Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. May 6, 2022; 10(13): 4171-4176
Published online May 6, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i13.4171
Published online May 6, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i13.4171
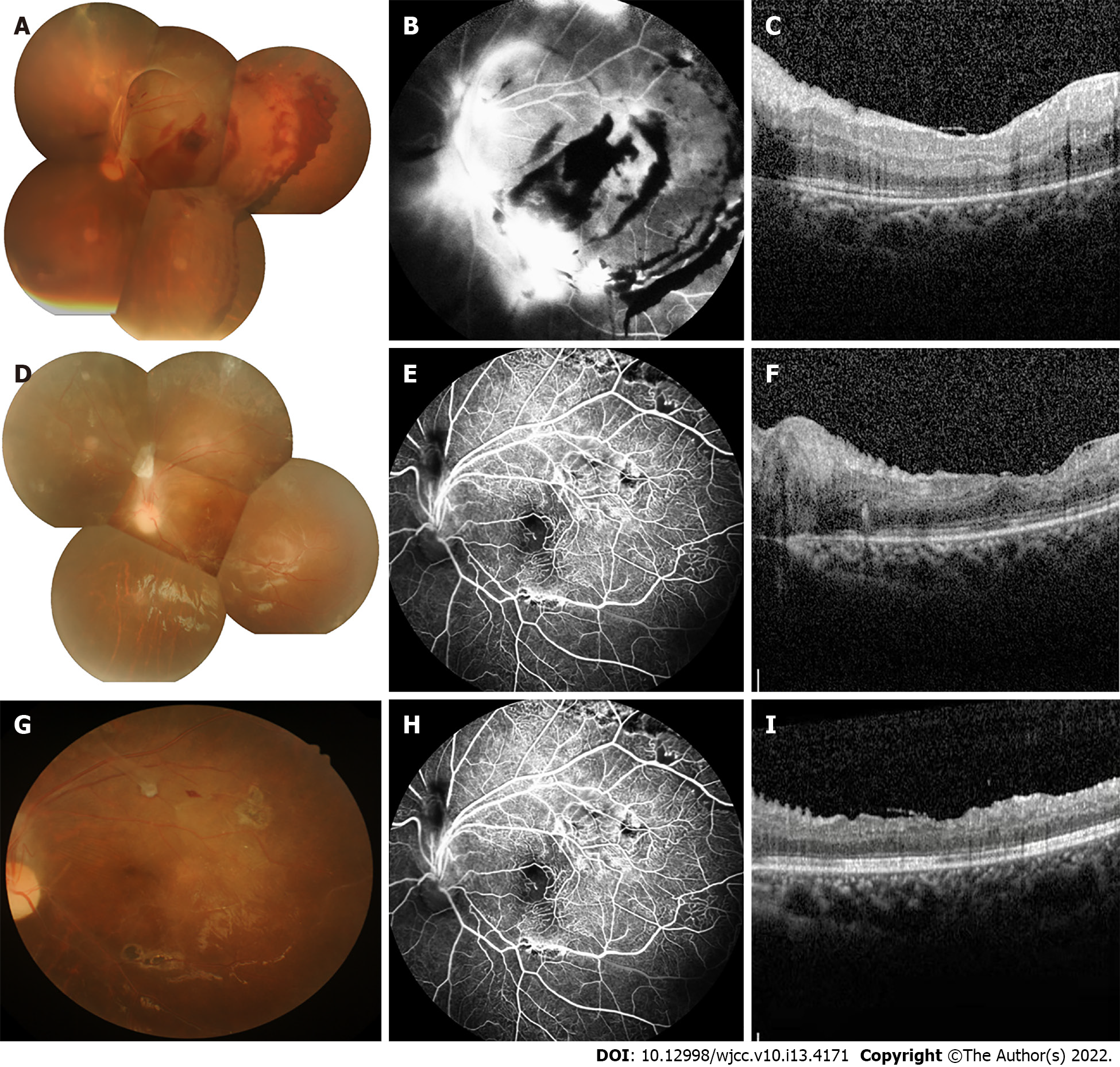
Figure 2 Imaging examinations.
A: Conventional fundus camera imaging revealed numerous hemorrhages and exudates with tractional retinal detachment; B: Fundus fluorescein angiography (FFA) showed inferior temporal vascular occlusion; retinal vascular endings and optic disc surface capillaries were dilated, and neovascular-like hyperfluorescence with non-perfused areas were seen; C: Two-day postoperative macular optical coherence tomography (OCT) showed normal central macular architecture and epiretinal membrane; D: Conventional fundus camera imaging revealed retinal flat-mount with the absorption of retinal hemorrhage; E: FFA revealed non-perfusion in the peripheral retinal vessels; F: Macular OCT showed retinal flattening with edema and a small amount of exudation; G: No obvious morphological change was found by fundus photography; H: Peripheral retinal lamellar non-perfused area with hyperfluorescence of neovascularization and fluorescein infiltration visible in the upper retina seen on FFA; I: Retinal exudation and edema were reduced compared to previous macular OCT.
- Citation: Cai YR, Liang Y, Zhong X. Late contralateral recurrence of retinal detachment in incontinentia pigmenti: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(13): 4171-4176
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i13/4171.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i13.4171