buccal and lingual sides of the left mandibular ramus; B: Osteolytic type. Axial SCT with soft-tissue window showed a confined soft tissue mass (arrow) at the lingual side of the left mandibular ramus; C: Osteoblastic type. Axial SCT with bone window showed increased radiodensity of the lesion (arrow) with a sclerotic margin; D: Mixed type. Oblique sagittal cone beam CT showed both osteolytic and osteoblastic lesions (arrow) with a moth-eaten margin, and an “ivory” pattern of osseous tumour matrix was centred in the left mandibular at the location of mental foramen; E: Cystic type. Partial panorama reconstruction radiograph showed homogeneous radiodensity of the lesion (arrow) in the anterior part of the maxilla with a geographic margin. Teeth displacement and root resorption were observed; F: Alveolar bone resorption type. Axial SCT with bone window showed bone destruction was confined to the alveolar bone with a geographic margin. A soft tissue component was at the buccal side.
- Citation: Shan S, Liu S, Yang ZY, Wang TM, Lin ZT, Feng YL, Pakezhati S, Huang XF, Zhang L, Sun GW. Oral and maxillofacial pain as the first sign of metastasis of an occult primary tumour: A fifteen-year retrospective study. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(14): 4436-4445
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i14/4436.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i14.4436